Civil Guard (Spain) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Civil GuardGuardia Civil |
|
|---|---|

Emblem of the Civil Guard
|
|
| Abbreviation | GC |
| Motto | El honor es mi divisa Honour is my badge |
| Agency overview | |
| Formed | May 13, 1844 |
| Employees | 85,426 total (2020) and 77,223 active (2020) |
| Jurisdictional structure | |
| Operations jurisdiction | Spain |
| General nature | |
| Specialist jurisdictions |
|
| Operational structure | |
| Headquarters | Calle de Guzmán el Bueno, 110, 28003 Madrid, Spain |
| Elected officers responsible |
|
| Agency executive |
|
| Parent agency | Directorate-General of the Civil Guard |
| Notables | |
| Award | |
The Civil Guard (in Spanish, Guardia Civil) is one of Spain's two national police forces. It is a special type of police force called a gendarmerie, which means it has a military nature. It handles police duties for civilians but is managed by both the Ministry of the Interior and the Ministry of Defence.
The Civil Guard is often called the benemérita, which means "meritorious" or "reputable." In surveys, Spaniards often say it is the national institution they value the most. The Civil Guard not only works in Spain but also takes part in peacekeeping missions in other countries. It is a member of the European Gendarmerie Force.
As part of its job, the Civil Guard patrols rural areas, highways, and ports. The National Police handles safety in the cities. The Civil Guard officers are often stationed in special buildings called casas cuartel, which are both a police station and a place for officers to live.
Contents
History of the Civil Guard
How the Civil Guard Started
The Civil Guard was created in 1844 by the 2nd Duke of Ahumada during the reign of Queen Isabel II. Before this, law enforcement was handled by a group called the "Holy Brotherhood." This older system was not very effective, and criminals could easily escape by moving to a different area.

The first police academy for the Civil Guard was set up in Valdemoro, near Madrid, in 1855. Graduates received the famous tricorne hat, a three-cornered hat that is still part of their formal uniform.
One of the first major jobs of the Civil Guard was to stop bandits on the roads, especially in the region of Andalusia. This area was known for robberies of travelers and business people. The Civil Guard worked hard to make the roads safe for everyone.
The Civil Guard was also created to help keep order in the countryside. It was designed to be a mobile force that could travel to remote areas. Its members, called guardias, still patrol in pairs, which is called a pareja. One officer takes the lead while the other provides backup.
The Spanish Civil War (1936–1939)
During the Spanish Civil War, the Civil Guard was divided. About half of its members stayed loyal to the Spanish Republic, while the other half joined the rebel forces. The leader of the corps, Inspector General Sebastián Pozas, remained loyal to the government. The force was effective for both sides during the conflict.

After the Civil War
After the war, during the government of General Francisco Franco (1939–1975), the Civil Guard was combined with another police force, the Carabineros. Some people have criticized the Civil Guard for being too strict during this time, especially in rural areas where there was less oversight.
Even after this period, some members of the Civil Guard were involved in politics. On February 23, 1981, a Civil Guard officer named Lt. Col. Antonio Tejero took part in a failed attempt to overthrow the government, known as the 23-F coup. He and 200 other members briefly took over the Spanish parliament building. The coup failed after King Juan Carlos appeared on television and spoke out against it.
The Modern Civil Guard
Today, the Civil Guard has many important duties. It is the largest police force in Spain based on the area it covers.
Some of its main responsibilities include:
- Police work in all areas of Spain except for cities with more than 20,000 people.
- Patrolling highways.
- Protecting the King of Spain and the Spanish Royal Family.
- Acting as military police during missions in other countries.
- Fighting smuggling.
- Controlling customs at ports and airports.
- Airport security.
- Guarding prisons.
- Controlling weapons licenses.
- Protecting Spain's borders.
- Handling bombs and explosives (the TEDAX unit).
- Leading high-risk special operations (the UEI unit).
- Acting as a coast guard.
- Gathering intelligence to fight terrorism (SIGC).
- Cybercrime investigation.
- Mountain search and rescue (GREIM).
- Enforcing environmental laws (SEPRONA).
International Missions
The Civil Guard has served as peacekeepers in many United Nations missions around the world. These missions have taken place in countries like Bosnia and Herzegovina, Haiti, and Iraq.
In Afghanistan, a special unit of the Civil Guard called the GAR (Rapid Action Group) helped protect the European Union's representative. Later, they helped train the Afghan police. Civil Guard units have also been sent to Iraq to train and assist Iraqi police in their fight against ISIS.
Traditions and Uniforms
The Civil Guard has many unique traditions and symbols.
- Motto: The motto is "Honor is my badge."
- Symbol: The symbol includes the Royal Crown of Spain, a sword, and a fasces (a bundle of rods with an axe).
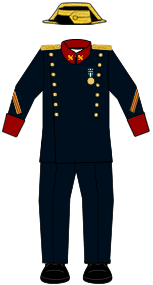
- The Tricorn Hat: The most famous part of the Civil Guard's uniform is the tricornio, a three-cornered hat made of black patent leather. It is now worn mostly for ceremonies and parades.
- Patron Saint: The patron saint of the Civil Guard is Our Lady of the Pillar, declared by royal decree in 1913.

