List of pharaohs facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Pharaoh of Egypt |
|
|---|---|

|
|

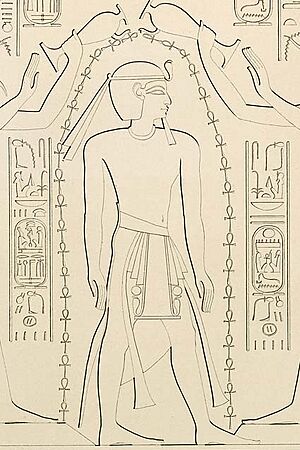
A typical depiction of a pharaoh.
|
|
| Details | |
| Style | Five-name titulary |
| First monarch | Narmer (a.k.a. Menes) |
| Last monarch | Nectanebo II (last native) Cleopatra & Caesarion (last actual) |
| Formation | c. 3100 BC |
| Abolition | 343 BC (last native pharaoh) 30 BC (last Greek pharaohs) |
| Residence | Varies by era |
| Appointer | Divine right |
This is a list of the pharaohs who ruled Ancient Egypt. A pharaoh was the most powerful person in ancient Egypt. They were the religious and political leader of the people. This list begins in the Early Dynastic Period, around 3100 BC. It ends with the Ptolemaic Dynasty, when Egypt became a part of Rome in 30 BC.
The dates given are close guesses. The list of pharaohs uses the dates of Ancient Egypt, which were figured out by the Petrie Museum of Egyptian Archaeology.
Old Records of Pharaohs
Historians have found old lists of pharaohs. These lists help us learn about who ruled Egypt. However, none of them are complete. Some important lists include:
- Palermo Stone
- Turin King List
- Manetho's book, Aegyptiaca (History of Egypt)
- Abydos King List
- Karnak Tablet
- Saqqara Tablet (found in 1861, lists kings from the 1st to 12th dynasties)
Legendary Rulers
Before human pharaohs, ancient Egyptians believed that gods ruled Egypt. These were called "god kings." The old lists of kings have different names for these god kings.
| Turin King List | Manetho (Greek name) |
What they were known for |
|---|---|---|
| Ptah | Hephaestus (Ptah) |
Craftsmen & Creation |
| Ra | Helios (Apollo) |
The Sun |
| Shu | Aelos or Agathosdaimon (Shu) |
Air |
| Geb | Gaia (Demeter) |
The Earth |
| Osiris | Hades | The Afterlife |
| Seth | Typhon (Set) |
Chaos |
| Horus | Ares | War |
| Thoth | Athena | Knowledge |
After the god kings, there were rulers who were part god and part human. The old lists also have different names for these rulers.
| Turin King List | How long they ruled | Manetho | How long they ruled |
|---|---|---|---|
| Second dynasty of gods | unknown | Dynasty of Halfgods | unknown |
| Three Achu-Dynasties | unknown | 30 Kings from Memphis | 1790 years |
Early Egypt: The Archaic Period
The Archaic period includes the Early Dynastic Period. During this time, Lower Egypt (the northern part) and Upper Egypt (the southern part) were separate kingdoms.
Early Dynastic: Lower Egypt (North)
Lower Egypt was the northern part of the Nile and the Nile Delta. This list might not be complete:
| Name | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|
| Wazner | Only on the Palermo Stone | c. 3100 BC? |
| Double Falcon | Known from finds in Sinai and Lower Egypt | c. 3200 BC? |
Early Dynastic: Upper Egypt (South)
Upper Egypt was the Nile Valley, south of the Delta. This list might not be complete:
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scorpion I | Oldest tomb at Umm el-Qa'ab had a scorpion symbol. | c. 3200 BC? | |
| Iry-Hor |
|
Possibly ruled just before Ka. | c. 3150 BC? |
| Ka |
|
May have ruled just before Narmer. | c. 3100 BC |
| King Scorpion |
|
Might be the same person as Narmer. | c. 3150 BC |
| Narmer |
|
The king who united Upper and Lower Egypt. | c. 3150 BC |
First Dynasty
The First Dynasty ruled from about 3150 to 2890 BC. This was a very important time for Egypt's early history.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Narmer |
|
Believed to be the same person as Menes. He united Upper and Lower Egypt. | c. 3150 BC |
| Hor-Aha |
|
— | c. 3050 BC |
| Djer |
|
— | 41 years |
| Djet |
|
— | 10 years |
| Merneith |
|
A female ruler who was a Regent for Den. She might have ruled as pharaoh herself. | — |
| Den |
|
The first pharaoh shown wearing the double crown of Egypt. | 42 years |
| Anedjib |
|
— | 10 years |
| Semerkhet |
|
— | 9 years |
| Qa'a |
|
— | 2916?–2890 BC |
After the First Dynasty, there might have been two short-lived pharaohs:
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sneferka |
|
Ruled for a very short time. | c. 2900 BC |
| Horus Bird |
|
Ruled for a very short time. | c. 2900 BC |
Second Dynasty
The Second Dynasty ruled from about 2890 to 2686 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hotepsekhemwy |
|
— | 25–29 years |
| Raneb |
|
His name might be read as Nebra. | 10–14 years |
| Nynetjer |
|
May have divided Egypt among his successors. | 43–45 years |
| Khasekhem(wy) |
|
He reunited Egypt after a time of trouble around 2690 BC. | 17–18 years |
The Old Kingdom
The Old Kingdom was a time of great success and building in Egypt. This was the first of three "Kingdom" periods, which were high points for Egyptian civilization. It lasted from the Third Dynasty to the Sixth Dynasty (2686–2181 BC). Many experts also include the 7th and 8th Dynasties in this period. The Old Kingdom was followed by a time of disunity called the First Intermediate Period.
The capital city of Egypt during the Old Kingdom was Memphis. This is where Djoser set up his court. The Old Kingdom is famous for the many pyramids built as tombs for the pharaohs. Because of this, it is often called "the Age of the Pyramids."
Third Dynasty
The Third Dynasty ruled from 2686 to 2613 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Djoser |
|
He ordered the first pyramid in Egypt, known as The Step Pyramid. It was built by his chief architect and scribe, Imhotep. | 19 or 28 years around 2670 BC |
| Sekhemkhet |
|
Imhotep also helped build his unfinished step pyramid. | 2649–2643 BC |
| Huni |
|
May have started the Meidum pyramid. | 2637–2613 BC |
Fourth Dynasty
The Fourth Dynasty ruled from 2613 to 2498 BC. This dynasty included the pharaohs who built the Great Pyramids: Khufu (Cheops), Khafra (Chephren), and Menkaura (Mycerinus).
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sneferu |
|
He built the Meidum Pyramid and the Bent Pyramid. He also built the first "true" pyramid, the Red Pyramid. |
|
| Khufu |
|
Known as Cheops in Greek. He built the Great Pyramid of Giza. |
|
| Djedefra (Radjedef) |
|
Believed to have created the Great Sphinx of Giza as a monument to his father. |
|
| Khafre |
|
Known as Chephren in Greek. His pyramid is the second largest in Giza. Some say he built the Great Sphinx. |
|
| Menkaura |
|
Known as Mycerinus in Greek. His pyramid is the third and smallest in Giza. |
|
| Shepseskaf |
|
He did not build a pyramid. Instead, he had the Mastabat el-Fara'un built for himself. |
|
Fifth Dynasty
The Fifth Dynasty ruled from 2498 to 2345 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Userkaf |
|
Buried in a pyramid in Saqqara. He built the first solar temple at Abusir. |
|
| Sahure |
|
He moved the royal burial ground to Abusir, where he built his pyramid. |
|
| Unas |
|
His pyramid has the earliest known pyramid texts inscribed on its walls. |
|
Sixth Dynasty
The Sixth Dynasty ruled from 2345 to 2181 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Teti |
|
He might have been murdered by Userkare. |
|
| Meryre Pepi I |
|
— |
|
| Neferkare Pepi II |
|
He might have been the longest-reigning ruler in human history, possibly ruling for 94 years. |
|
| Merenre Nemtyemsaf II |
|
He was a pharaoh who ruled for a short time, possibly an old son of Pepi II. |
|
First Intermediate Period
The First Intermediate Period (2181–2060 BC) was a time of change and disunity in Egypt. It happened between the end of the Old Kingdom and the start of the Middle Kingdom.
The Old Kingdom quickly fell apart after Pepi II died. He had ruled for a very long time, and his old age made his rule less effective.
Egypt split into two kingdoms again, and local leaders had to deal with a terrible famine.
Around 2160 BC, a new group of pharaohs tried to reunite Lower Egypt from their capital in Herakleopolis Magna. Another group of pharaohs in Thebes was reuniting Upper Egypt. A fight between these two groups was bound to happen.
Around 2055 BC, Mentuhotep II defeated the Herakleopolitan pharaohs and reunited Egypt. This marked the beginning of the Middle Kingdom.
Seventh and Eighth Dynasties (combined)
The Seventh and Eighth Dynasties ruled from about 2181 to 2160 BC. Many of these kings ruled for only a short time from Memphis. Egypt was divided into many competing regions.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Menkare |
|
||
| Neferkare (III) Neby |
|
He started building a pyramid in Saqqara. | |
| Qakare Ibi |
|
He built a pyramid at Saqqara. | 2169–2167 BC |
Ninth and Tenth Dynasties
The Ninth Dynasty ruled from 2160 to 2130 BC. The Tenth Dynasty ruled over Lower Egypt from 2130 to 2040 BC. These dynasties were local rulers during the time of disunity.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meryibre Khety I (Acthoes I) |
|
Manetho wrote that Achthoes was the first pharaoh in this dynasty. | 2160–? |
| Merykare |
|
— | ?–2040 BC |
Eleventh Dynasty
The Eleventh Dynasty was a local group from Upper Egypt. They ruled from 2134 to 1991 BC. This dynasty eventually reunited Egypt.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intef the Elder |
|
A local ruler from Thebes. He is now considered the first king of the 11th Dynasty. | — |
| Mentuhotep I |
|
A Theban ruler who may have ruled independently. |
|
| Intef II |
|
He conquered Abydos and its region. |
|
| Intef III |
|
He conquered Asyut. |
|
The Middle Kingdom
The Middle Kingdom (2060–1802 BC) began after the First Intermediate Period and ended before the Second Intermediate Period. During this time, Egypt started trading with other countries. This opening of trade eventually led to the downfall of the Middle Kingdom, caused by an invasion from the Hyksos.
Eleventh Dynasty (continued)
The second part of the Eleventh Dynasty is considered part of the Middle Kingdom.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mentuhotep II |
|
He reunited all of Egypt around 2015 BC, starting the Middle Kingdom. |
|
| Mentuhotep III |
|
He sent the first expedition to Punt during the Middle Kingdom. |
|
Twelfth Dynasty
The Twelfth Dynasty ruled from 1991 to 1802 BC. Later Egyptians thought this was their greatest dynasty.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amenemhat I |
|
He took power after overthrowing Mentuhotep IV. He was later murdered. |
|
| Senusret I (Sesostris I) |
|
He built the White Chapel. |
|
| Senusret III (Sesostris III) |
|
He was the most powerful pharaoh of the Middle Kingdom. |
|
| Amenemhat III |
|
— |
|
| Sobekneferu |
|
A rare female ruler. |
|
Second Intermediate Period
The Second Intermediate Period (1802–1550 BC) was a time of trouble. It was between the end of the Middle Kingdom and the start of the New Kingdom. During this time, the Hyksos people arrived in Egypt and became the Fifteenth Dynasty.
The Thirteenth Dynasty was weaker than the Twelfth Dynasty. It could not hold onto all of Egypt. Around 1805 BC or 1710 BC, a ruling family in Xois broke away. They formed the Fourteenth Dynasty.
The Hyksos first appeared around 1720 BC. They took control of the town of Avaris. Around 1650 BC, the Hyksos conquered Memphis, ending the 13th Dynasty.
Later, the Egyptian rulers in Thebes formed the Seventeenth Dynasty. This dynasty, led by pharaohs like Seqenenre Tao, Kamose, and Ahmose, eventually forced the Hyksos out of Egypt. This led to the New Kingdom.
