Dipteris conjugata facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Dipteris conjugata |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Dipteris conjugata in Taiwan | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Dipteris
|
| Species: |
conjugata
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Phymatodes conjugata (Reinwardt) C. Presl. |
|
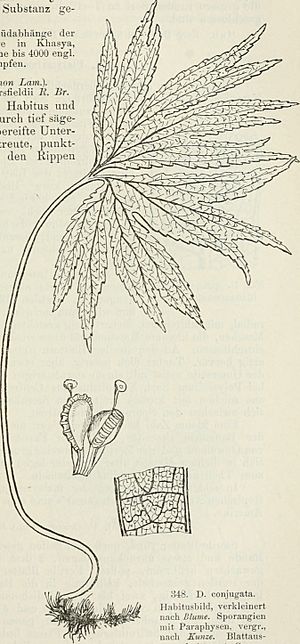
The Dipteris conjugata is a special type of fern. It has a creeping stem called a rhizome that grows underground. From this rhizome, tall stems grow upwards, holding beautiful green fronds (which are like fern leaves). These fronds are divided into many parts, with edges that look like teeth.
You can find this fern growing in open areas, on mountain ridges, and at the edges of forests. It lives in warm and mild parts of Asia, Australia, and some islands in the Pacific Ocean. People have also used it a little bit for traditional medicine.
Contents
What Does This Fern Look Like?
This fern has a special underground stem called a rhizome. It creeps along the ground and is covered with shiny black or reddish-brown hairs. These hairs can be up to 5 millimeters long. The rhizome itself can be 1 centimeter or more thick.
The fern also has tall stalks, called stipes, which grow from the rhizome. These stalks can be from 0.4 to 2.0 meters (about 1.3 to 6.5 feet) tall. They have some hairs at the bottom but are smooth higher up. They are usually straw-colored to brown.
The large fronds, or leaf blades, grow from these stalks. They can be as wide as 1 meter (about 3 feet).
The Fronds: A Closer Look
The fronds are usually a mid-green or dark-green color on top, but they are lighter underneath. Each frond is about 0.5 to 0.7 meters (about 1.6 to 2.3 feet) long and wide. They are split into two large, fan-shaped halves right from the base. Each half is then divided further into four or more smaller parts, which are also lobed. The very tips of these lobes are narrow and have deeply toothed edges.
The veins in the fronds branch out many times, like a fork. Each lobe has 2 to 4 main veins. When the fronds are young, they are covered with a layer of soft, downy hairs.
On the underside of the fronds, you'll find many tiny bumps called sori. These are where the fern produces its spores, which are like seeds for ferns. These sori are scattered unevenly and come in different sizes and shapes. They don't have a protective cover (called an indusia), but they do have small, club-shaped support structures called paraphyses.
What's in a Name? The Fern's Taxonomy
This fern has different names in different places! In Fiji, it's known as koukoutangane. In Thailand, it's called bua chaek, and in Singapore, it's bua cek.
In Chinese script, it's written as 双扇蕨 or 破傘蕨. In China, it's known as shuang shan jue.
The second part of its scientific name, conjugata, comes from Latin. It means "joined together" or "paired," which refers to how the leaf has one pair of leaflets.
The fern was first officially described by a scientist named Caspar Georg Carl Reinwardt in 1828.
Where Does This Fern Grow?
The Dipteris conjugata fern is native to many parts of the world. You can find it in warm and mild areas of Asia, in Australia, and on some islands in the Pacific Ocean.
Its Global Home
In temperate Asia, it grows in the Ryukyu Islands of Japan. In tropical Asia, it's found in places like Papua New Guinea, Cambodia, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Hainan (in China), Taiwan, India, Indonesia, Malaysia (even on the slopes of Mount Ophir), and the Philippines.
Beyond Asia, it also grows in Queensland in Australia, and on the islands of New Caledonia and Fiji.
Where It Likes to Live
D. conjugata prefers to grow on clay slopes, in open areas, on ridges, and at the edges of forests. In some parts of Indonesia, it grows along rivers next to Nypa Palms. In Borneo, it's often seen with other ferns like Histiopteris incisa and Lygodium circinnatum along forest paths. In New Caledonia, it likes sunny spots by the road. This fern is also common in forest edges where there's a lot of rain.
You can find this fern at different heights above sea level. In China, it grows between 500 to 1200 meters (about 1,640 to 3,937 feet) high. In Malaysia, it's found from 300 to 1700 meters (about 984 to 5,577 feet). In Singapore, it grows from 300 to 2900 meters (about 984 to 9,514 feet) high, sometimes even on coastal cliffs where there's a risk of landslides.
How Is This Fern Protected?
In Singapore, Dipteris conjugata is listed as Critically Endangered in their 2008 Red Data Book. This means it's at a very high risk of disappearing from the wild there. For example, in the Labrador Nature Reserve in Singapore, a large group of these ferns almost vanished by 2001.
To help save this fern, staff from the National National Biodiversity Centre regularly check on its growth. They use tools like parangs (a type of knife) and secateurs (pruning shears) to cut away other plants that might harm the fern. These harmful plants include invasive weeds like Simpuh Air (Dillenia suffruticosa), the Weeping Fig (Ficus benjamina), and another fern called Resam (Dicranopteris linearis).
However, in other parts of the world, this fern is doing much better. It's listed as Least Concern (LC), which means it's widespread and not currently facing any major threats.
Can You Grow This Fern?
Sometimes, Dipteris conjugata is planted as an ornamental plant in Singapore because it looks so nice.
It can grow in soils that are poor or well-drained. It's also pretty resistant to most diseases and pests, which makes it easier to care for.
You can find specimens of this fern growing in botanical gardens, like the Cibodas Botanical Garden in West Java, Indonesia. There are also plants in the Fernarium of Univerisiti Kebangsaan in Malaysia.
What Is This Fern Used For?
This fern has been used as a medicinal plant for different health issues. In southern Thailand, the roots are collected for traditional medicine. In Fiji, it's used to help with male reproductive problems.
It also has another interesting use! In the highlands of Mindanao in the Philippines, the large fronds of this fern are used as an umbrella to keep people dry.