Fermionic condensate facts for kids
A fermionic condensate, also called a fermi condensate, is a very special state of matter. It's like a super-liquid (superfluid) and is quite similar to another cool state of matter called a Bose–Einstein condensate.
The main difference is what these states are made of. Bose-Einstein condensates are made from tiny particles called bosons. Bosons are "social" and like to group together. But fermi condensates are made from particles called fermions. Fermions are "anti-social" and usually don't like to stick together. Scientists have to use special tricks to make them form a condensate.
This amazing state of matter was first created in December 2003 by Deborah Jin and her team. Dr. Jin worked at the National Institute of Standards and Technology at the University of Colorado. Her team made a fermi condensate by cooling a cloud of potassium-40 atoms. They cooled them down to an incredibly low temperature – less than a millionth of a degree Celsius above absolute zero. Absolute zero is the coldest possible temperature, about -273.15°C. This is the same super-cold temperature needed to make a Bose–Einstein condensate. The process of cooling a gas until it becomes a condensate is called condensation.


Contents
What are Fermions and Bosons?
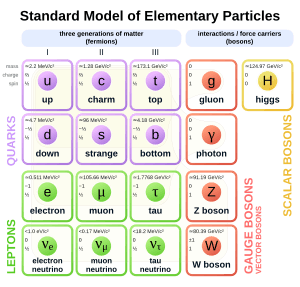
Bosons and fermions are tiny subatomic particles, even smaller than an atom. The main difference between them comes from how their parts (like electrons, neutrons, and protons) add up.
- An atom is made of bosons if it has an even number of electrons.
- An atom is made of fermions if it has an odd number of electrons, neutrons, and protons.
For example, a gluon is a type of boson. The potassium-40 atoms that Deborah Jin used are fermions.
Bosons like to clump together and are attracted to each other. But fermions don't form clumps. In fact, they usually repel each other and are often found in straight lines. This is because fermions follow a rule called the Pauli exclusion principle. This rule says that no two fermions can be in the exact same "quantum state" at the same time. Think of it like two people not being able to stand in the exact same spot at the exact same moment.
How Fermi Condensates are Like Bose–Einstein Condensates
Like Bose–Einstein condensates, fermi condensates will coalesce, meaning the tiny particles that make them up will grow together into one single entity. Both Bose–Einstein condensates and fermi condensates are also man-made states of matter. The particles that form these states have to be super-cooled artificially to get their special properties.
Both states of matter also have no viscosity. Viscosity is how thick or sticky a liquid is (like honey is more viscous than water). So, having no viscosity means they can flow perfectly without any resistance or slowing down.
Making Fermi Condensates with Helium-3
Creating a fermi condensate is very tricky. Remember, fermions usually repel each other because of the Pauli exclusion principle. But Deborah Jin and her team found a way to make them merge.
They used a magnetic field to change the "anti-social" fermions. The fermions started to lose some of their usual properties and began to act a bit like bosons. This allowed separate pairs of fermions to merge together, over and over again.
Dr. Jin believes that this pairing process is similar to what happens in Helium-3, which is also a superfluid. Based on this, scientists can guess that fermionic condensates will also flow without any viscosity.
Fermionic Condensates and Superconductivity
Another related and very interesting idea is superconductivity. In superconductivity, electrons pair up and can flow with zero viscosity. This is a big deal because it could lead to cheaper and cleaner ways to get electricity. It might even be used to power levitating trains or hover-cars in the future!

The problem right now is that most superconductors only work at extremely cold temperatures, around -135°C. This means using things like liquid nitrogen to cool them down, which is difficult and expensive. Scientists are trying to find or create materials that are superconductors at room temperature. In fact, a Nobel Prize will be given to whoever succeeds in making a room-temperature superconductor.
Dr. Jin's team thinks that if they can replace the paired electrons in superconductors with their paired fermions, it might be possible to create a room-temperature superconductor. This would be a huge breakthrough!
See also
 In Spanish: Condensado fermiónico para niños
In Spanish: Condensado fermiónico para niños
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |


