Khufu facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Khufu |
|
|---|---|
| Cheops, Suphis, Chnoubos, Sofe | |

The Statue of Khufu in the Cairo Museum
|
|
| Pharaoh | |
| Reign | c. 2589 – c. 2566 BC 28–29 years (4th Dynasty) |
| Predecessor | Sneferu |
| Successor | Djedefre |
| Consort | Meritites I, Henutsen |
| Children | Kawab, Djedefre, Khafre, Djedefhor, Hetepheres II, Minkhaf I, Khufukhaf I, Babaef, and Horbaef |
| Father | Possibly Sneferu |
| Mother | Possibly Hetepheres I |
| Died | c. 2566 BC |
| Burial | Great Pyramid of Giza, Giza, Egypt |
| Monuments | Great Pyramid of Giza Khufu ship |
Khufu, also known as Cheops, was an ancient Egyptian king, or pharaoh, who ruled during the Fourth Dynasty. This was in the early part of Egypt's Old Kingdom period, around 2589 to 2566 BC. Khufu became king after his father, Sneferu. He is most famous for ordering the construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza, which is one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
Most of what we know about Khufu comes from inscriptions found in his burial area at Giza and from later historical writings. The only complete statue of Khufu is a small ivory figure found in 1903. Many other statues and buildings from his time have been lost or are only found in pieces.
Ancient Egyptian and Greek historians wrote about Khufu around 300 BC. These accounts sometimes described him differently. During the Old and New Kingdom periods, Khufu was remembered positively. However, later Greek historians like Manetho, Diodorus, and Herodotus gave a more negative picture of his rule. This has led to different ideas about what Khufu was really like.
Contents
Khufu's Royal Name
Khufu's name was connected to the god Khnum, who was seen as a god of creation. This might show that Khnum was becoming more important in Egyptian religion at the time. Pharaohs often linked their official names to gods to show their divine connection. Khufu's full name, Khnum-khufu, means "Khnum protects me."
While we say "Khufu" today, his name was likely pronounced differently in ancient times. The ancient Greeks called him Khéops or Cheops, and sometimes Súphis. Arab historians, who wrote many stories about the Giza pyramids, called him Saurid or Salhuk.
Khufu's Family
Khufu had a large royal family. It is believed that his father was Sneferu, another famous pharaoh. This belief comes from ancient traditions where the eldest son usually inherited the throne.
In 1925, the tomb of Queen Hetepheres I was discovered near Khufu's pyramid. It contained many valuable items. Inscriptions in the tomb called her "mother of a king" and mentioned King Sneferu. This suggested she was Sneferu's wife and Khufu's mother. However, some experts now wonder if Khufu was Sneferu's biological son. This is because Hetepheres I did not have the title "king's wife." Instead, she had a unique title meaning "king's bodily daughter." This has led some to think that Sneferu might have made Khufu his heir through marriage, and Khufu then honored his mother by giving her a special title.
Important Family Members
Here are some of Khufu's confirmed family members:
Spouses:
- Meritites I: Khufu's first wife.
- Henutsen: Khufu's second wife.
Brothers and Sisters:
- Hetepheres: Married to Ankhhaf.
- Ankhhaf: Khufu's older brother.
- Nefermaat: Half-brother, known for his tomb at Meidum.
- Rahotep: Older brother or half-brother. His famous statue with his wife Nofret is in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo.
Sons:
- Kawab: Likely the eldest son and heir, but he passed away before Khufu.
- Djedefre: Became the next pharaoh after Khufu.
- Khafre: Later became pharaoh after Djedefre.
- Djedefhor: Also mentioned in ancient texts.
- Babaef I
- Khufukhaf I
- Minkhaf I
- Horbaef
Daughter:
- Hetepheres II: Married to Prince Kawab and later to King Djedefre.
Grandchildren:
- Mindjedef
- Meresankh III: A queen of Egypt.
Nephews and Nieces:
- Hemiunu: He was in charge of building Khufu's Great Pyramid.
Khufu's Reign
It's not entirely clear how long Khufu ruled. Ancient records suggest he ruled for about 28 to 29 years. Some historians like Herodotus and Manetho claimed he ruled for much longer, but these numbers are now thought to be exaggerated.
Political Activities
Khufu's activities within Egypt are known from building inscriptions and statues. His name appears in places like Elkab and Elephantine, and in quarries at Hatnub and Wadi Hammamat.
Expeditions to Wadi Maghareh
Khufu sent expeditions to Wadi Maghareh in the Sinai. This area was rich in turquoise and copper. Like other kings, he sought these valuable materials for Egypt.
Discoveries at Wadi al-Jarf
Recently, important discoveries were made at the ancient port of Wadi al-Jarf on the Red Sea coast. In 2011, archaeologists found hundreds of papyrus fragments dating back 4,500 years to Khufu's reign. These papyri are the oldest ever found in Egypt.
One special document is the diary of Merer, an official involved in building the Great Pyramid. His diary gives us a glimpse into the daily lives of people during the Fourth Dynasty. These discoveries show that Khufu's administration was well-organized, sending food and supplies to workers. The port was important for bringing precious materials like copper and turquoise from the Sinai.
Monuments and Statues
Khufu's reign is best known for its grand monuments.
Statues of Khufu
The most complete statue of Khufu is a small ivory figurine. It shows the king wearing the Red Crown of Lower Egypt, seated on a throne. He holds a flail, a symbol of royalty. This figurine was found in 1903 at Abydos.
Some experts believe this statuette was made much later than Khufu's time. They point out that its style is different from other statues of kings from the Old Kingdom. For example, the throne's backrest is shorter than usual for that period. However, it remains a unique and important piece.
Other fragments of statues, made of alabaster and travertine, have been found with Khufu's name. These show that many larger statues of the king once existed.
Reliefs of Khufu
Khufu is also shown in several relief carvings found in his burial complex. These reliefs were made from polished limestone and once decorated the walls of his temples and causeway.
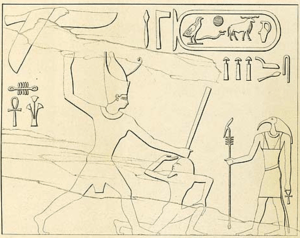
One relief shows Khufu's name with the phrase "Building of the sanctuaries of the gods." Another depicts oxen being prepared for sacrifices. A third shows archers getting ready for battle, which is one of the earliest images of royal warfare. Another relief shows the king with the double crown hunting a hippopotamus.
Interestingly, none of Khufu's reliefs show him offering to a god. This is unusual compared to other pharaohs and might have influenced later Greek historians who claimed Khufu closed temples.
The Great Pyramid Complex

Khufu's pyramid complex is located on the Giza plateau. He chose this high location so his pyramid would be easily seen. Khufu named his pyramid Akhet-Khufu, meaning "horizon of Khufu."
The Great Pyramid of Giza is enormous, originally about 147 meters (481 feet) tall. It was covered in smooth, white limestone, which made it shine brightly. The pyramid's inner passages and chambers are made of polished granite.
Inside the pyramid are three main chambers:
- The King's Chamber: This is where Khufu's sarcophagus (stone coffin) was placed.
- The Queen's Chamber: Its exact purpose is still debated, but it might have held a statue of Khufu's spirit.
- The Underworld Chamber: This chamber is unfinished and lies beneath the pyramid's foundation. It suggests that the original plan for the pyramid might have changed during construction.
A remarkable feature inside is the Grand Gallery, a tall, long passage with a special arched ceiling. This design helped to support the massive weight of the stones above the King's Chamber.
Around the pyramid, there was an enclosure wall and Khufu's mortuary temple, where rituals for the deceased king would take place. A long causeway connected this temple to a valley temple, which is now mostly lost.
To the east of the pyramid are the tombs of princes and princesses. Three smaller pyramids, known as the queens' pyramids, belong to Khufu's queens, Hetepheres, Meritites I, and possibly Henutsen. On the south side, pits for Khufu's funerary boats were found, including the famous Khufu ship.

The famous Great Sphinx of Giza is also a possible part of Khufu's complex. This huge limestone statue has the body of a lion and the head of a human, wearing a royal headdress. It was carved directly from the Giza plateau. It's still debated who ordered its construction, with Khufu, his son Djedefre, and his son Khafre being the main candidates. The Sphinx likely served as a guardian of the sacred Giza cemetery.
Khufu in Later Egyptian Traditions
Khufu was honored with a special cult after his death, especially during the Old Kingdom. Many priests served in his mortuary cult, which was important for the economy.
Middle Kingdom Stories
During the Middle Kingdom, Khufu was sometimes seen as a patron saint. His name appeared in lists of kings and was found on items at important pilgrimage sites.
A famous story from the 13th Dynasty, called the Papyrus Westcar, features King Khufu. In this story, Khufu meets a magician named Dedi who performs magic. Khufu is shown as both curious and fair. He tests Dedi's powers but also rewards him generously. This story shows Khufu as a complex character, which historians still discuss today.
New Kingdom and Later
During the New Kingdom, Khufu's burial site at Giza became important again. Kings like Amenhotep II and Thutmose IV built monuments near the Great Sphinx. Later, a temple for the goddess Isis was built near one of Khufu's queens' pyramids. Priests serving Isis also served Khufu, showing his lasting importance.
In the Late Period, many scarabs (small amulets) with Khufu's name were sold, possibly as good luck charms.
Khufu in Ancient Greek Traditions
Greek historians wrote about Khufu centuries after his reign, and their accounts sometimes differed from Egyptian ones.
Manetho's Account
The Egyptian historian Manetho called Khufu "Sûphis" and said he ruled for 63 years. Manetho also mentioned a story that Khufu had written a sacred book.
Herodotus's Account
The Greek historian Herodotus described Khufu as a harsh and cruel ruler. In his book Historiae, he wrote that Khufu closed all the temples and forced all Egyptians to work on his pyramid. Herodotus claimed that 100,000 men worked for three months at a time, for many years, to build the causeway and the pyramid.

Herodotus also told a story that Khufu, needing money, asked his daughter to collect funds in an unusual way. She then used some of this money to build a smaller pyramid for herself, which stands in front of the Great Pyramid. Herodotus's account suggests that Egyptians disliked Khufu and his successor, Khafre, because of their harsh rule.
Diodorus of Sicily's Account
Another ancient historian, Diodorus, also claimed that Khufu was disliked by his people. He wrote that Khufu's sarcophagus and body were secretly moved to a hidden tomb because people hated him so much. Diodorus, however, thought Herodotus's stories were "fairy tales." He also mentioned that the Egyptians of his time were unsure who built the pyramids.
Khufu in Arabic Traditions
When Arabs conquered Egypt in 642 AD, they found the pyramids but couldn't read the ancient hieroglyphs. So, Arab historians created their own theories and stories about who built them.
One well-known story comes from the book Hitat by Al-Maqrizi in 1430. Many Arab writers believed the Great Pyramid was built by the god Hermes (whom Arabs called Idris).
Al-Maqrizi also wrote that Khufu, sometimes called Saurid, built the pyramids after having nightmares about a devastating flood. To protect his treasures and books of wisdom, Khufu built the three pyramids of Giza.
Modern Egyptological Views
Today, experts have studied how Khufu's reputation changed over time. They compare ancient Egyptian records with later Greek and Arabic writings.
Many Egyptologists believe that the negative stories from Greek historians like Herodotus were a form of defamation. These historians lived about 2,000 years after Khufu and might have based their stories on outdated or misunderstood information. Also, Egyptian beliefs changed over time. The massive tombs of the Old Kingdom might have seemed excessive to later generations, and this negative view could have been applied to Khufu.
Some experts also point out that the Coptic (a later form of Egyptian) reading of Khufu's name, "Shêfet," could mean "bad luck" or "sinful." This negative meaning might have influenced Greek and Roman writers.
However, other Egyptologists suggest that ancient historians might have heard negative stories from ordinary people living near the pyramids. Even if Khufu's name survived for a long time, different groups of people might have had different opinions about him.
Modern scholars also advise caution with Arabic stories. These medieval writers often adapted Egyptian kings and gods into biblical figures, following their own religious beliefs. For example, the god Thoth became the prophet Henoch, and Khufu was often replaced by other legendary figures.
See also
 In Spanish: Keops para niños
In Spanish: Keops para niños
- Egyptian pyramid construction techniques
- Fourth Dynasty of Egypt family tree
- Khufu ship