Nilo-Saharan languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Nilo-Saharan |
|
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution: |
Central and East Africa |
| Linguistic classification: | One of the world's primary language families |
| Subdivisions: |
Berta
Fur
Gumuz
Koman
Kuliak
Kunama
Maban
Saharan
Songhay
Central Sudanic
Eastern Sudanic (includes Nilotic)
? Kadu
? Mimi-D
? Shabo
|
| Ethnologue code: | nilo-saharan |
| ISO 639-2 and 639-5: | ssa |
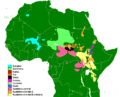
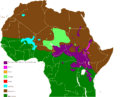
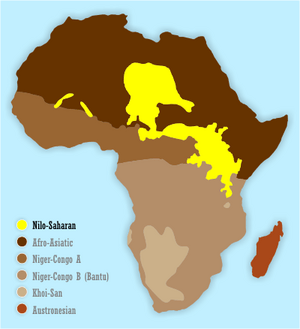 Map showing the distribution of Nilo-Saharan languages
|
|
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a large group of African languages. About 50 million people speak these languages. They mostly live near the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers. You can find Nilo-Saharan languages spoken across 17 countries in the northern half of Africa. This area stretches from Algeria to Benin in the west, from Libya to the Democratic Republic of the Congo in the middle, and from Egypt to Tanzania in the east.
Contents
What Are Nilo-Saharan Languages?
Nilo-Saharan languages are a major language family. This means they are a group of languages that are believed to have come from a single, older language. Think of it like a family tree, where different languages are branches from the same root. Scientists who study languages, called linguists, group them based on shared words and grammar.
Where Are These Languages Spoken?
These languages are mainly spoken in a wide area of Africa. This region includes parts of the Sahel and Sudan regions. The name "Nilo-Saharan" comes from the Nile River and the Sahara Desert. This helps you imagine the vast area where these languages are found.
How Many People Speak Them?
Around 50 million people speak Nilo-Saharan languages. Many of these speakers belong to groups like the Nilotic peoples. These groups live in countries such as South Sudan, Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania.
Branches of Nilo-Saharan Languages
The Nilo-Saharan family is very diverse. It includes many different groups, or "branches," of languages. Some of the main branches are:
- Eastern Sudanic: This is the largest branch. It includes the important Nilotic group. Nilotic languages are spoken by many people in East Africa.
- Central Sudanic: Languages in this group are found in countries like Chad and the Central African Republic.
- Saharan: These languages are spoken in and around the Sahara Desert.
- Songhay: This group includes languages spoken along the Niger River.
- Maban: These languages are found in Chad and Sudan.
There are also smaller groups like Berta, Fur, Gumuz, Koman, Kuliak, Kunama, and Kadu. Linguists are still studying these languages. They want to understand how they are all connected.
Why Are They Important?
Studying Nilo-Saharan languages helps us learn about the history of Africa. It also teaches us about the movements of people over thousands of years. These languages are a big part of the cultural richness of the continent. They show how different groups of people have interacted and developed over time.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Lenguas nilo-saharianas para niños
In Spanish: Lenguas nilo-saharianas para niños