Heterotroph facts for kids
A heterotroph is a living thing that cannot make its own food. Instead, it gets its energy and nutrients by eating other living things or their remains. This includes plants, animals, or other organic matter. The word "heterotroph" was first used in biology in 1946.
Contents
What Are Heterotrophs?
Heterotrophs are found in all major groups of life, including Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. This means you can find them among animals, fungi, some bacteria, and protists. Even some parasitic plants are heterotrophs.
Most plants are autotrophs. This means they make their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water. This process is called photosynthesis. They create oxygen and complex food compounds. Some plants, like carnivorous plants, eat insects to get extra nutrients, but they still make most of their food through photosynthesis.
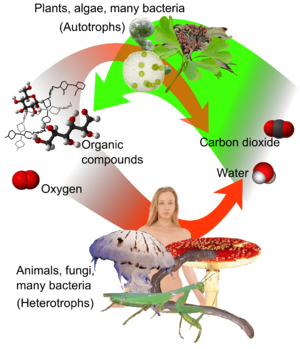
Autotrophs use energy from the sunlight to turn simple things like carbon dioxide into food. Think of it this way: heterotrophs (like animals) eat either autotrophs (like plants) or other heterotrophs.
Heterotrophs can use all the energy they get from food for growing and reproducing. Autotrophs, on the other hand, have to use some of their energy to make their own food first.
Types of Heterotrophs
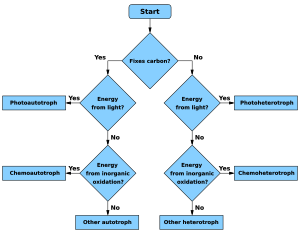
Heterotrophs can be grouped by where they get their energy.
- If a heterotroph uses chemical energy, it's called a chemoheterotroph. Humans and mushrooms are examples of these.
- If it uses light for energy, it's a photoheterotroph. Some types of bacteria, like green non-sulfur bacteria, are photoheterotrophs.
Heterotrophs can also be organotrophs or lithotrophs.
- Organotrophs get energy by eating carbohydrates, fats, and proteins from plants and animals.
- Lithoheterotrophs get energy from inorganic compounds. These can be things like ammonium, nitrite, or sulfur.
Heterotrophs in Food Chains
In a food chain, a heterotroph is known as a consumer. Consumers cannot make their own food. They either eat the food that producers make (like plants) or they eat other organisms. All animals are consumers. To survive, consumers must get food from other living things. There are three main types of consumers:
Herbivores
Consumers that only eat plants are called herbivores. The word "herbivore" comes from Latin words meaning "grass" and "to eat." A giraffe is a good example of a herbivore.
Carnivores
Consumers that only eat animals are called carnivores. This word comes from Latin words meaning "flesh" and "to eat." A tiger is an example of a carnivore.
Omnivores
Consumers that eat both plants and animals are called omnivores. This word comes from Latin words meaning "all" and "to eat." Humans are a great example of an omnivorous consumer.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Heterótrofo para niños
In Spanish: Heterótrofo para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |