Green Cove Springs, Florida facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Green Cove Springs, Florida
|
|
|---|---|
| City of Green Cove Springs | |

Images from top, left to right: Clay County Courthouse, the springs, Clay County Courthouse, St. Mary's Episcopal Church, Clay Theatre, Clay County Historical Museum
|
|
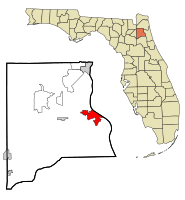
Location in Clay County and the state of Florida
|
|
| Country | United States of America |
| State | Florida |
| County | Clay |
| Settled | 1816 |
| Incorporated | November 2, 1874 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Council-Manager |
| Area | |
| • Total | 10.27 sq mi (26.59 km2) |
| • Land | 7.53 sq mi (19.50 km2) |
| • Water | 2.74 sq mi (7.09 km2) |
| Elevation | 16 ft (5 m) |
| Population
(2023)
|
|
| • Total | 10,130 |
| • Density | 1,345.29/sq mi (519.49/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP code |
32043
|
| Area code(s) | 904, 324 |
| FIPS code | 12-27400 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0283381 |
Green Cove Springs is a city in Clay County, Florida, United States. It is also the county seat, which means it's where the county government is located. Green Cove Springs is part of the larger Jacksonville metropolitan area. In 2020, about 9,786 people lived here. This was a big jump from 6,908 people in 2010.
The city gets its name from the St. Johns River. The river bends here, and the area is surrounded by trees that stay green all year.
Contents
History
The Green Cove Springs area has been home to people for over 7,000 years. Native Americans were first drawn to a warm mineral spring here. This spring was even called the "Original Fountain of Youth" by locals. In the 1800s, many people came to visit the spring. More than a dozen hotels were built nearby for them.
Today, the spring water, which smells a bit like sulfur, fills a public swimming pool. After that, it flows into the St. Johns River. The area was first developed in 1816 by George J. F. Clarke. He was given land to build a sawmill. Green Cove Springs was first called White Sulfur Springs in 1854. It was renamed in 1866 and became the county seat of Clay County in 1871.
For a long time, farming and tourism were the main ways people made money here. But by the late 1800s, Henry Flagler's railroad started taking tourists to other parts of Florida. In 1895, a very cold winter, called the Great Freeze, ruined the area's citrus crops. This caused tourism to almost stop.
Things started to improve in the 1920s as more people traveled by car. This brought tourists back to the city. However, the Great Depression in the 1930s ended this period of growth.
Florida's first women's club was started in Green Cove Springs in 1883. This group, called the Village Improvement Association, worked to make the town more beautiful. They also opened the town's first public library.
New growth came to Green Cove Springs just before and during World War II. On September 11, 1940, the U.S. Navy opened Naval Air Station Lee Field. This base was named after Ensign Bejamin Lee, a pilot who died in World War I. In August 1943, the base was renamed Naval Air Station Green Cove Springs. It had four long asphalt runways. After the war, it became a smaller naval air station.
Thirteen piers were built along the St. Johns River near the base. These piers held a "mothball fleet" of about 500 Navy ships. These ships were kept ready in case they were needed again. In 1960, the Navy closed the base and the pier facility. Some ships were given to other countries, and others were moved.
In 1984, the city took over the old naval base. It is now used for business and industry as the Clay County Port and Reynolds Industrial Park. The old airfield is now a private airport called Reynolds Airpark. It has one runway that is still used.
Green Cove Springs is the hometown of Charles E. Merrill (1885–1956). He was one of the people who started the famous company Merrill Lynch. The city's spring is even mentioned in a poem by his son, James Merrill.
Another famous person from Green Cove Springs is Augusta Savage (1892–1962). She was an important African-American sculptor. She was a leader during the Harlem Renaissance art movement.
Locally, Green Cove Springs is known for Gustafson's Farm. This company sells milk and dairy products all over Florida. The main Gustafson Dairy Farm is in Green Cove Springs. It is one of the largest privately owned dairy farms in the southeastern United States. It started in 1908 and covers almost 10,000 acres (40 km2). The packaging for Gustafson products shows pictures of the founders, Frank and Agnes Gustafson.
Some scenes for the 1971 monster movie Blood Waters of Dr. Z were filmed here. This movie was later made fun of on the TV show Mystery Science Theater 3000.
Historic Places
These places in Green Cove Springs are listed on the National Register of Historic Places:
- Clay County Courthouse
- Green Cove Springs Historic District
- St. Mary's Church
- “The Hellhouse” which was the original rehearsal studio for the band Lynyrd Skynyrd
Geography
Green Cove Springs is located on the eastern edge of Clay County. It sits right along the St. Johns River.
U.S. Route 17 goes through the middle of the city. It leads north about 28 miles (45 km) to Jacksonville. It goes south about 26 miles (42 km) to Palatka. State Road 16 goes west from the city center. It leads about 27 miles (43 km) to Starke. State Road 16 also goes east from US 17. It crosses the St. Johns River over the Shands Bridge. This road leads to St. Augustine, about 25 miles (40 km) to the east.
By the late 2020s, a new major toll road called the First Coast Expressway will be built. This road will go around the west and south sides of Green Cove Springs. It will connect two major highways, I-10 and I-95.
