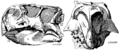Psittacosaurus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids PsittacosaurusTemporal range: Lower Cretaceous
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Infraorder: | |
| Family: |
Psittacosauridae
|
| Genus: |
Psittacosaurus
Osborn, 1923
|
| Species | |
Osborn, 1923
Young, 1958
Sereno et al., 1988
Sereno & Zhao, 1988
Buffetaut & Suteethorn, 1992
Russell & Zhao, 1996
Russell & Zhao, 1996
Xu, 1997
Voronkevich, 1998
Zhou et al., 2006 |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Protiguanodon Osborn, 1923 |
|
Psittacosaurus was a small dinosaur that lived a long, long time ago. It was a type of ceratopsian dinosaur, but it looked quite different from the famous Triceratops. Psittacosaurus lived in what is now Asia during the Lower Cretaceous period, about 130 to 100 million years ago.
Unlike later ceratopsians, Psittacosaurus walked on two legs. It also didn't have any horns or a big bony frill on its head. What made it a ceratopsian was its special beak, which looked a bit like a parrot's beak. This dinosaur is famous because scientists have found many different species of it. There are between nine and eleven recognized species! Their fossils have been found in China, Mongolia, Russia, and possibly Thailand.
All Psittacosaurus species were plant-eaters, also known as herbivores. They were about the size of a gazelle. They had a strong, high beak on their upper jaw. At least one species even had long, quill-like structures on its tail and lower back. These quills might have been used to show off or for defense. Psittacosaurus was an early ceratopsian, meaning it lived before dinosaurs like Protoceratops and the huge Triceratops. Even so, it shared some features with its later relatives.
What Did Psittacosaurus Look Like?
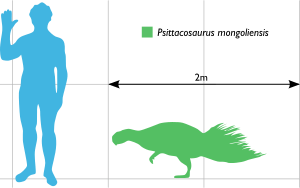
The different species of Psittacosaurus varied a bit in size and the shape of their skulls. However, they all had a similar body plan. The most well-known species, P. mongoliensis, could grow up to 2 meters (6.5 feet) long. It likely weighed more than 20 kilograms (44 pounds).
Some species were similar in size to P. mongoliensis, like P. lujiatunensis and P. neimongoliensis. Others, such as P. sinensis, were a bit smaller. The smallest known species, P. ordosensis, was about 30% smaller than P. mongoliensis. The largest ones, P. lujiatunensis and P. sibiricus, weren't much bigger than P. mongoliensis.
The body of Psittacosaurus was typical for a small, two-legged ornithischian dinosaur. It had only four fingers on its 'hand' (called the manus), while most other ornithischians had five. Its four-toed back feet were similar to many other small, two-legged dinosaurs.
The Unique Skull and Beak
The skull of Psittacosaurus was very special compared to other plant-eating dinosaurs of its time. It was very tall but short, almost round in some species. The part of the skull in front of the eye socket (called the orbit) was very short.
Both the upper and lower jaws had a strong, parrot-like beak. This beak was made of special bones and was probably covered in keratin. Keratin is the same tough material that makes up your fingernails and bird beaks. This sharp beak helped Psittacosaurus crop or cut tough plant material.
Psittacosaurus skulls shared some features with later ceratopsians. For example, they had a unique bone at the tip of the upper jaw and wide jugal (cheek) bones. But, they didn't have the big bony neck frills or horns that you see on dinosaurs like Triceratops. P. sibiricus did have some bony bumps on its skull, but scientists think these developed separately and weren't related to the horns of later ceratopsians.
Images for kids
-
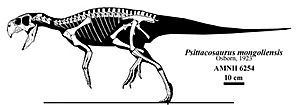
Holotype of P. mongoliensis (specimen AMNH 6254), American Museum of Natural History
-
Type skull of P. mongoliensis from Osborn, 1923
-
P. mongoliensis specimen AMNH 6254 with gastroliths in its stomach region (arrow)
-
Fossil of Repenomamus robustus, juvenile Psittacosaurus remains preserved in its stomach
See also
 In Spanish: Psittacosaurus para niños
In Spanish: Psittacosaurus para niños