Lake Oroville facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Lake Oroville |
|
|---|---|

View looking South over main basin area of Lake Oroville, towards Oroville Dam, seen at center left.
|
|
| Location | Oroville East, Butte County, California |
| Coordinates | 39°32′14″N 121°29′00″W / 39.53722°N 121.48333°W at Oroville Dam |
| Lake type | Reservoir |
| Primary inflows | North Fork Feather River, Middle Fork Feather River, West Branch Feather River, South Fork Feather River, various other smaller streams |
| Primary outflows | Feather River |
| Catchment area | 3,950 square miles (10,200 km2) |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Built | 1961 (Construction started on Oroville Dam) 2017-2019 (Spillway Rebuilt) |
| First flooded | 1969 |
| Water volume | 3,537,577 acre-feet (4.363537×109 m3) |
| Shore length1 | 167 miles (269 km) |
| Surface elevation | 901 feet (275 m) |
| Frozen | Never |
| Islands | Bloomer Island, Foreman Island, others unnamed |
| Settlements | Oroville |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Lake Oroville is a huge man-made lake in northern California. It was created by building the Oroville Dam across the Feather River. This important lake is located about 5 miles (8.0 km) northeast of the city of Oroville.
Lake Oroville is the second-largest reservoir in California. It's a key part of the California State Water Project. The lake helps store water, control floods, and provides fun recreation. It also releases fresh water to help the environment and protect fish.
The lake is famous for bass fishing. You can also find coho salmon here. These salmon are raised at the Feather River Fish Hatchery, which is a very important part of Lake Oroville.
Contents
History of Lake Oroville

For many years, the Konkow Maidu people lived in the area where Lake Oroville is now. They settled along the Feather River. Many towns, including Oroville, were originally Maidu lands.
In 2002, a study looked at the history of the Lake Oroville area. It found 250 sites from prehistoric times. These sites show how Native Americans lived along the Feather River. Another 478 sites were from the Gold Rush era. These sites included homes, caves, rock art, and even old cemeteries.
The discovery of gold in 1848 changed everything for the Native Americans. White miners quickly moved into their lands. In April 1848, just three months after gold was found at Sutter's Mill, John Bidwell discovered gold on the Feather River. This spot is now known as Bidwell Bar.
News of the California Gold Rush spread fast. By 1850, Butte County alone had over 3,000 miners.
Construction on the Oroville Dam began in 1957. Workers first had to move Highway 70 and the Western Pacific Railroad. A few years later, the partially built dam helped stop a big flood on the Feather River in December 1964. This saved the Sacramento Valley from severe flooding. The lake was officially filled in 1969.
How Lake Oroville Works
Lake Oroville and the Oroville Dam are part of a big water system. This system includes the Hyatt Powerplant, which generates electricity. It also has the Feather River Fish Hatchery and other facilities.
The lake gets its water from the North Fork, Middle Fork, West Branch, and South Forks of the Feather River. This river system covers a huge area of 3,611 square miles (9,350 km2). Lake Oroville can hold over 3,500,000 acre-feet (4.3 km3) of water. It is the second-largest reservoir in California, after Shasta Lake.
Lake Oroville is very important for managing floods. It also helps keep water clean and supports healthy fish populations downstream. During warm weather, a lot of the water comes from melting snow. About 40 percent of the lake's yearly water comes in from April to July.
The lake's storage and water releases are key to the Oroville Complex. This makes it a major part of California's water supply.
Spillway Emergency in 2017
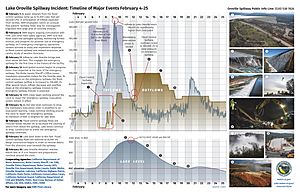
In February 2017, there was a lot of rain. This caused damage to the main concrete spillway of the dam. Because of this damage, less water could be released. The lake level rose to 101% of its capacity. This caused the emergency spillway to overflow for the first time ever.
When the emergency spillway overflowed, severe erosion was seen below it. People worried that the emergency spillway might fail. This led to a large evacuation of people living downstream.
Repairs to the emergency spillway were done in two phases. Phase 1 was finished in 2017, and Phase 2 was completed in 2018.