Thirteenth Dynasty
The Thirteenth Dynasty ruled from 1802 to around 1649 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sekhemre Khutawy Sobekhotep |
|
He started the 13th Dynasty. | 1802–1800 BC |
| Khaankhre Sobekhotep |
|
He ruled for about 3 years. | 1780–1777 BC |
| Awybre Hor I |
|
Famous for his untouched tomb treasures and Ka statue. | 1777–1775 BC |
| Sobekhotep III |
|
He ruled for four years and two months. | c. 1755–1751 BC |
| Neferhotep I |
|
He ruled for 11 years. | 1751–1740 BC |
| Sobekhotep IV |
|
He ruled for 10 or 11 years. | 1740–1730 BC |
| Merneferre Ay I |
|
He was the longest-reigning king of this dynasty. | 23 years, 8 months and 18 days, 1701–1677 BC |
Fourteenth Dynasty
The Fourteenth Dynasty was a local group from the eastern Delta. They ruled from about 1805 BC or 1710 BC until around 1650 BC. Many of their rulers had West Semitic names, suggesting they came from the land of Canaan.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yakbim Sekhaenre |
|
Dates are not certain. | 1805–1780 BC |
| Sheshi |
|
Dates are not certain. | 1745–1705 BC |
| Nehesy |
|
He ruled for a short time. He might have been a son of Sheshi. | c. 1705 BC |
Fifteenth Dynasty (Hyksos)
The Fifteenth Dynasty was started by the Hyksos people. They came from the Fertile Crescent region. They ruled over much of the Nile region from 1674 to 1535 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Khyan |
|
He conquered Thebes near the end of his rule. | 30–40 years |
| Apepi |
|
He ruled for 40 years or more. | — |
| Khamudi |
|
— | 1555–1544 BC |
Sixteenth Dynasty
The Sixteenth Dynasty was a native Theban dynasty. It began around 1650 BC and was conquered by the Hyksos 15th Dynasty around 1580 BC. The 16th Dynasty only ruled over Upper Egypt.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Djehuti | — | 3 years | |
| Sobekhotep VIII | — | 16 years | |
| Nebiryraw I Sewadjenre |
|
— | 26 years |
Seventeenth Dynasty
The Seventeenth Dynasty was based in Upper Egypt. They ruled from 1650 to 1550 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rahotep |
|
— |
|
| Sobekemsaf I |
|
He ruled for at least seven years. | — |
| Seqenenre Tao |
|
He died in battle against the Hyksos. |
|
| Kamose |
|
— |
|
The New Kingdom
The New Kingdom (1550–1077 BC) was a time when Egypt became a powerful empire. It was between the Second Intermediate Period and the Third Intermediate Period.
During the New Kingdom, Egypt's armies captured nearby countries. Egypt controlled Nubia in the south and held lands in the Near East. Egyptian armies fought with Hittite armies for control of modern-day Syria. At this time, Egypt controlled more land than ever before.
Two of the most famous pharaohs of the New Kingdom are Akhenaten and Ramesses II. Akhenaten tried to start a new religion that worshipped only the god Aten. This is sometimes seen as the first time a ruler tried to create a religion with only one god. Ramesses II was a strong military leader. He tried to take back lands in what is now modern Israel/Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria. At the Battle of Qadesh, he led the Egyptian armies against the Hittite king Muwatalli II.
Eighteenth Dynasty
The Eighteenth Dynasty ruled from about 1550 to 1292 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ahmose I, Ahmosis I |
|
He was the brother of Kamose. He conquered northern Egypt from the Hyksos. | c. 1550–1525 BCE |
| Amenhotep I |
|
— | 1541–1520 BC |
| Thutmose I |
|
— | 1520–1492 BC |
| Hatshepsut |
|
She was the second known female ruler. | 1479–1458 BC |
| Thutmose III |
|
He is often called the "Napoleon of Egypt." He expanded Egyptian rule into the Levant. | 1479–1425 BC |
| Amenhotep III The Magnificent King |
|
He ruled Egypt when it was at its most powerful. He had more monuments built than any other pharaoh. | 1390–1352 BC |
| Akhenaten or Amenhotep IV |
|
He started a sun-based religion called Atenism. His original name meant "Amun is pleased." | 1352–1334 BC |
| Tutankhamun |
|
He is commonly believed to be the son of Akhenaten. He probably brought back the old religion. He is also known as the boy king. | 1333–1324 BC |
| Ay |
|
He was a close advisor to pharaohs before him. He is thought to have been the real power during Tutankhamun's rule. | 1324–1320 BC |
| Horemheb |
|
He was a former General and advisor to Tutankhamun. | 1320–1292 BC |
Nineteenth Dynasty
The Nineteenth Dynasty ruled from 1292 to 1186 BC. It included one of the greatest pharaohs, Rameses II the Great.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seti I |
|
— | 1290–1279 BC |
| Ramesses II the Great |
|
He is often linked to Moses. He fought the Hittites at the Battle of Kadesh in 1275 BC. A peace treaty was signed in 1258 BC. | 1279–1213 BC |
| Merneptah |
|
A stela (stone slab) describes his campaigns. It is the only ancient Egyptian record to mention "Israel." | 1213–1203 BC |
| Tausret |
|
A female ruler. She was probably the wife of Seti II. | 1191–1190 BC |
Twentieth Dynasty
The Twentieth Dynasty ruled from 1190 to 1077 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ramesses III |
|
He fought the Sea Peoples in 1175 BC. He was killed in a plot. | 1186–1155 BC |
| Ramesses XI |
|
His rule ended with power being shared. The High Priest of Amun ruled in the south, and Smendes I ruled in the north. | 1107–1077 BC |
Third Intermediate Period
The Third Intermediate Period (1077–732 BC) marked the end of the New Kingdom. After the Egyptian empire fell apart, some dynasties of Libyan origin ruled Egypt. This time is also known as the Libyan Period.
