New Netherland facts for kids
New Netherland was an important colony in North America. It belonged to the Dutch Empire. The Dutch called it Nieuw-Nederland. It existed from 1614 to 1664, and again from 1673 to 1674.
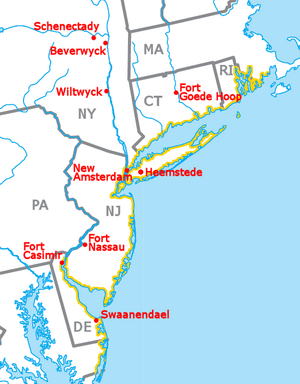
This colony was a key place for the fur trade. Its main city, the capital, was New Amsterdam. Today, this city is known as New York City. Another important trading post was Fort Orange. This place is now called Albany, New York. Most settlers lived in these towns. Many also lived along the Hudson River between them. Some brave settlers lived in more distant parts of the colony.
During the Anglo-Dutch Wars, England took over New Netherland. England then divided the land. This created the English colonies of New York and New Jersey. Parts of New Netherland were also given to other colonies. These included Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and Maryland.
Contents
Why the Dutch Came to America
The Dutch were great sailors and traders. They wanted to find new trade routes. They also wanted to find valuable goods. In the early 1600s, they explored North America. They found many beavers and other animals. Their furs were very popular in Europe. So, the Dutch decided to set up trading posts. This was the start of New Netherland.
Early Explorers and Settlements
In 1609, Henry Hudson, an English explorer working for the Dutch, sailed up a big river. This river is now named the Hudson River after him. He was looking for a shortcut to Asia. He didn't find one, but he found a rich land. This land was full of resources.
The first Dutch trading posts were built around 1614. These were small forts. They helped traders collect furs from Native Americans. Over time, more people came to live there. They built farms and homes.
Life in New Netherland
Life in the colony was a mix of cultures. People from many different countries lived there. They spoke different languages. This made New Netherland a very diverse place. The Dutch allowed people of different religions to live there. This was not common in other colonies at the time.
Trade and Economy
The main business was the fur trade. Traders exchanged European goods like tools and cloth for furs. The furs were then sent back to Europe. Farming was also important. Settlers grew crops like corn and wheat. They also raised animals. This helped the colony feed itself.
Relations with Native Americans
The Dutch had complex relationships with the Native American tribes. They traded furs peacefully with many tribes. However, there were also conflicts. These often happened over land or resources. The Dutch bought land from Native Americans. But sometimes, misunderstandings led to fights.
The End of Dutch Rule
New Netherland was a valuable colony. England wanted to control more of North America. The English and Dutch were often rivals. They fought several wars, known as the Anglo-Dutch Wars.
English Takeover
In 1664, English warships arrived in New Amsterdam. The Dutch governor, Peter Stuyvesant, wanted to fight. But the people of New Amsterdam did not. They knew they could not win. So, Governor Stuyvesant surrendered the colony. The English renamed New Amsterdam to New York. They named the colony New York too.
Brief Return of Dutch Control
In 1673, during another Anglo-Dutch War, the Dutch briefly recaptured New York. They held it for about a year. But in 1674, a peace treaty was signed. The Dutch gave New Netherland back to the English for good. This officially ended Dutch control in North America.
Legacy of New Netherland
Even though Dutch rule ended, New Netherland left a lasting mark. Many places in New York still have Dutch names. For example, Brooklyn, Harlem, and The Bronx. The idea of religious freedom and diverse cultures also started in New Netherland. This helped shape what New York City is today.
Images for kids
-
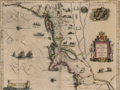
Map based on Adriaen Block's 1614 expedition to New Netherland, featuring the first use of the name. It was created by Dutch cartographers in the Golden Age of Dutch exploration (ca. 1590s–1720s) and Netherlandish cartography (ca. 1570s–1670s).
-
Map of New Netherland and New England, with north to the right
-
The West India House in Amsterdam, headquarters of the Dutch West India Company from 1623 to 1647
-
The storehouse of the Dutch West India Company in Amsterdam, built in 1642, became the headquarters of the board in 1647 because of financial difficulties after the loss of Dutch Brazil.
-
St. Mark's Church in-the-Bowery, site of Peter Stuyvesant's grave
-
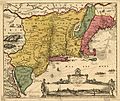
Nicolaes Visscher I (1618–1679), Novi Belgii Novæque Angliæ, reprint of 1685 which is not a completely correct representation of the situation at the time. The border with New England had been adjusted to 50 miles (80 km) west of the Fresh River, while the Lange Eylandt towns west of Oyster Bay were under Dutch jurisdiction.
-
The original settlement has grown into the largest metropolis in the United States, seen here in 2006
-
The Noort Rivier was one of the three main rivers in New Netherland.
See also
 In Spanish: Nuevos Países Bajos para niños
In Spanish: Nuevos Países Bajos para niños
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |