East Jersey facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Province of East Jersey
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1674–1702 | |||||||||||
|
Flag
|
|||||||||||
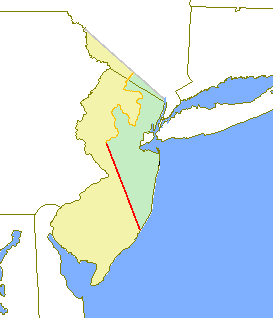
The original provinces of West and East Jersey are shown in yellow and green, respectively. The Keith Line is shown in red, and the Coxe–Barclay Line is shown in orange.
|
|||||||||||
| Status | Colony of Kingdom of England | ||||||||||
| Capital | Perth Amboy | ||||||||||
| Common languages | English, Dutch | ||||||||||
| Religion | Puritanism | ||||||||||
| Government | Proprietary colony | ||||||||||
| Lord Proprietor | |||||||||||
|
• 1674-1680
|
Sir George Carteret (initial) | ||||||||||
| Governor | |||||||||||
|
• 1674–1682
|
Philip Carteret (first) | ||||||||||
|
• 1699–1702
|
Andrew Hamilton (last) | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
|
• Established
|
1674 | ||||||||||
|
• Disestablished
|
1702 | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
The Province of East Jersey was an English colony in North America. It existed from 1674 to 1702. It was one of two parts that made up the Province of New Jersey. The other part was West Jersey. In 1702, East and West Jersey joined together. They formed the single Province of New Jersey, which later became the U.S. state of New Jersey. The main town, or capital, of East Jersey was Perth Amboy.
Contents
East Jersey: A Colony's Story
Early Settlements and People
Before it became East Jersey, this area was part of New Netherland. This was a Dutch colony. The Dutch started settlements like Pavonia in 1633. They also founded Vriessendael in 1640 and Achter Kol in 1642. These early settlements faced challenges from conflicts.
In 1660, the Dutch founded Bergen, New Netherland. This became the first lasting European settlement in what is now New Jersey. However, in 1664, English forces took over New Amsterdam. This meant the English gained control of the area.
Between 1664 and 1674, many new settlers arrived. They came from other parts of America. These included New England, Long Island, and the West Indies. Towns like Elizabethtown and Newark were settled by Puritans. These were people who wanted to practice their religion freely. South of the Raritan River, Quakers from Long Island also settled.
Dividing the Land: Counties and Towns
In 1675, East Jersey was divided into four counties. These were Bergen, Essex, Middlesex, and Monmouth. This helped with managing the area.
There were seven main towns in East Jersey. These included Shrewsbury and Middleton. Other towns were Piscataway and Woodbridge. Also, Elizabethtown, Newark, and Bergen were important. By 1684, about 3,500 people lived in East Jersey.
The Proprietors and Their Influence
East Jersey was a Proprietary colony. This meant it was owned by a group of people called "proprietors." Many of these proprietors were Quakers. Robert Barclay, a leading Quaker, was governor for much of the 1680s. However, the Quakers did not have a huge impact on the government.
In 1682, Barclay and other Scottish proprietors started building Perth Amboy. This town became the capital of East Jersey. In 1687, King James II allowed ships to use Perth Amboy as a port. This helped the colony's trade.
Border Disputes and Unification
Deciding the exact border between East and West Jersey was often difficult. There were many arguments over land ownership. These disputes caused problems for the colony. The people living there often disagreed with the proprietors. The proprietors usually lived in England and were not in the colony.
These arguments continued for many years. Eventually, the disputes became too much. In 1702, the proprietors gave up their rights to govern. They handed control over to Queen Anne's government. This led to East and West Jersey being united. They became one single royal colony, the Province of New Jersey.
Governors of East Jersey (1674–1702)
Here are the main governors who led East Jersey:
| Philip Carteret | 1674–1682 | |
| Robert Barclay | 1682–1688 | |
| Edmund Andros | 1688–1689 | Governed as part of the Dominion of New England |
| Andrew Hamilton | 1692–1697 | |
| Jeremiah Basse | 1698–1699 | |
| Andrew Hamilton | 1699–1702 |
See also
 In Spanish: Jersey Oriental para niños
In Spanish: Jersey Oriental para niños


