Jackson Lake Dam facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Jackson Lake Dam |
|
|---|---|

Looking west in June 1997 from the
north shore of the Snake River |
|
|
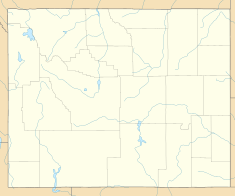
Location of Jackson Lake Dam in Wyoming#USA
|
|
| Location | Teton County, Wyoming, in Grand Teton National Park |
| Coordinates | 43°51′27.53″N 110°35′22.54″W / 43.8576472°N 110.5895944°W |
| Construction began | 1911 |
| Opening date | 1916 |
| Operator(s) | U.S. Bureau of Reclamation |
| Dam and spillways | |
| Type of dam | Concrete gravity with earth embankment wings |
| Impounds | Snake River |
| Height | 65 ft (20 m) |
| Length | 4,920 ft (1,500 m) |
| Width (crest) | 24 ft (7.3 m) |
| Width (base) | 72 ft (22 m) |
| Spillway type | gated overflow |
| Spillway capacity | 8690cfs at 6790 ft |
| Reservoir | |
| Creates | Jackson Lake |
| Total capacity | 847,000 acre-feet (1.045 km3) |
| Catchment area | 1,824 sq mi (4,720 km2) |
The Jackson Lake Dam is a large structure made of concrete and earth. It's located in the western United States, specifically in northwestern Wyoming. This dam is built at the end of Jackson Lake, which is found inside Grand Teton National Park in Teton County.
The Snake River starts its long journey from this dam. It flows for about 800 miles (1,287 km) through Wyoming, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington. Finally, it joins the Columbia River in eastern Washington. The main reason for this dam is to store water for farms in Idaho. This water is used to irrigate crops as part of a big project called the Minidoka Project. Jackson Lake was a natural lake, but the dam made it much deeper to hold more water.
Contents
Building the Jackson Lake Dam
The very first dam at Jackson Lake was built between 1906 and 1907. It was a simple dam made of logs. This log dam made the lake level go up by 22 feet (6.7 meters). However, it broke in 1910.
So, a new, stronger dam was needed. A new dam, made of concrete and earth, was built in stages from 1911 to 1916. This new dam raised the lake's water level even more, about 30 feet (9.1 meters) higher than its natural level. This allowed the lake to store a huge amount of water: 847,000 acre-feet (1.045 km³) of water!
The engineer who designed this new dam was Frank A. Banks. He later became famous for overseeing the building of the massive Grand Coulee Dam.
Why Was the Dam Built?
The main goal of the Jackson Lake Dam was to create a large water storage area for the Minidoka Project. This project helps provide irrigation water from the Snake River to farms in Idaho. Jackson Lake holds and releases water that is then collected by other dams, like the Minidoka Dam and American Falls Dam, which are more than 100 miles (160 km) downstream.
When the dam was first built, the area around Jackson Hole and the Teton Range was not yet protected. Grand Teton National Park was created in 1929, but Jackson Lake was not part of it at first.
Later, in 1950, Jackson Lake became part of Grand Teton National Park. When the dam was built, no one cleared the trees from the lake's edges. So, when the water rose, many dead trees were left standing. This messy view, along with muddy areas when the water level dropped, helped convince people not to build more dams in Yellowstone National Park.
Making the Dam Stronger
In 1976, the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, which operates the dam, studied many dams. They found that Jackson Lake Dam could be damaged if a strong earthquake (magnitude 5.5 or higher) happened nearby.
After a big earthquake in Idaho in 1983 (the Borah Peak earthquake), the dam was made stronger. This work happened between 1986 and 1989. The Bureau of Reclamation believed the dam could then survive a very powerful earthquake, like a magnitude 7.5 quake on the Teton fault. However, some studies since then have raised questions about this.
Jackson Lake Dam: Quick Facts
The U.S. Bureau of Reclamation owns and runs the Jackson Lake Dam. They keep the water level high to provide water for farms downstream.
Here are some interesting facts about the dam:
- Type: It's a concrete gravity dam with earthen parts on the sides.
- Area it drains: The dam collects water from an area of 1,824 square miles (4,724 km²).
- Lake elevation (height above sea level):
- Normal full level: 6,760 feet (2,060.5 meters)
- Highest possible level: 6,769 feet (2,063.2 meters)
- Lowest possible level: 6,730 feet (2,051.3 meters)
- Usable water storage: The dam can hold 847,000 acre-feet (1.045 km³) of water.
- Top of dam height: 6,777 feet (2,065.6 meters)
- Length of the top: 4,920 feet (1,499.6 meters)
- Width of the top: 24 feet (7.3 meters)
- Width at the bottom: 72 feet (22 meters)
- Total height of the structure: 65 feet (19.8 meters)
Images for kids
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |