Natural regions of Germany facts for kids
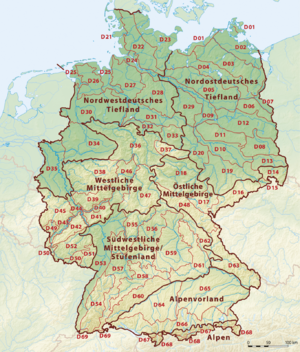
Germany is a country in Europe with many different kinds of landscapes. From flat plains to tall mountains, each area has its own special features. Scientists and geographers divide Germany into "natural regions." These regions are areas that share similar landforms, climate, and even types of plants and animals. Understanding these regions helps us learn about Germany's amazing geography.
Contents
Regions of Germany
Germany can be divided into several major natural regions. Each region has its own unique look and feel, from flat plains to rolling hills and high mountains.
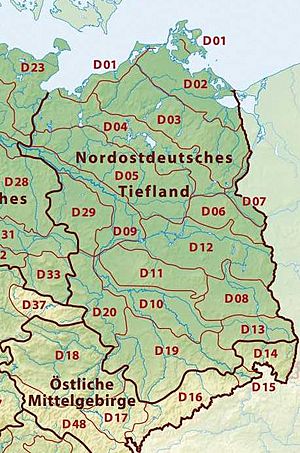
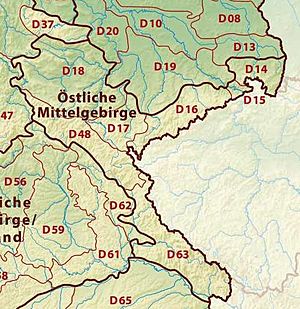
Northeast German Plain
This large, flat area covers much of northeastern Germany. It's known for its lowlands, lakes, and rivers.
- Mecklenburg Coastal Lowland: This area is right by the coast.
- Northeast Mecklenburg Lowland: Includes parts near the Szczecin Lagoon.
- Mecklenburg Lake Plateau Hinterland: An area behind the main lake district.
- Mecklenburg Lake Plateau: Famous for its many beautiful lakes.
- Mecklenburg-Brandenburg Plateau and Upland: A mix of flat areas and slightly higher lands.
- Southwest Foreland of the Mecklenburg Lake Plateau
- North Brandenburg Plateau and Upland
- Luchland
- East Brandenburg Plateau
- Oder Valley: The valley of the Oder River.
- Lusatian Basin and Spreewald: Includes the unique Spreewald forest with its many small canals.
- Spreewald
- Lusatian Basin and Lower Lusatian Heath
- Middle Elbe Plain: The flat land around the middle part of the Elbe River.
- Elbe-Mulde Plain
- Fläming Heath
- Brandenburg Heath and Lake District: An area with heathlands and many lakes.
- Central Brandenburg Plateaux and Lowland
- East Brandenburg Heath and Lake District
- Upper Lusatian Plateau
- Saxon Lowland: A new, larger region that includes:
- Saxon Upland and Ore Mountain Foreland: This area includes the Ore Mountain Foreland and the Saxon Upland (which has the Leipziger Land).
- Upper Lusatia: This part excludes the Lusatian Upland.
- Eastern Harz Foreland and Börde: The land in front of the Harz mountains.
- Wendland and Altmark
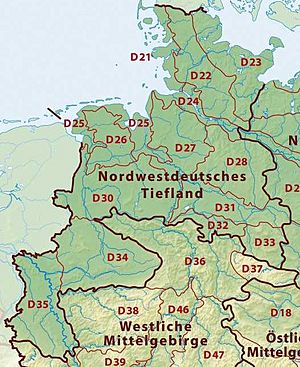
Northwest German Plain
This plain is located in the northwest of Germany, closer to the North Sea. It features marshlands and sandy plains.
- Schleswig-Holstein Marsch: Flat, low-lying land near the coast.
- Schleswig-Holstein Geest: Higher, sandy plains.
- Schleswig-Holstein Uplands: Slightly higher areas.
- Lower Elbe Marsch: Marshlands along the lower Elbe River.
- Ems and Weser Marsch: Marshlands near the Ems and Weser rivers.
- East Frisian Geest: Sandy plains in East Frisia.
- Stade Geest
- Lüneburg Heath: A famous heathland area.
