History of dance facts for kids

The history of dance is a bit tricky to learn about because dance doesn't usually leave behind physical objects like tools or cave paintings. It's hard to say exactly when dance became a part of human culture. Dance styles are different all over the world. They show the unique culture and feelings of a community. Dance can help tell a story, share feelings, and connect people.
Contents
Early Dance Forms
Dancing might have been something early humans did even before they fully evolved. Dance has been a big part of ceremonies, rituals, celebrations, and entertainment for a very long time. We find clues about dance from ancient times. For example, there are 10,000-year-old paintings in the Bhimbetka rock shelters in India. Also, Egyptian tomb paintings from around 3300 BC show people dancing. Many dances we see today come from these old, traditional, and ceremonial dances.
Connecting Through Movement
Dance may have helped early humans work together and survive. Studies show that good dancers often have genes linked to being good at social communication.
The word "kinesthetic" helps us understand how dance communicates. It means knowing how your own body moves. When someone dances with their whole body and feelings, they send a message to the audience. Dance moves and music are very important. When a group dances together, holding hands or shoulders, it makes them feel connected.
Fun Folk Celebrations
Many early dances were part of rituals for gods. People believed these gods needed to be entertained for peace. Dance is still used in many celebrations today. Throughout history, dance has been used for community gatherings, harvests, and worship. Dance started as folk dances and grew into court performances. Now, we see dance in theaters and movies.
Dances for Rituals and Healing
Dance was often part of religious or spiritual rituals. For example, a rain dance might be performed during dry times. Ancient Chinese texts mention shamans dancing for rain. Dance was also important in ancient Egypt's religious rites. It is still a big part of many African ceremonies. Ritual dances are also performed in temples and at religious festivals. Examples include the Rasa ritual dances in India and the Cham dances in Tibet.
Dance was also used to help people heal. Many cultures, from the Brazilian rainforest to the Kalahari Desert, used dance for this. In medieval Europe, people danced the danses macabres. They thought it would protect them from sickness. However, sometimes people danced so much they became exhausted.
A legend from Sri Lanka says that Kandyan dances started 2500 years ago. It was a magic dance ritual that cured a king of a mysterious illness.
Sharing Stories and Feelings
One of the first structured uses of dance was for telling myths. It was also used to show feelings for others. Before people wrote things down, dance was a way to pass stories from one generation to the next.
In ancient Greece, the poet Homer wrote about chorea (χορεία), a type of dance. The early Greeks used dance to show all kinds of feelings. For example, a dance of the Furies could scare anyone who watched it. The Greek philosopher Aristotle thought dance was like poetry. He said dancers could show feelings and actions with rhythm and movement. Greek sculptors even studied dancers' poses to create their art.
Dance Around the World
Asia

Indian Classical Dance
An early book about dance is the Natya Shastra. This book is the basis for modern classical Indian dances like Bharathanatyam.
When the British ruled India, public dance performances were not allowed. Many people did not approve of them. In 1947, India became free. This allowed dance to become popular again. Old dance forms and regional styles were rediscovered. New dances were created, blending old traditions with new ideas.
In Sri Lanka, an ancient book called Mahavamsa says that when King Vijaya arrived in 543 BCE, he heard music and dancing from a wedding. The dances of Sri Lanka come from ancient tribes and myths. The classical Kandyan dances of Sri Lanka have a very complex rhythm system. Cymbals called thalampataa help keep the beat.
Chinese Dance

China has a long history of dance. Some dances mentioned in old texts, like sleeve dances, are still performed today. Some early dances were part of spiritual rituals. Folk dances also became court dances. Important ancient dances were the ceremonial yayue from the Zhou dynasty (around 1000 BC). Dance in China reached its peak during the Tang dynasty. During this time, dancers from all over the world performed for the emperor.
Later, Chinese opera became very popular. Many dances became part of the opera. Women's dance also declined after the Song dynasty because of footbinding. This practice may have started from dancers wrapping their feet. The most famous Chinese traditional dances are the dragon dance and lion dance. The lion dance was described in the Tang dynasty in a form similar to today's dance.
Iranian Dance
Ancient Times

People in the Iranian plateau have known about dance for a very long time. They used dance in music, plays, dramas, and religious rituals. They used masks, animal costumes, and musical instruments. Dance, play, and drama were used for celebrations, mourning, and worship. Old artifacts from Iran show pictures of dancers and performers from as early as 6000 BC.
Later History

One of the oldest known dances from ancient Iran was a dance for the god Mithra. This dance involved sacrificing a bull and was meant to bring strength to life. The Greek historian Herodotus wrote about ancient Persian dance. Over time, as foreign powers took over Persia, old dance traditions slowly disappeared.
After the Iranian Revolution in 1979, dancing was no longer allowed in public. This was due to new rules about how people should behave. Many talented Persian dancers moved to other countries. They continued to dance and teach in places like Europe and the United States.
Europe

