Moolock Mountain facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Moolock Mountain |
|
|---|---|

Southeast aspect, seen from Preacher Mountain
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 4,965 ft (1,513 m) |
| Prominence | 925 ft (282 m) |
| Isolation | 1.81 mi (2.91 km) |
| Parent peak | Bessemer Mountain (5,166 ft) |
| Geography | |
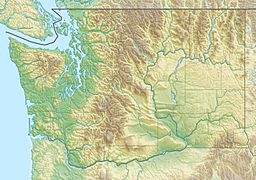
| Location | King County, Washington state, US |
| Parent range | Cascade Range |
| Topo map | USGS Mount Si |
| Climbing | |
| Easiest route | hiking |
Moolock Mountain is a tall peak in Washington state. It stands about 4,965 feet (1,513 meters) high. This mountain is in King County. It is located on the western side of the Cascade Mountains. This area is part of the Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest.
Moolock Mountain is special because it rises very steeply from the land around it. Its closest taller neighbor is Bessemer Mountain, about 1.8 miles (2.9 km) away. Green Mountain is also nearby, about 2.5 miles to the southwest. Rain and snowmelt from the mountain flow into parts of the Snoqualmie River. The mountain itself doesn't have an official name. However, it sits right above Lake Moolock, which does have an official name. The word "Moolock" comes from the Chinook Jargon language. It means "elk."
Contents
Understanding the Climate Around Moolock Mountain
Moolock Mountain is in a "marine west coast" climate zone. This type of climate is found in western North America. Most weather systems start over the Pacific Ocean. They then travel east toward the Cascade Mountains.
When these weather systems reach the mountains, they are forced to rise. This causes them to drop their moisture. This moisture falls as rain or snow onto the Cascades. This process is called Orographic lift. Because of this, the west side of the Cascades gets a lot of rain and snow. This is especially true during the winter months.
The snow here tends to be wet and heavy. This can create a danger of avalanches. During winter, the weather is usually cloudy. But in summer, high-pressure systems over the Pacific Ocean often bring clear skies.
How the Cascade Mountains Formed
The Cascade Mountains began forming millions of years ago. This was during the late Eocene Epoch. Over two million years ago, during the Pleistocene period, glaciers played a big role. These huge ice sheets moved forward and backward many times. As they moved, they scraped the land. This left behind piles of rock and debris.
The last time glaciers retreated from this area was about 14,000 years ago. By 10,000 years ago, they had moved north of the Canada–US border. The river valleys in the area have a U-shape. This shape was created by these recent glaciers. The mountains' tall peaks and deep valleys were formed by two main processes. These are uplift (when land pushes up) and faulting (when cracks form in the Earth's crust). These processes worked together with glaciation.
Gallery
See also
- Geology of the Pacific Northwest
 | Isaac Myers |
 | D. Hamilton Jackson |
 | A. Philip Randolph |