The city covers a total area of about 10.27 square miles (26.6 km2). About 7.53 square miles (19.5 km2) of this is land. The rest, about 2.74 square miles (7.1 km2), is water.
Population and People
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1880 | 320 | — | |
| 1890 | 1,106 | 245.6% | |
| 1900 | 929 | −16.0% | |
| 1910 | 1,319 | 42.0% | |
| 1920 | 2,093 | 58.7% | |
| 1930 | 1,719 | −17.9% | |
| 1940 | 1,752 | 1.9% | |
| 1950 | 3,291 | 87.8% | |
| 1960 | 4,233 | 28.6% | |
| 1970 | 3,857 | −8.9% | |
| 1980 | 4,154 | 7.7% | |
| 1990 | 4,497 | 8.3% | |
| 2000 | 5,378 | 19.6% | |
| 2010 | 6,908 | 28.4% | |
| 2020 | 9,786 | 41.7% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 10,130 | 46.6% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
Population in 2010 and 2020
The tables below show the different groups of people living in Green Cove Springs.
| Race | Pop 2010 | Pop 2020 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White (NH) | 4,920 | 6,862 | 71.22% | 70.12% |
| Black or African American (NH) | 1,291 | 1,275 | 18.69% | 13.03% |
| Native American or Alaska Native (NH) | 19 | 26 | 0.28% | 0.27% |
| Asian (NH) | 66 | 153 | 0.96% | 1.56% |
| Pacific Islander or Native Hawaiian (NH) | 12 | 25 | 0.17% | 0.26% |
| Some other race (NH) | 4 | 42 | 0.06% | 0.43% |
| Two or more races/Multiracial (NH) | 113 | 427 | 1.64% | 4.36% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 483 | 976 | 6.99% | 9.97% |
| Total | 6,908 | 9,786 |
In 2020, there were 9,786 people living in the city. There were 2,997 households and 2,046 families. In 2010, there were 6,908 people, 2,379 households, and 1,737 families.
Religion
Catholic Churches
Sacred Heart Catholic Church is part of the Diocese of St. Augustine. It started as a mission in 1874 and now serves the city.
Protestant Churches
Hickory Grove Baptist Church is the oldest Protestant church in Green Cove Springs. Other Baptist churches include First Baptist, First African Missionary Baptist, and Mount Pleasant Missionary Baptist.
St. Mary's is the main Episcopal Church in Green Cove Springs.
United Methodist Church and Mount Zion African Methodist are the two Methodist churches.
There is also a Congregationalist church in Green Cove.
Education
Green Cove Springs is part of the Clay County School District. The city has Charles E. Bennett Elementary School, Green Cove Springs Jr. High School, and the Bannerman Learning Center. Clay High School is just outside the city limits.
Notable People
Many interesting people have come from Green Cove Springs:
- Kevin Allen (born 1965), a racing driver
- Cliff Avril (born 1986), a player in the National Football League
- Charles Thomas Butler (1906–1964), a Major League Baseball pitcher
- Frank J. Canova Jr. (born 1956), an engineer who helped invent the smartphone
- Caeleb Dressel (born 1996), a swimmer and seven-time Olympic gold medalist
- Will Holden (born 1993), a player in the National Football League
- Charles E. Merrill (1885–1956), a famous businessman and giver of money to good causes
- Maxey Dell Moody Jr. (1913–1987), who started MOBRO Marine, Inc.
- Augusta Fells Savage (1892–1962), a sculptor and art teacher, important during the Harlem Renaissance
Museums
- Clay County Historical Society Museum
- Military Museum of North Florida
Transportation
Roads
 SR 16 East - Leonard C. Taylor Parkway
SR 16 East - Leonard C. Taylor Parkway SR 16 West - Idlewild Avenue / Ferris Street
SR 16 West - Idlewild Avenue / Ferris Street US 17 - (North/South) Orange Avenue
US 17 - (North/South) Orange Avenue
The center of Green Cove Springs is where US 17 and Florida 16 meet. Just outside the city, Florida 16 East leads to the Shands Bridge. This bridge is long and narrow and crosses the St. Johns River. It connects Green Cove Springs to St. Johns County.
Public Transportation
Green Cove Springs has a public transportation system called Clay Community Transportation (CCT). This is part of the Jacksonville Transit Authority (JTA). CCT has two bus lines that go through Green Cove Springs:
- Clay Blue Line - This line connects Green Cove Springs to other towns like Penney Farms, Fleming Island, and Orange Park. It also goes to Naval Air Station Jacksonville.
- Clay Green Line - This line connects Green Cove Springs to Doctor's Inlet, Fleming Island, Penney Farms, and Keystone Heights.
Trains
Even though no trains stop in Green Cove Springs for passengers, a train line does run right through the middle of the city.
Airports
Green Cove Springs has two airports:
- Reynolds Airpark (formerly Naval Auxiliary Air Station Lee Field) - This used to be a Navy air strip but is now privately owned.
- Haller Airpark - This is a smaller private airport used for local and personal flights.
See also
 In Spanish: Green Cove Springs para niños
In Spanish: Green Cove Springs para niños





