Dutch Empire facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Dutch Empire
|
|
|---|---|
|
Flag
|
|
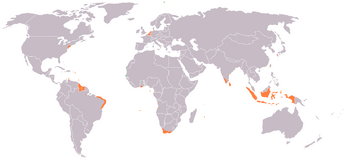
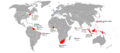
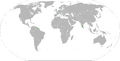
An anachronous map of the Dutch colonial Empire. Light green: territories administered by or originating from territories administered by the Dutch East India Company; dark green the Dutch West India Company.
Countries today
|
The Dutch Empire was a collection of lands controlled by the Dutch Republic. This republic was also known as the United Provinces. Like Portugal and Spain, the Dutch created their own colonial empire. This meant they took control of lands far away from their home country.
The Dutch were very good at shipping and trading. They used these skills to build their empire. At the same time, they were fighting to be independent from Spain. Along with the British, the Dutch were among the first to build colonies. These colonies were often run by large trading companies. The most famous were the Dutch East India Company and the Dutch West India Company.
Brave explorers like Willem Barents, Henry Hudson, and Abel Tasman went on many voyages. They discovered new places around the world for Europeans.
The Dutch navy grew very strong. Because of this, the Netherlands became a leading power in global trade. This happened in the second half of the 17th century. This time is known as the Dutch Golden Age. However, the Netherlands later lost many of its colonies and its global power to the British. This happened when French armies took over the Netherlands during the French Revolutionary Wars.
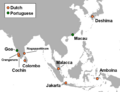
The remaining parts of the Dutch Empire, like the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia), stayed under Dutch control. This lasted until after World War II. After the war, many European colonies gained their independence.
Today, the Netherlands is part of a group of countries called the Kingdom of the Netherlands. This kingdom includes the Netherlands itself, plus Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten.
Images for kids
-
The formal declaration of independence of the Dutch provinces from the Spanish king, Philip II
-
São Luís, Maranhão, Dutch Brazil
-
Overview of Fort Zeelandia on the island of Formosa, 17th century
-
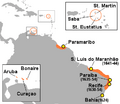
Dutch conquests in the West Indies and Brazil
-
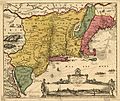
Reprint of a 1650 map of New Netherland
-
Dejima trading post in Japan, c. 1805
-
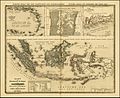
Map of the Dutch colonial possessions around 1840. Included are the Dutch East Indies, Curaçao and Dependencies, Suriname, and the Dutch Gold Coast.
-
Sukarno, leader of the Indonesian independence movement
-
Boer Voortrekkers in South Africa
-
Dutch family in Java, 1902
-
New Amsterdam as it appeared in 1664. Under British rule it became known as New York.
-
Christian cross, altar, pulpit, and organ in the Dutch Reformed Church in Vosburg, South Africa.
-
Dutch plantation in Mughal Bengal, 1665
See also
 In Spanish: Imperio neerlandés para niños
In Spanish: Imperio neerlandés para niños
 | George Robert Carruthers |
 | Patricia Bath |
 | Jan Ernst Matzeliger |
 | Alexander Miles |