Uniforms Today
The Civil Guard wears different uniforms depending on their job. The traditional formal uniform is still used for ceremonies. For daily work, officers now wear a more modern and comfortable uniform, which includes a green polo shirt, cargo pants, and a baseball cap.
| Uniforms of the Civil Guard | |||||||
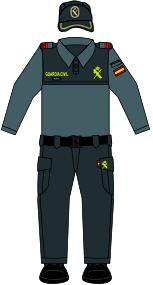 |
 |
 |
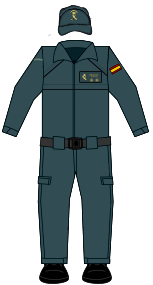 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
Road waistcoat |
Motorcyclist ATGC |
Coveralls |
Summer |
|
|
Winter |
 |
 |
 |
 |
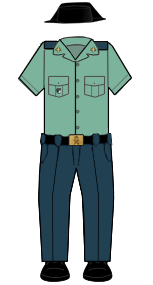 |
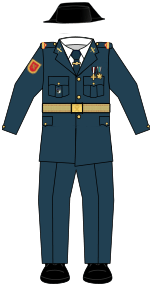 |
 |
 |
|
Rescue |
Diver |
Military Police |
Winter |
Summer |
|
|
Historic |
Special Units
The Civil Guard has many specialized units for different tasks.
 UAR (Unidad de Acción Rural) – A tactical unit for rural areas.
UAR (Unidad de Acción Rural) – A tactical unit for rural areas. Seguridad Ciudadana – The main Public Order and Prevention service.
Seguridad Ciudadana – The main Public Order and Prevention service. GEAS (Grupo Especial de Actividades Subacuáticas) – The diving unit.
GEAS (Grupo Especial de Actividades Subacuáticas) – The diving unit. GRS (Grupo de Reserva y Seguridad) – The Security Group, used for riot control.
GRS (Grupo de Reserva y Seguridad) – The Security Group, used for riot control. SEMAR (Servicio Marítimo) – The Naval Service, which patrols the coast.
SEMAR (Servicio Marítimo) – The Naval Service, which patrols the coast. SEPRONA (Servicio de Protección de la Naturaleza) – The Nature Protection Service.
SEPRONA (Servicio de Protección de la Naturaleza) – The Nature Protection Service. SAER (Servicio Aéreo) – The Air Service.
SAER (Servicio Aéreo) – The Air Service. Servicio Cinológico – The K-9 Unit, with dogs trained to find illegal substances and explosives.
Servicio Cinológico – The K-9 Unit, with dogs trained to find illegal substances and explosives. GREIM (Grupos de Rescate e Intervención en Montaña) – The Mountain and Speleology Rescue unit.
GREIM (Grupos de Rescate e Intervención en Montaña) – The Mountain and Speleology Rescue unit. Agrupación de Tráfico – The Traffic Group, which patrols highways.
Agrupación de Tráfico – The Traffic Group, which patrols highways. GAR (Grupo de Acción Rápida) – A special anti-terrorist unit.
GAR (Grupo de Acción Rápida) – A special anti-terrorist unit. UCO (Unidad Central Operativa) – A unit for complex, nationwide investigations.
UCO (Unidad Central Operativa) – A unit for complex, nationwide investigations. UEI (Unidad Especial de Intervención) – The Special Intervention Unit for very high-risk situations.
UEI (Unidad Especial de Intervención) – The Special Intervention Unit for very high-risk situations.
How to Join the Civil Guard
To become a member of the Civil Guard, a person must meet these requirements:
- Be a Spanish citizen.
- Speak Spanish well.
- Be between 18 and 31 years old (or 16 for cadets).
- Meet height requirements (over 1.65m for men, 1.55m for women).
- Have completed high school.
- Be in good health.
- Know how to swim.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Guardia Civil para niños
In Spanish: Guardia Civil para niños
- Emblems of the Spanish Civil Guard
- Civil Guard (disambiguation)
- Guardia de Asalto
- Policía Armada
- Policía Nacional
- Republican National Guard (Portugal)
- Civil Guard (Philippines)
- Operation Anubis