Twenty-First Dynasty
The Twenty-First Dynasty was based at Tanis. They ruled from 1069 to 943 BC. Their power was mostly limited to Lower Egypt.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nesbanebdjed I |
|
Also known as Smendes I. | 1077–1051 BC |
| Psusennes I |
|
Also known as the Silver Pharaoh. | 1047–1001 BC |
Twenty-Second Dynasty
The pharaohs of the Twenty-Second Dynasty were from Libya. They ruled from around 943 to 728 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shoshenq I |
|
— | 943–922 BC |
| Osorkon I |
|
— | 922–887 BC |
Twenty-Third Dynasty
The Twenty-Third Dynasty was another Libyan group. They were based at Herakleopolis and Thebes. They ruled from 837 to about 735 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Takelot II |
|
He is now known to be the founder of the 23rd Dynasty. | 837–813 BC |
| Osorkon III |
|
He recovered Thebes and became king. | 795–767 BC |
Twenty-Fourth Dynasty
The Twenty-fourth Dynasty was a short-lived rival dynasty in the western Delta. There were only two pharaohs, ruling from 732 to 720 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tefnakhte |
|
— | 732–725 BC |
| Bakenrenef |
|
— | 725–720 BC |
The Late Period
The Late Period runs from 732 BC until Egypt became a province of Rome in 30 BC. This time included periods when Egypt was ruled by people from Nubia, Persia, and Macedon.
Twenty-Fifth Dynasty (Nubian)
Nubians invaded Lower Egypt and took the throne under Piye. They already controlled Thebes and Upper Egypt. Piye's conquest of Lower Egypt started the Twenty-fifth Dynasty, which ruled until 656 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piye |
|
He was King of Nubia. He conquered Egypt in his 20th year. | 752–721 BC |
| Shabaka |
|
— | 721–707/706 BC |
| Taharqa |
|
— | 690–664 BC |
| Tantamani |
|
He lost control of Upper Egypt in 656 BC when Psamtik I took over Thebes. | 664–653 BC |
The Nubians were forced out of Egypt and went back to Nubia. They set up a kingdom there.
Twenty-Sixth Dynasty
The Twenty-sixth Dynasty ruled from around 672 to 525 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Necho I |
|
He was killed by an invading Kushite force in 664 BC. He was the father of Psamtik I. | 672 – 664 BC |
| Psamtik I |
|
He reunited Egypt. He was the son of Necho I and father of Necho II. | 664 – 610 BC |
| Necho II |
|
He is likely the pharaoh mentioned in several books of the Bible. | 610 – 595 BC |
| Ahmose II |
|
He was the last great ruler of Egypt before the Persian conquest. | 570 – 526 BC |
| Psamtik III |
|
He ruled for about six months before being defeated by the Persians and executed. | 526 – 525 BC |
Twenty-Seventh Dynasty (Persian)
Egypt was conquered by the Persian Empire in 525 BC. The Persians ruled until 404 BC. The Persian kings were considered pharaohs during this time, forming the "Twenty-seventh" Dynasty.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cambyses II |
|
He defeated Psamtik III at the Battle of Pelusium in 525 BC. | 525 – 521 BC |
| Darius I |
|
— | 521 – 486 BC |
| Xerxes I |
|
— | 486 – 465 BC |
| Artaxerxes I Longhand |
|
— | 464 – 424 BC |
Twenty-Eighth Dynasty
The Twenty-eighth Dynasty lasted only six years, from 404 to 398 BC, with one pharaoh.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amyrtaeus | He was a descendant of the 26th Dynasty pharaohs. He led a successful revolt against the Persians. | 404 – 398 BC |
Twenty-Ninth Dynasty
The Twenty-ninth Dynasty ruled from 398 to 380 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nefaarud I |
|
Also known as Nepherites. He defeated Amyrtaeus and had him executed. | 398 – 393 BC |
| Hakor |
|
He overthrew his predecessor Psammuthes. | 393 – 380 BC |
Thirtieth Dynasty
