Upper Paleolithic facts for kids
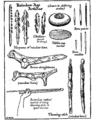
The Upper Paleolithic period is the last part of the Paleolithic (or Old Stone Age) era. It lasted from about 40,000 to 10,000 years ago. During this time, early humans became very skilled at making tools for hunting and fishing. They also started creating amazing cave paintings. A big change in this period was the complete disappearance of Neanderthals. This left Homo sapiens (modern humans) as the only human species on Earth.
In places like Europe, Asia, and Africa, this time is known as the final part of the Old Stone Age.
The first modern human fossils found in Western Europe are about 36,000 years old. These important finds were made in a stone cave in Romania called Peștera cu Oase.
The famous Lascaux cave paintings also come from this time. They are located in France and have been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1979. People in the Upper Paleolithic also started having burial rituals and showing respect for their ancestors. This suggests they might have believed in an afterlife.
Ancient Art: Venus Figurines
One of the earliest types of art from this period are the Venus figurines. These are small statues of women, often shown as pregnant. They have been found across a huge area, from Western Europe all the way to Siberia. Most of these figurines are between 20,000 and 30,000 years old.
Two figurines have been found that are much, much older. The Venus of Tan-Tan, found in Morocco, is thought to be 300,000 to 500,000 years old. The Venus of Berekhat Ram, found on the Golan Heights, is dated to 200,000 to 300,000 years ago. These might be some of the very first objects ever made that look like a human.
These figurines were made from different materials. People used various kinds of stone, bones, and ivory. Some were even made from clay and then hardened by fire. This shows some of the earliest known uses of ceramics.
Today, we don't know for sure what these figurines meant to the people who made them. There are two main ideas:
- They might have been symbols of human fertility, or they might have been used in rituals to help people have children.
- They could have represented goddesses of fertility.
Scientists know these figurines were not linked to the fertility of farm fields. This is because agriculture (farming) had not been invented yet when these figurines were made.
The two much older figurines (Tan-Tan and Berekhat Ram) might have been partly shaped by nature. However, the Venus of Tan-Tan was covered with a substance that looked like paint, containing iron and manganese. The Berekhat Ram figurine also shows marks that suggest someone worked on it with a tool. A study from 1997 said that these marks could not have been made by nature alone.
Amazing Cave Paintings
Cave paintings are artworks found on the walls or ceilings of caves. Many of the most famous cave paintings come from the Paleolithic Age, dating from about 15,000 to 30,000 years ago. Some of the most well-known are in the Altamira cave in Spain and the Lascaux cave in France. There are about 350 caves in Europe where these ancient paintings have been discovered.
Usually, the paintings show animals like aurochs (an extinct type of wild cattle), bisons, or horses. We don't know exactly why these paintings were made. They weren't just decorations for homes, as the caves where they are found often don't show signs that people lived there.
One of the oldest painted caves is Chauvet in France. The paintings in this cave fall into two groups. One group is dated to around 30,000 to 33,000 years ago, and the other to 26,000 or 27,000 years ago. These are some of the oldest known cave paintings. Scientists used radiocarbon dating on charcoal from the drawings and torch marks to figure out their age. The oldest paintings are dated to about 32,900 years ago.
Some archaeologists have questioned these dates. They point out that people painted differently in different periods. They also wonder about the source of the charcoal used and how large the painted areas are.
The artists from the Paleolithic era were very skilled. They understood perspective and knew different ways to draw things. They were also very good at observing how the animals they painted behaved. Some paintings even show animals in motion. These paintings might have been important for ancient rituals or ceremonies.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Bradshaw rock paintings found in the north-west Kimberley region of Western Australia.
-
Lascaux, a UNESCO World Heritage Site with famous cave paintings.
See also
 In Spanish: Paleolítico superior para niños
In Spanish: Paleolítico superior para niños