Franco-Prussian War facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Franco-Prussian War |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the wars of German unification | |||||||||
 (clockwise from top right)
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
|
Total deployment:
Initially:
Peak field army strength:
|
Total deployment:
Initially:
Peak field army strength:
|
||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
144,642
|
756,285
|
||||||||
| ~250,000 civilians dead, including 162,000 Germans killed in a smallpox epidemic spread by French POWs | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
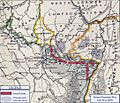
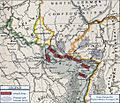
The Franco-Prussian War was a big conflict between France and Prussia. Some German states allied with Prussia also joined the fight. This war was largely started by Otto von Bismarck, who was Prussia's top leader. He wanted to bring all the German states together into one strong country. Bismarck planned to do this by having them fight a common enemy: France. He made sure to annoy the French Emperor, Napoleon III, until France declared war. The war began on July 19, 1870, and ended on May 10, 1871. Prussia and its allies won.
Contents
Why the War Started
The Franco-Prussian War happened for several reasons. One main reason was that France worried about a strong Protestant country growing on its border. France had helped Prussia win a war against Austria in 1866. But France did not want the northern and southern German states to join together.
The Spanish Throne Offer
In 1869, the throne of Spain was offered to a prince from the Prussian royal family. This family was called the Hohenzollerns. France found out and demanded that Prussia refuse the offer. France did not want to be surrounded by Hohenzollern rulers.
Bismarck's Clever Plan
The prince said no to the Spanish throne. But France wanted Prussia to officially refuse it too. The Prussian King Wilhelm I sent a message to the French Emperor, Napoleon III. He said the prince would not become king of Spain.
However, Otto von Bismarck, Prussia's leader, changed this message. He made it sound like his king had insulted the French ambassador. This edited message, called the Ems Telegram, was released to the public. It was part of Bismarck's plan to unite the German states. Both sides became very angry. France declared war on July 19, 1870. The southern German states fully supported Prussia.
How the War Ended
Prussia and its German allies had a bigger army than France. This was because Prussia used conscription, meaning many citizens had to join the army. The Prussian army also had better weapons, training, and leaders. For example, the Prussian General Staff was very well organized.
Key Battles and French Defeat
The Prussian army had some older weapons, but their new Krupp mobile artillery (heavy guns) were much better than France's old guns. Important victories for Prussia included Sedan, Mars-la-Tour, Gravellote, and Metz. They even captured Emperor Napoleon III at Metz.
After Napoleon III was captured, French leaders formed a new government. This new government, called the French Third Republic, continued fighting for a few more months. But after the Germans took over Paris, France finally agreed to make peace.
What Happened Next
After the war, France had to give Prussia some areas that spoke mainly German. These areas were the provinces of Alsace and Lorraine. Prussia then worked to unite all the independent German states into one country. This new country became the powerful German Empire. This event is known as the Unification of Germany.
Images for kids
-
Napoleon III and Bismarck talk after Napoleon's capture at the Battle of Sedan, by Wilhelm Camphausen
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra franco-prusiana para niños
In Spanish: Guerra franco-prusiana para niños