- Dümmer and Ems-Hunte Geest:
- Dümmer Geest Lowland
- Ems-Hunte Geest
- Weser-Aller Plain
- Lower Saxony Börde: Fertile plains in Lower Saxony.
- North Harz Foreland: The area in front of the Harz mountains.
- Westphalian Lowland or Basin (Münster Lowland): A flat basin area.
- Lower Rhine Plain and Cologne Lowland:
- Cologne Lowland
- Lower Rhine Plain
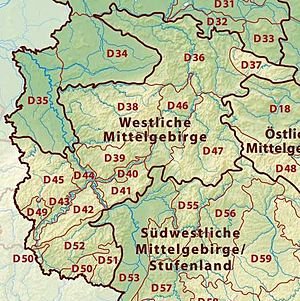
Western Central Uplands
These are the hilly and mountainous areas in the western part of central Germany. They are often covered in forests.
- Lower Saxon Hills: Includes the Weser and Leine Uplands.
- Lower Weser Uplands
- Upper Weser Uplands
- Leine Uplands
- Harz: A well-known mountain range.
- Sauerland (Süderbergland)
- Westerwald
- Gießen-Koblenz Lahn Valley: The valley of the Lahn River.
- Taunus
- Hunsrück
- Moselle Valley: The valley of the Moselle River, famous for its vineyards.
- Middle Rhine: Includes the Siebengebirge hills.
- Eifel: Includes the Venn Foreland.
- East Eifel
- West Eifel
- Venn Foreland
- West Hesse Highlands
- East Hesse Highlands
- Bitburg Land (Gutland)
- Palatine-Saar Muschelkalk Region
- Palatinate Forest (the Haardt): A large forest area.
- Saar-Nahe Hills or Upland
Eastern Central Uplands
These are the central hilly and mountainous areas in the eastern part of Germany.
- Saxon Highlands and Uplands: A larger region that includes:
- Upper Lusatia: Specifically the Upper Lusatian Plateau.
- Saxon-Bohemian Chalk Sandstone Region
- Ore Mountains (Erzgebirge): A mountain range rich in minerals.
- Vogtland
- Thuringian Basin including outer plateaus:
- Southern plateau of the Thuringian Basin
- Thuringian Basin
- Thuringian-Franconian Upland
- Upper Palatine-Bavarian Forest
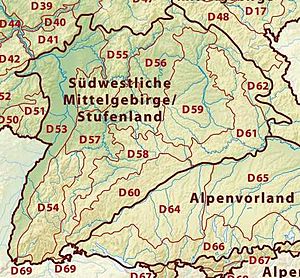
South German Scarplands
This region in southern Germany is known for its "scarplands," which are areas where layers of rock have been eroded, creating step-like landscapes.
- Upper Rhine Plain: The flat plain along the upper Rhine River.
- Southern Upper Rhine Plain
- Middle Upper Rhine Plain
- Northern Upper Rhine Plain
- Rhine-Main Lowland
- Black Forest: A large, famous forested mountain range.
- Odenwald, Spessart and South Rhön
- Mainfranken Plateau
- Gäu Plateaus
- Swabian Keuper-Lias Plains
- Franconian Keuper-Lias Plains
- Swabian Jura: A limestone plateau.
- Franconian Jura
- Upper Palatinate-Upper Main Hills
- Dinkelberg and Upper Rhine Valley
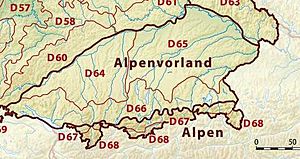
Alpine Foreland and Alps
This region in the very south of Germany includes the flat land leading up to the Alps and a small part of the Alps themselves.
- Iller-Lech Plateau
- Lower Bavarian Uplands and Isar-Inn Gravel Plateau:
- Isar-Inn Gravel Plateau
- Lower Bavarian Uplands
- Southern Alpine Foreland: The flat land in front of the Alps.
- Swabian-Bavarian Foreland
- Northern Limestone Alps: The northern edge of the Alps mountain range.
North and Baltic Seas
These regions cover the sea areas off Germany's northern coast.
- German Bight: The bay area of the North Sea, excluding the Heligoland rock.
- Dogger Bank and adjacent central North Sea: A large sandbank in the North Sea.
- Western Baltic: The western part of the Baltic Sea.
- Eastern Baltic: The eastern part of the Baltic Sea.
Images for kids