Mesolithic facts for kids

Reconstruction of a "temporary" Mesolithic house in Ireland; waterside sites offered good food resources.
|
|
| Alternative names | Epipaleolithic (for the Near East) |
|---|---|
| Geographical range | Europe |
| Period | Middle of Stone Age |
| Dates | 20,000 to 8,000 BP (Southwest Asia) 15,000–5,000 BP (Europe) |
| Preceded by | Upper Paleolithic |
| Followed by | Neolithic |
The Mesolithic was a time in human history. It was a period of change between the Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) and the Neolithic (New Stone Age). This period is part of the larger Stone Age.
During the Paleolithic, people were mostly hunter-gatherers. They moved around to find food. In the Neolithic, people started to become farmers. They lived in settlements, grew wheat, and had domesticated animals. They also used many different tools and made pottery.
The Mesolithic was a transition period. It happened at different times in different parts of the world. Mesolithic tools were often small and made by chipping stone. These tools were used for hunting and gathering. They included things like arrowheads. Neolithic tools were often polished and much more varied. These tools were used by people who had started to settle down and farm.
The word 'Mesolithic' was first used in 1877. However, it became popular much later. This was thanks to Vere Gordon Childe's book The dawn of Europe (1947). Sometimes, the term 'Epipalaeolithic' is used instead, especially for the Near East.
Contents
What Made the Mesolithic Special?
The main way to tell the Mesolithic apart is by its tools. People in the Mesolithic used small, chipped stone tools. In the Neolithic, people mostly stopped using these. Instead, they used polished stone tools.
Here are some ways Mesolithic culture was different from the Paleolithic:
- The tools were more varied than older Paleolithic tools.
- People focused on making small, even tiny, tools. These tiny tools are called microliths.
- Mesolithic people also used more wooden handles for their tools.
- They started using the adze. This was a carpentry tool with a wooden handle. The blade was at a right angle to the handle.
- The domestication of animals began. One of the earliest signs of this is a dog buried with a human. This happened 12,000 years ago in Palestine.
The Fertile Crescent and the Ice Age
The Fertile Crescent was the first place to move out of the Paleolithic. This area is in the Near East. Here, farming started early, even before the last Pleistocene ice age ended. Because of this, the Mesolithic period was quite short there. In areas not much affected by the ice age, the term "Epipaleolithic" is sometimes used.
Other parts of the world felt the end of the last ice age more strongly. These places had a much longer Mesolithic era. This period lasted for thousands of years. In Northern Europe, people lived well. They found lots of food in the marshlands. These conditions led to unique human behaviors. We can see these in the tools and other things found from that time. These conditions also delayed the start of the Neolithic period in northern Europe. It didn't begin there until around 4000 BC (6,000 years ago).
Mesolithic People in Europe
Scientists have studied the bones of a 7,000-year-old man. He was found in north-west Spain. Genetic research showed he had blue eyes and dark skin. His genes for skin color were like those of his ancestors. This means he likely had dark hair and brown skin.
Researchers were surprised by this. They thought that European people developed light skin very quickly. Dark skin protects people from UV rays from the sun. This is important in warmer places. In northern areas, UV rays are less of a problem. However, getting enough vitamin D can be an issue. Our skin makes vitamin D when exposed to sunlight. So, having lighter skin is helpful in much of Europe. It allows more sunlight to be absorbed.
Earlier research looked at many different groups of people. It showed that at least three groups of ancestors contributed to today's Europeans.
Images for kids
-
The Mesolithic begins during the latest Pleistocene, characterized by a progressive rise of temperatures, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution during the Holocene. Evolution of temperature in the Post-Glacial period according to Greenland ice cores.
-
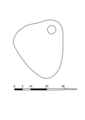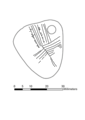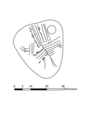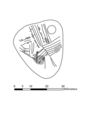
Animated image showing the sequence of engravings on a pendant excavated from the Mesolithic archaeological site of Star Carr in 2015
See also
 In Spanish: Mesolítico para niños
In Spanish: Mesolítico para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |