Neurological disorder facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Neurological disorder |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
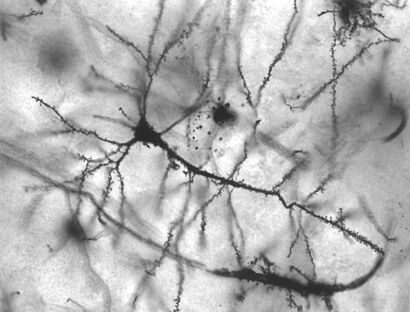
| Neurons in person with epilepsy, 40x magnified |
A neurological disorder is any problem with your nervous system. Your nervous system includes your brain, spinal cord, and all the nerves throughout your body. These disorders happen when something goes wrong with how these parts work. This could be a problem with their structure, their chemistry, or their electrical signals.
When the nervous system isn't working right, it can cause many different symptoms. For example, someone might have paralysis (can't move a part of their body), muscle weakness, or trouble with coordination. They might lose their sense of touch, have seizures, feel confused, or experience pain. There are many types of neurological disorders. Some are quite common, while others are very rare.
Doctors and other health experts can help people with neurological disorders. They might suggest ways to prevent problems, make lifestyle changes, or try physiotherapy. Other treatments include neurorehabilitation (helping the brain and nerves recover), pain management, medication, or even operations. The World Health Organization (WHO) said in 2006 that about one billion people worldwide are affected by neurological disorders. They also noted that unfair access to healthcare and social stigma (negative feelings from others) make these problems worse.
Contents
What Causes Neurological Disorders?
Your brain and spinal cord are well-protected. They are covered by tough membranes and surrounded by the bones of your skull and spine. A special barrier called the blood–brain barrier also keeps harmful chemicals out. However, even with all this protection, they can still be damaged. Nerves usually lie deep under your skin, but they can also get hurt.
The tiny cells that make up your nervous system, called neurons, can be affected. The way these neurons connect and send signals can also be disrupted. If nerves in your arms or legs are damaged, they might be able to repair themselves a bit. But in the brain and spinal cord, this kind of repair is much harder.
Many things can cause neurological problems. These include:
- Genetic disorders: Problems passed down through families.
- Problems from birth: Issues that are present when a baby is born.
- Infections: Like viruses or bacteria attacking the nervous system.
- Lifestyle or environmental health issues: Such as pollution or not getting enough nutrients (malnutrition).
- Injuries: Like brain damage, spinal cord injury, or nerve injury.
- Other health problems: Sometimes, a problem in another part of the body affects the nervous system. For example, cerebrovascular disease involves problems with blood vessels that supply the brain. Autoimmune disorders happen when your body's own defense system attacks healthy cells.
Sometimes, doctors can't find a clear cause for neurological symptoms. These are called "idiopathic" conditions. It's thought that some neurological disorders might start after a viral infection that wasn't noticed at the time. For example, the Hepatitis E virus, which often doesn't cause symptoms at first, might lead to neurological problems later.
Your cells have special ways to fix damaged DNA. If these repair systems don't work well, it can lead to neurological disorders. Neurons use a lot of oxygen, which can cause damage to their DNA over time. Problems with DNA repair are linked to conditions like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia.
How Are Neurological Disorders Grouped?
Neurological disorders can be put into groups in different ways. They can be grouped by where the problem is in the body, what kind of problem it is, or what caused it. The main way to divide them is into problems with the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) or the peripheral nervous system (nerves outside the brain and spinal cord).
Here are some common types of neurological disorders:
| Nervous system | |
|---|---|
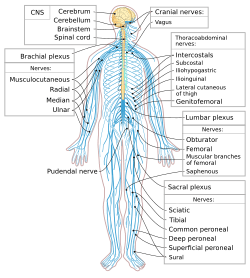 |
|
| Human nervous system |
- Brain disorders: These affect how your brain works.
- Apraxia: Trouble with doing planned movements.
- Agnosia: Difficulty recognizing things or people.
- Amnesia: Problems with memory.
- Aphasia: Issues with language and speaking.
- Dysarthria: Trouble with clear speech.
- Spinal cord disorders: Problems affecting the spinal cord, like injuries or inflammation.
- Peripheral neuropathy and other peripheral nervous system disorders: Problems with the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
- Cranial nerve disorders: Affecting specific nerves in your head, like Trigeminal neuralgia which causes face pain.
- Autonomic nervous system disorders: Problems with the part of the nervous system that controls automatic body functions like breathing and heart rate.
- Seizure disorders: Such as epilepsy, which causes seizures.
- Movement disorders: Affecting how you move, like Parkinson's disease (causing tremors and stiffness) or Tourette's syndrome (causing tics).
- Multiple sclerosis and related disorders: Conditions where the immune system attacks the protective covering of nerves.
- Sleep disorders: Like narcolepsy, which causes extreme daytime sleepiness.
- Speech disorders: Such as stuttering.
- Headaches: Including migraines (severe headaches) and tension headaches.
- Pain conditions: Like fibromyalgia, which causes widespread body pain.
- Delirium and dementia: Conditions that affect thinking, memory, and behavior, such as Alzheimer's disease.
- Stroke: When blood flow to part of the brain is stopped or reduced, damaging brain cells.
- Tumors of the nervous system: Growths, which can be cancerous or non-cancerous.
- Brain infections: Like Meningitis, which is an inflammation of the membranes around the brain and spinal cord.
- Prion diseases: A rare type of infectious disease affecting the brain.
Some neurological disorders, like Tourette's syndrome and Parkinson's disease, can be treated with surgery.
How Neurological Disorders Affect Thinking
Doctors can do a neurological examination to see how a neurological problem affects brain functions like behavior, memory, or cognition (thinking). Specialists in behavioral neurology and clinical neuropsychology focus on this area. They use special tests to find and track problems with mental functioning, especially after a brain injury.
Sometimes, a problem with thinking or behavior is noticed first. Then, further tests might show an underlying neurological disorder. It can be tricky to tell the difference between disorders treated by neurologists (nerve doctors) and mental disorders treated by psychiatrists (mental health doctors). However, neuropsychiatry is a field that deals with mental disorders caused by specific diseases of the nervous system.
In some cases, people have neurological symptoms, but doctors can't find a clear physical cause. These are sometimes called "functional" symptoms. Examples include "functional" seizures or weakness in a limb. These cases can be complicated. Sometimes, they are thought to be linked to emotional states or stress.
On the other hand, some conditions are clearly neurological, even if they seem unusual. For example, phantom pain is when someone feels pain in a limb that is no longer there. Synesthesia is when senses get mixed up, like seeing colors when you hear music. Alien hand syndrome is when a person's hand seems to move on its own, without conscious control.
Conditions like learning disabilities or intellectual disability are usually not considered neurological disorders themselves. However, biological psychiatry tries to understand mental disorders by looking at how they are linked to the nervous system. Brain scans (neuroimaging) can help rule out other medical conditions like brain tumors. In research, these scans can show how mental difficulties are connected to brain function or structure. Many different fields work together to understand how our minds work. The exact difference between neurological and mental disorders can sometimes be a topic of discussion.
See also
- Central nervous system
- Human brain
- Mental disorder
- Neuroplasticity
- Peripheral nervous system