Old Kingdom of Egypt facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Old Kingdom of Egypt
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 2686 BC–c. 2181 BC | |||||||||
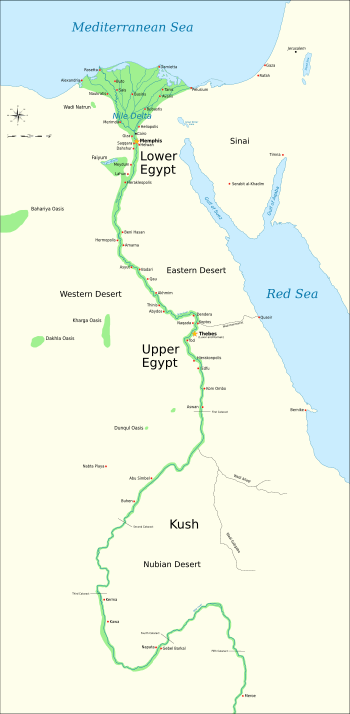
During the Old Kingdom of Egypt (circa 2686 BC – circa 2181 BC), Egypt consisted of the Nile River region south to Elephantine, as well as Sinai and the oases in the western desert.
|
|||||||||
| Capital | Memphis | ||||||||
| Common languages | Ancient Egyptian | ||||||||
| Religion | Ancient Egyptian religion | ||||||||
| Government | Divine absolute monarchy | ||||||||
| Pharaoh | |||||||||
|
• c. 2686–c. 2649 BC
|
Djoser (first) | ||||||||
|
• c. 2184–c. 2181 BC
|
Last king depends on the scholar, Neitiqerty Siptah (6th Dynasty) or Neferirkare (7th/8th Dynasty) | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
|
• Established
|
c. 2686 BC | ||||||||
|
• Disestablished
|
c. 2181 BC | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
The Old Kingdom was a special time in Egypt. It happened around 3000 BC. During this period, Egyptian civilization reached its first big peak. It was the first of three "Kingdom" times in Egypt. These periods show when Egypt was strong and its culture was at its best. The other two are the Middle Kingdom and the New Kingdom.
The Old Kingdom lasted from about 2686 BC to 2181 BC. It included the Third through the Sixth Dynasties of Egyptian rulers. Some experts also include the Seventh and Eighth Dynasties. These later dynasties kept the government centered in Memphis. After the Old Kingdom, Egypt went through a time of trouble. This period is called the First Intermediate Period.
Contents
The Age of Pyramids
The main city of Egypt during the Old Kingdom was Memphis. This era is famous for the huge pyramids that were built. These pyramids were special tombs for the Pharaohs. Pharaohs were the kings of Egypt. People believed they were chosen by the gods. They thought the pharaohs would join the sun-god Ra after they died.
Building the First Pyramids
The very first pyramid was designed by a smart adviser named Imhotep. He worked for King Djoser. Imhotep hoped the pyramid would help the king reach Ra easily. These giant tombs were built on the west side of the Nile River. This was because the sun seemed to set there. That's why the Old Kingdom is sometimes called "The Age of the Pyramids."
The Great Pyramid of Giza
One of the most famous pharaohs was Khufu, also known as Cheops. He ordered the building of the Great Pyramid at Giza. Giza is a place near modern-day Cairo. People believed the pharaoh's soul would live forever. So, they put food, clothes, and other valuable items in the pyramid rooms. These were for Khufu to use in the afterlife.
The Great Pyramid is one of the original Seven Wonders of the World. It was as tall as a 40-story building. It took about 100,000 workers around 20 years to build it. They used simple ramps and their own strength. They had to move and lift 2.3 million blocks of limestone. Each block weighed about 2.5 tons. Farmers, slaves, and groups of men worked on the pyramid. They were paid with valuable goods, not money. Ancient Egyptians did not use coins.
The Great Sphinx
To protect the pyramids, a giant stone statue was made. It was called the Great Sphinx. It was placed close to the pyramids. The Great Sphinx has the head of a man and the body of a lion. Its paws are about 50 feet long!
End of the Old Kingdom
Over time, the power of the pharaohs weakened. Eventually, priests and nobles gained more control. They took over from the pharaohs. This led to the end of the Old Kingdom.
Images for kids
-
The Pyramid of Djoser at Saqqara.
-
Temple of Djoser at Saqqara
-
Head of a King, c. 2650–2600 BC, Brooklyn Museum.
-
Khufu, the builder of the Great Pyramid at Giza
See also
 In Spanish: Imperio Antiguo de Egipto para niños
In Spanish: Imperio Antiguo de Egipto para niños