From Court Dances to Ballet (15th–19th Centuries)
Ballet dancing started in the Italian royal courts in the 15th century. Dance teachers would teach steps to nobles. The court would perform together for fun. This continued for hundreds of years. In the 17th century, court ballet became very popular under King Louis XIV of France.
By the 18th century, ballet moved from royal courts to the Paris Opéra. A composer and dancer named Jean-Baptiste Lully helped ballet become a more serious art form. Professional dancers, not just nobles, began to perform.
During the 18th century, ballet changed from a court spectacle to its own performance art. Ballet shows started to tell stories. Dancers used expressive movements to show how characters felt. This dramatic style was called ballet d'action. For the first time, ballet tried to show human emotions directly from the dancers. Dancers stopped wearing masks so their faces could show feelings.
Costumes at this time were very stiff. Dancers' movements were limited by heavy fabrics and tight corsets. Costumes often hid the dancer's body, making it hard to see the fancy steps. In 1760, choreographer Jean Georges Noverre called for changes. He wrote Letters on Dancing and Ballets. Noverre said costumes should be made of light fabrics that move with the body. Dancers also started wearing soft slippers that fit snugly. This helped ballerinas feel confident enough to dance on their toes. These more natural costumes allowed dancers to try new movements, eventually leading to dancing on pointe.
The Romanticism era brought ballets about fantasy, mystery, and faraway lands. These ballets focused on emotions and spiritual worlds. This was the true beginning of pointe-work. On her toes, the ballerina (like the famous Marie Taglioni) seemed to float across the stage. She looked like a magical being who barely touched the ground. During this time, the male dancer became less important. He was often just there to lift the ballerina. This changed in the early 20th century with the rise of male ballet stars like Vaslav Nijinsky and the Ballets Russes. By then, ballet had developed into the art form we know today, with its costumes, choreography, and stories. Nijinsky also brought athleticism into ballet. His dances were seen as new and daring then, but now they are considered some of the first contemporary ballets.
Early 20th Century: From Ballet to Modern Dance
In the early 20th century, the Ballets Russes started to change ballet. Since then, dancers have kept trying to break away from classical ballet rules. Today, ballet includes many different styles of music, costumes, and multimedia. The lines that define classical ballet are always changing.
The 20th century was a time of huge creative growth for dancers and choreographers. It was also a time when the idea of "dance" became much wider. The Ballets Russes was a turning point for ballet in the West. They worked with famous artists like Coco Chanel and Pablo Picasso.
Africa
African dance mostly refers to dance styles from Sub-Saharan Africa. Many of these dances are based on traditional rhythms and music. Modern African dance styles are deeply connected to culture and tradition. Many tribes have people whose job is to pass down dance traditions. These dances have been taught for centuries, often without changes. Each tribe created its own unique dance style. These styles fall into three main groups based on their purpose.
First, there is religious dancing. Many tribes believe this dancing brings peace, health, and good fortune. Religious dances often included masked performers who acted as spirits. Religion was a part of all traditional African life, and it still affects African dance today.
Second, there was griotic dance. This type of dance told a story. It is named after a griot, who is a traditional storyteller in West Africa. Some griotic dances were only performed by the tribe's griot. Today, dance groups perform these same dances.
Third, there are ceremonial dances. These dances are performed at events like weddings, anniversaries, and coming-of-age ceremonies. However, many dances had more than one purpose. Dance was often very important for a ruler to keep their status in the tribe. When Europeans colonized Africa, some African dance styles disappeared. Other styles mixed with each other or with dances from outside Africa.
African Dance and Slavery
When people were taken from Africa and sold as slaves, starting in the 1500s, they brought their dance styles with them. Whole cultures were brought to the New World. This was especially true in places like Brazil, where slaves had more freedom to keep their cultures. African dance styles mixed with new cultural experiences to create new dances. For example, slaves changed high-energy stepping dances to shuffling dances to avoid upsetting their masters.
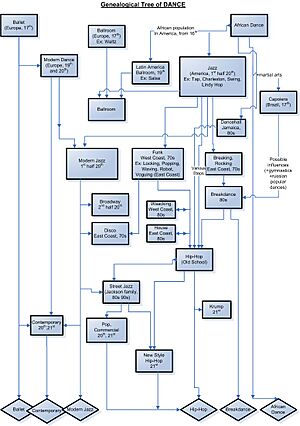
In North America, slaves had less freedom to continue their culture and dance. However, many of these dances have grown into modern styles. Examples include African-American dance and Brazilian dance. For instance, the Calenda dance in Brazil came from tribal dances. The Calenda then became the Cakewalk, which was danced to make fun of plantation owners. The Cakewalk later turned into the Charleston. Capoeira was a martial art from Africa. Enslaved Africans disguised it as a dance so plantation owners would not suspect them.
Modern Dance (Late 20th and Early 21st Centuries)
Postmodern Dance
After modern dance became popular in the early 20th century, postmodernism grew in the 1960s. Postmodern dance focused on simple things. It celebrated the beauty of everyday movements and untrained bodies. The famous "No" manifesto by Yvonne Rainer rejected costumes, stories, and fancy elements. It favored raw, simple movement. However, soon sets, decorations, and surprising elements came back into modern dance.
Street Dance and Hip-Hop
At the same time, mass culture saw the rise of street dance. In 1973, the famous group Jackson 5 performed a dance called the Robot on TV. This dance was popular in Richmond, California. This event, and later performances by black dancers on Soul Train, started a street culture revolution. B-boying in New York, Locking in Los Angeles, Popping in Fresno, California, Boogaloo in Oakland, California, and Robot in Richmond, California, all had their own creative beginnings in the late 1960s and 1970s. Each style has its own history, practices, and innovators.
Hip-hop dance began when Clive Campbell, also known as Kool DJ Herc, came to New York from Jamaica in 1967. He brought reggae music with him. He is known for being the first DJ to use two turntables and two copies of the same record to create his music. He extended the "breaks" in songs. These were the parts where the drum beats were strongest. This allowed him to create a culture of "break boys" and "break girls" who danced during these breaks. These dancers, called b-boys and b-girls, created breakdancing. Breakdancing is now a key part of hip-hop dance.
See also
 In Spanish: Historia de la danza para niños
In Spanish: Historia de la danza para niños
 | William L. Dawson |
 | W. E. B. Du Bois |
 | Harry Belafonte |