Grace Church (Ca Ira, Virginia) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Grace Church |
|
|---|---|

A front view of Grace Church, taken in October 2008.
|
|
| Religion | |
| Affiliation | Episcopal Church in the United States of America |
| Ecclesiastical or organizational status | Parish church |
| Year consecrated | 1843 |
| Status | Rarely used |
| Location | |
| Location | Ca Ira, Virginia |
| Municipality | Littleton Parish |
| State | Virginia |
| Architecture | |
| Architect(s) | Dabney Cosby |
| Architectural type | Church |
| Architectural style | Greek Revival |
| General contractor | Valentine Parrish |
| Groundbreaking | 1840 |
| Completed | 1843 |
| Materials | Brick |
| U.S. National Register of Historic Places | |
| Added to NRHP | October 30, 1980 |
| NRHP Reference no. | 80004185 |
| Designated | June 17, 1980 |
| Reference no. | 024-0009 |
| Website | |
| none | |
Grace Church, also known as Grace Episcopal Church, is a historic Episcopal church in Cumberland County, Virginia. It was designed by Dabney Cosby, an architect who once helped Thomas Jefferson.
The church is the only large building left from the old town of Ca Ira. Because of its beautiful design and important history, Grace Church was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1980.
Contents
History of the Church and Town
In the early 1800s, Ca Ira was a small farming town in Virginia. It was officially created in 1796. The town's name, Ca Ira, is French. It likely came from a popular song during the French Revolution, which many Virginians supported at the time.
By 1836, Ca Ira was a busy village with about 210 people. It had 40 houses, a few stores, a mill, and a tobacco warehouse.
Building a New Church
Construction on Grace Church began in 1840. The land for the church was donated by a man named Valentine Parrish. He also acted as the main builder for the project. The architect was Dabney Cosby, who had worked with Thomas Jefferson to build parts of the University of Virginia.
Cosby and Parrish had worked together before. An enslaved man named Albert Mann, who lived on the Parrish plantation, is said to have done the woodwork and framing for the church.
When Grace Church was finished in 1843, it became the grandest building in town. It served the people of Ca Ira and the families who owned large farms, called plantations, nearby.
A Town Disappears
For a while, the town of Ca Ira grew. But after the Civil War, people began to move away. By the late 1800s, the town had almost disappeared.
As the town emptied, Grace Church was also abandoned. For many years, it stood empty along with the other buildings.
In 1928, a group called the Ca Ira Restoration Society was formed. It was made up of the descendants of the church's first members. They raised money to repair and restore the beautiful old building.
Today, Grace Church is carefully preserved. To keep its special status, it must hold at least one religious service every year.
A Look Inside and Out
Grace Church is a great example of how different building styles were mixed in the 1800s. It combines ideas from ancient Roman, Greek, and Gothic designs. The building has a classic temple shape and is made with beautiful brickwork, showing the influence of Thomas Jefferson's style.
Exterior Design
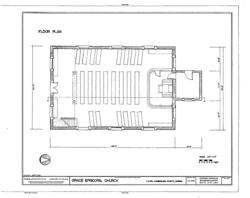
The church is a rectangular brick building, about 32 feet wide and 48 feet long. It has a small room called a vestry attached to the back. The walls are made of handmade bricks, and the builders used different patterns to create a detailed look.
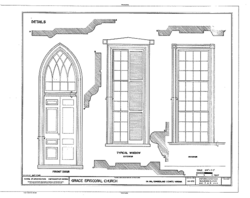
All sides of the church have large windows with shutters. Above the main entrance is a pointed window with a special pattern. The roof is made of slate from nearby Buckingham County. It has a triangular shape at the front and back, which is called a pediment. A small wooden cross was added to the top of the front pediment in the 1950s.
One interesting feature is a special window on the east side that opens all the way to the floor. Local stories say this "jib window" was used during funerals.
Interior Features
Inside, the church is one large room. The original wooden benches, or pews, are still there. They are arranged to create two main aisles for people to walk down.
A balcony, called a gallery, runs along the back wall. It is held up by two large columns. A small, enclosed staircase leads up to the gallery.
The pulpit, where the church leader speaks, is attached to the front wall. It is decorated with a pattern called a Greek fret, which was a popular design at the time. This shows that the architect, Dabney Cosby, knew about the latest styles from popular building books.
The church also has two old wood-burning stoves made of cast iron. These stoves were made by a company in Philadelphia and Baltimore.
The Church Cemetery
Behind the church, in a wooded area, is a small cemetery. It's not known when the first person was buried here. The oldest readable headstones are from the 1880s.
Many of the older grave markers are so worn that they can't be read anymore. Some have been replaced with new stones. The cemetery is still used by some local families today. Two soldiers who fought for the Confederate Army are also buried here.
Why is Grace Church Important?
Grace Church is a special place for several reasons.
- It was designed by Dabney Cosby, an important architect who worked with Thomas Jefferson.
- It is a well-preserved example of a country church that mixes several popular 19th-century styles.
- It is one of the last remaining buildings from the lost town of Ca Ira, serving as a reminder of the community that once thrived there.
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |