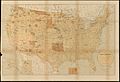
Indian reservation facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Indian reservations |
|
|---|---|
| Also known as: Domestic Dependent Nation |
|
 |
|
| Category | Autonomous administrative divisions |
| Location | United States of America |
| Created | 1658 (Powhatan Tribes) |
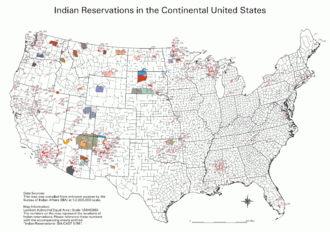
| Number | 326 (map includes the 310 as of May 1996) |
| Populations | 123 (several) - 173,667 (Navajo Nation) |
| Areas | ranging from the 1.32-acre (0.534 hectares) Pit River Tribe's cemetery in California to the 16 million-acre (64 750 square kilometers) Navajo Nation Reservation located in Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah |
An Indian reservation is a special area of land in the United States. These lands are managed by Native American tribes themselves. They work with the U.S. Bureau of Indian Affairs, but they are not controlled by state governments. There are currently 326 Indian reservations across the country.
Not all Native American tribes have their own reservations. Sometimes, two or more tribes might share one reservation. Many Native Americans and Alaska Natives now live in big cities. Places like Phoenix and Los Angeles are home to many Native Americans.
Some Indian reservations are very large. Twelve reservations are bigger than the state of Rhode Island. Nine reservations are even larger than Delaware. Some states have many reservations, while others have none at all.
The main government on an Indian reservation is the tribal council. This means the tribal council makes the rules, not the federal, state, or county governments. Reservations often have their own ways of governing. These systems might be similar to or different from governments outside the reservation.
Contents
How Indian Reservations Started
The United States started creating reservations for Native Americans in the late 1860s. This was during the time of President Ulysses S. Grant. The relationship between settlers and Native Americans had become difficult. Settlers were taking over Native American hunting grounds and natural resources.
President Grant wanted to find a way to keep the peace. He created a plan to change how the Indian Service worked. The goal was to move different tribes from their original homes to new areas of land. He sent Quakers to help manage these new areas. Their aim was to help the tribes adapt to American ways of life. However, this idea was later stopped.
The Indian New Deal
The Indian Reorganization Act of 1934 was also called the Indian New Deal. Its main goal was to stop forcing Native Americans to change their ways. Instead, it aimed to protect tribal land and bring back tribal governments. It also worked to help tribes improve their economies.
For the next twenty years, the U.S. government invested in reservations. They helped build things like roads and schools. They also improved health care. Over two million acres (8,000 km2) of land were given back to various tribes.
Life on Reservations
Many Native Americans living on reservations work with the federal government. They do this through two main groups. These are the Bureau of Indian Affairs and the Indian Health Service.
Some people on Indian reservations face challenges. For example, Shannon County, South Dakota is home to the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation. This area is known as one of the poorest counties in the nation.
Gambling on Reservations
In 1979, the Seminole tribe in Florida opened a big bingo hall on their reservation. The state tried to close it, but the courts said no. Later, a court case called California v. Cabazon Band of Mission Indians and the Indian Gaming Regulatory Act confirmed this right.
These laws said that Native American tribes can have gambling businesses on their reservations. These businesses, like casinos and hotels, attract many tourists. This brings in money for the tribes.
Interesting Facts About Indian Reservations
- The 326 Indian reservations in the U.S. cover about 2.3% of the whole country.
- More than 1 million Native Americans live on reservations.
- The Navajo Nation Reservation is the largest in the U.S. It covers 16 million acres across Arizona, Utah, and New Mexico.
- Important U.S. laws that help protect Native Americans include the Indian Citizen Act, the Indian Reorganization Act, and the Indian Civil Rights Act.
- 25 states have reservations. California alone has 121 reservations.
- As of 2021, the U.S. government recognizes 574 Native American tribes.
- Heart disease is the leading cause of death for American Indians.
- Families living on their own land are often more successful than those on shared land.
Images for kids
-
Most Indian reservations, like the Laguna Indian reservation in New Mexico (pictured here in March 1943), are in the western United States, often in regions suitable more for ranching than farming.
-
Wagon loaded with squash, Rosebud Indian Reservation, ca. 1936
-
Fort Stanwix, New York
-
Red Cliff Indian Reservation in Wisconsin during their annual pow wow
See also
 In Spanish: Reserva india para niños
In Spanish: Reserva india para niños