The Thirtieth Dynasty ruled from 380 BC until Egypt came under Persian rule again in 343 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nectanebo I |
|
Also known as Nekhtnebef. He started the last dynasty of native Egyptians. | 380 – 362 BC |
| Senedjemibre Nakhthorhebyt (Nectanebo II) |
|
He was the last native ruler of ancient Egypt. | 360 – 343 BC |
Thirty-First Dynasty (Persian)
Egypt again came under the control of the Achaemenid Persians. The Persian rulers from 343 to 332 BC are sometimes called the Thirty-first Dynasty.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artaxerxes III | Egypt came under Persian rule for the second time. | 343–338 BC | |
| Darius III | Upper Egypt returned to Persian control in 335 BC. | 336–332 BC |
Argead Dynasty (Macedonian)
The Macedonians, led by Alexander the Great, began the Hellenistic period. This happened when Alexander captured Persia and Egypt. The Argeads ruled from 332 to 309 BC.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alexander the Great |
|
Macedon took over Persia and Egypt. | 332–323 BC |
| Alexander IV of Macedon |
|
He was the son of Alexander the Great and Roxana. | 317–309 BC |
Ptolemaic Dynasty (Greek)
The second Hellenistic dynasty was the Ptolemies. They ruled Egypt from 305 BC until Egypt became a part of Rome in 30 BC. If two dates overlap, it means two rulers shared power at the same time.
The most famous member of this dynasty was Cleopatra VII. She is known simply as Cleopatra today. She was involved with the Roman dictator Julius Caesar and later with the Roman general Mark Antony. She had children with both of them. Cleopatra tried to join Egypt and Rome politically. This plan failed after Caesar's death and Mark Antony's defeat.
Caesarion (Ptolemy XV) was Cleopatra VII's oldest son. He was possibly the only son of Julius Caesar. He ruled jointly with his mother from 47 BC. After Cleopatra's death in 30 BC, he was the only pharaoh for a short time. It is believed he was killed by order of Octavian, who later became the Roman emperor Augustus.
| Name | Image | Notes | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ptolemy I of Egypt | He gave up his throne in 285 BC and died in 283 BC. | 305–285 BC | |
| Ptolemy II of Egypt | — | 288–246 BC | |
| Ptolemy III of Egypt | — | 246–222 BC | |
| Ptolemy IV of Egypt | — | 222–204 BC | |
| Ptolemy V of Egypt | Upper Egypt was in revolt from 207–186 BC. | 204–180 BC | |
| Ptolemy VI of Egypt | He died in 145 BC. | 180–164 BC | |
| Ptolemy VIII of Egypt | He was declared king by people in Alexandria in 170 BC. He ruled with Ptolemy VI of Egypt and Cleopatra II from 169 to 164 BC. | 171–163 BC | |
| Ptolemy IX of Egypt | He died in 80 BC. | 116–110 BC | |
| Ptolemy XII | He was the son of Ptolemy IX. He died in 51 BC. | 80– 58 BC | |
| Cleopatra VII | She ruled jointly with her father Ptolemy XII, her brother Ptolemy XIII, her brother-husband Ptolemy XIV, and her son Ptolemy XV. She is known simply as Cleopatra. | 51–30 BC | |
| Ptolemy XV of Egypt | He was the infant son of Cleopatra VII. He was 3 years old when he was declared co-ruler with Cleopatra. He was the last known ruler of ancient Egypt before Rome took over. | 44–30 BC |
Roman Rule
Cleopatra VII had relationships with the Roman dictator Julius Caesar and the Roman General Marc Antony. She ended her own life when Antony was defeated by Octavian (who later became Emperor Augustus). Egypt then became a province of Rome in 30 BC. Roman Emperors were given the title of Pharaoh, but only when they were in Egypt. One Egyptian king-list names the Roman Emperors as Pharaohs up to and including Decius. You can see more on the list of Roman Emperors.
See also
 In Spanish: Anexo:Faraones de Egipto para niños
In Spanish: Anexo:Faraones de Egipto para niños