Fun Things to Do at Lake Oroville
Lake Oroville offers many fun activities for visitors. The Lake Oroville Visitor Center has a museum, exhibits, and videos. You can also look through powerful telescopes from a 47-foot tall tower. From there, you can see the lake, the Sierra Nevada mountains, and the Sutter Buttes.
Fishing
Fishing at Lake Oroville State Recreation Area is excellent. You can catch different types of fish, including largemouth, smallmouth, and spotted bass. Other fish include Chinook salmon, catfish, and trout. The biggest Mackinaw trout caught here was nineteen pounds!
You can fish all year round. However, you need a California sport fishing license.
The California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA) has a safe eating advisory for fish from Lake Oroville. This is based on levels of mercury or PCBs found in the fish.
Boating
Boating is a popular activity all year. You can enjoy waterskiing, wakeboarding, and using houseboats. There are five multi-lane boat launch ramps around the lake. These include Bidwell Canyon and Lime Saddle.
You can rent boats and supplies at Bidwell Marina or Lake Oroville Marina. At the North Forebay, you can rent kayaks, canoes, sailboats, and paddleboats from the Forebay Aquatic Center.
Camping
Camping is another major activity. You can choose from campgrounds, floating campsites, boat-in camps, or equestrian campsites.
Feather River Fish Hatchery
The Feather River Fish Hatchery is a very important part of Lake Oroville. It helps keep healthy populations of Chinook salmon and steelhead trout in the Feather River.
There have been many attempts to raise fish in the Feather River over the years. Before the Oroville Dam was built, most fish hatcheries were further away. The current hatchery was built by the Department of Water Resources and the Department of Fish and Wildlife. This happened after the Oroville Dam was built in 1961. The dam blocked salmon and steelhead from reaching their old spawning areas. So, a special system was built to help adult fish get to the hatchery.
Today, the hatchery raises spring and fall-run Chinook salmon and steelhead. These fish are released into the Feather River, just below Lake Oroville. The hatchery has two main parts. One part has a fish barrier dam and an observation platform where you can see fish underwater. The other part has the spawning room and rearing ponds.
You can watch salmon spawning from mid-September to mid-November. Fish are in the rearing ponds all year.
Every year on the fourth Saturday of September, the Oroville Salmon Festival takes place. It happens at the hatchery and in downtown Oroville. It's the only salmon festival in California where people can see Chinook salmon being worked to collect and fertilize eggs.
Climate Around Lake Oroville
Lake Oroville has a Mediterranean climate. This means it has hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters. A large high-pressure area over the Pacific Ocean controls the weather here. In summer, it pushes storms away, leading to hot, dry weather. In winter, it moves south, allowing storms to bring rain and cooler temperatures.
The average high temperature for the year is about 75.2°F. The average low is 49°F. The coldest months are December and January, with average highs around 56°F. The warmest months are June, July, and August, with average highs around 93°F.
The area gets about 30.66 inches of rain each year. January is the wettest month, and July is the driest.
In 2015, Northern California had a severe drought. This caused the lake level to drop to only 39% of its capacity by January 2016. However, 2017 had a lot of rain, which helped fill the lake.
Wildlife and Fish Species
Fish Life Cycle
The Feather River Fish Hatchery raises two main types of fish: Chinook Salmon and Steelhead Trout.
Chinook Salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) are amazing fish. They are known as 'anadromous' fish. This means they are born in freshwater rivers, then travel to the ocean to grow into adults. After a few years, they return to the same freshwater rivers to lay their eggs. There are different groups of Chinook salmon in California. Some are considered a "Species of Concern" under the Federal Endangered Species Act. The hatchery helps these fish by raising and releasing both Fall and Spring Run Chinook salmon.
Steelhead Trout are a type of rainbow trout. They are also anadromous. They can lay eggs multiple times in rivers and creeks. Like salmon, they go to the ocean and then return to the rivers to start their life cycle again.
Images for kids
 | Calvin Brent |
 | Walter T. Bailey |
 | Martha Cassell Thompson |
 | Alberta Jeannette Cassell |