Great Bear Lake facts for kids
Great Bear Lake is a huge lake located in the Northwest Territories, Canada. It's special because it's the biggest lake that is completely inside Canada. It's also the fourth largest lake in North America and the eighth largest lake in the entire world! Imagine how big that is – it's like a small inland sea!
Contents
Exploring Great Bear Lake's Location and Size
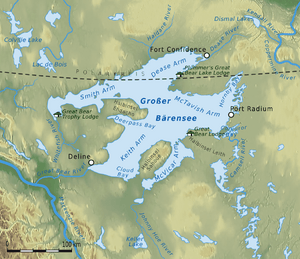
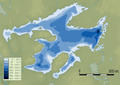
Great Bear Lake is found in the northern part of Canada, close to the Arctic Circle. This means it's in a very cold region, and parts of the lake can be covered in ice for many months of the year. The lake covers a massive area of about 31,153 square kilometers (12,028 square miles). That's bigger than some countries!
How Deep is Great Bear Lake?
This giant lake is also very deep. Its deepest point is about 446 meters (1,463 feet). To give you an idea, that's taller than the Empire State Building! Because it's so deep and cold, the water at the bottom stays very chilly all year round.
How Was the Lake Formed?
Great Bear Lake was formed a very long time ago by glaciers. During the last ice age, huge sheets of ice carved out the land. As the climate warmed, these glaciers melted, filling the deep hollows they had created with water. This process formed many of the large lakes in Canada, including Great Bear Lake.
Life Around Great Bear Lake
Despite the cold climate, Great Bear Lake and the land around it are home to many interesting plants and animals. The area is part of the boreal forest and tundra regions.
Animals of the Lake and Land
The lake is famous for its fish, especially lake trout and Arctic char. These fish are well-adapted to the cold, deep waters. On the land surrounding the lake, you might find animals like caribou, moose, grizzly bears, and wolf packs. Many different kinds of birds also visit the lake, especially during the warmer months when they come to nest and raise their young.
Plants and Trees
The land around Great Bear Lake is covered with coniferous forests, mostly spruce and pine trees. Closer to the Arctic Circle, the trees become smaller and eventually give way to tundra, where only small shrubs, mosses, and lichens can grow because the ground is frozen for most of the year.
Human History and Communities
People have lived around Great Bear Lake for thousands of years. The Dene people, an Indigenous group, have a deep connection to the lake and its lands. They have traditionally hunted, fished, and trapped in the area.
Délı̨nę: A Community on the Lake
One of the main communities on the shores of Great Bear Lake is Délı̨nę. This community is home to many Dene people. The name "Délı̨nę" means "where the water flows" in the North Slavey language, referring to the outlet of the Great Bear River. The people of Délı̨nę have a rich culture and history tied to the lake.
Historical Exploration
European explorers and fur traders also visited Great Bear Lake. In the past, the lake was an important route for the fur trade. Fort Confidence, a historic trading post, was built near the lake's outlet in the 19th century.
Great Bear Lake Today
Today, Great Bear Lake remains a vital part of the Northwest Territories. It's important for the local communities, providing food and a connection to their traditions. The lake is also a beautiful natural area, attracting some visitors who want to experience its wild beauty and learn about its unique environment. Protecting this amazing lake and its surrounding ecosystem is very important for future generations.
Images for kids
-
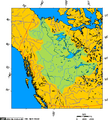
Mackenzie River drainage basin showing Great Bear Lake's position in the Western Canadian Arctic
-
Ruins of Fort Confidence at the mouth of the Dease River in 1911
-
The community of Délı̨nę on Great Bear Lake
More to Explore
 In Spanish: Gran Lago del Oso para niños
In Spanish: Gran Lago del Oso para niños