Pueblo I Period facts for kids
The Pueblo I Period (from 750 to 900 AD) was an important time for the Ancestral Puebloans. During this period, they started living in special buildings called pueblos. This era saw big changes in how they built homes, created art, and managed their water supply.
The Pueblo I Period is part of a way of classifying ancient cultures called the Pecos Classification. It's also known as the early "Developmental Pueblo Period." This time came after the Basketmaker III Era and before the Pueblo II Period.
Contents
Building Homes: Architecture of Pueblo I
During this period, people built and lived in pueblos. These were homes built on the ground with flat roofs.
Early Pueblo Homes: Jacal Construction
At the start of the Pueblo I Period, pueblos were made using a method called jacal construction. This involved using wooden posts to create a frame. Then, woven materials were added to the frame and covered with mud.
Later, people sometimes used stone slabs around the bottom of their homes. This made the buildings stronger.
Village Layout and Rooms
Pueblos often had several rooms. These rooms were built in a straight line or in a crescent (curved) shape. Sometimes, they even built homes two rows deep. These buildings had living rooms with fire pits and separate rooms for storage.
Historians believe that these changes in how villages were built show changes in how people lived together. It suggests they became a more organized group.
From Pit-Houses to Kivas
During this time, round pit-houses began to change. They slowly became ceremonial kivas. Kivas were special underground rooms used for religious ceremonies and community gatherings.
Growing Communities and Villages
Not all communities changed at the same speed during the Pueblo I Period. Some places didn't have the same pressures, like climate changes, that forced others to move quickly. So, some communities still lived in older Basket Maker settlements at the beginning of this period.
Larger Settlements
Pueblo I villages were much bigger than the earlier Basket Maker settlements. In the Four Corners area, the average number of pit-houses per settlement grew from 5-10 to 20-30. Some Pueblo I communities were very large. For example, Alkali Ridge in southeastern Utah had about 130 rooms built above ground. It also had 16 pit-houses and 2 kivas.
The most advanced communities, especially in the Chaco Canyon area, had "great houses," roads, and fancy kivas.
Life in Different Regions
- Dolores River Valley: In southwestern Colorado, people started building more above-ground structures and villages. These buildings often had rooms connected together, with windows facing south. Many rooms were used for storage. People began to gather in pit-houses for ceremonies, which later became kivas. They developed rituals, like prayers for rain and good harvests. Buildings were made from stone and wood, and sometimes adobe or masonry.
- San Juan River Valley: A settlement in the San Juan River Valley, New Mexico, was surrounded by large walls called palisades. Evidence suggests this village was destroyed, and many people died. This happened during a long drought. One idea is that the village was attacked for its food. After this event, many communities started building Pueblo I structures on higher, safer ground.
- Chaco Canyon: "Great houses" were built here in the mid-800s. These buildings were much larger than earlier homes. They were multi-story with high ceilings and very big rooms. They also had elaborate kivas. Builders used advanced masonry techniques to create strong and beautiful structures. Roads were also built. Other sites in Chaco Canyon were smaller settlements, similar to other Pueblo communities of the time. Their storage rooms were made of Jacal.
Farming and Water Management
By the Pueblo I Period, the Ancient Pueblo people relied heavily on agriculture. They faced times of low rainfall, like a major drought from 850–900 in the Petrified Forest National Park.
People likely settled on mesas and ridges to get more winter snow and summer rain. They also started using new ways to manage and save water. This included building reservoirs and special dams that held back silt (fine dirt). These methods helped them use their water supply wisely. They stored harvested corn in large clay pots with stone lids to protect it from animals and rot.
People also hunted animals, set traps, and gathered wild nuts, plants, and fruits.
Pottery and Art
Pottery became much more useful during the Pueblo I Period. They made many different kinds of pots, including ollas (large jars), pitchers, ladles, bowls, and dishes.
Plain gray pottery and gray pottery with designs around the neck were common. White pottery with black designs, made from plant-based pigments, and red pottery also appeared during this time.
Communities that didn't have good harvests often traded pottery for corn. This led to the creation of beautifully designed black-on-white pottery, which was good for trading.
Everyday Items: Other Material Goods
People in the Pueblo I Period continued to use many items from the earlier Basketmaker III Era. Here are some examples of their tools and goods:
- Stone tools, like axes and knives.
- Bone awls (pointed tools) used for weaving mats, sandals, and baskets from yucca plants.
- Pottery of various kinds.
- Manos and metates, which were stones used to grind corn and other plants.
- Digging sticks for farming.
- Bows and arrows for hunting.
- Items woven from yucca, such as sandals and rope.
- Blankets made from turkey feathers and yucca fibers.
- Clothing made from woven cotton, which they got through trade.
During this period, hard-backed cradle boards became common. These boards held babies tightly and safely, supporting their necks while mothers worked. The constant pressure from these boards caused the back of the babies' heads to flatten. This change can be seen in the skull shapes of people from this period.
Ancient Cultural Groups
The main cultural groups living during this period included:
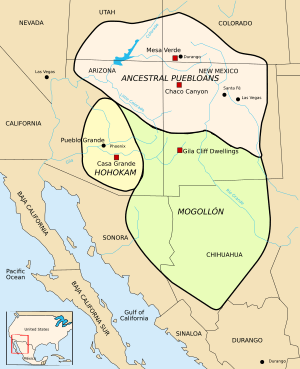
- Ancestral Puebloans – found in southern Utah, southern Colorado, northern Arizona, and northern and central New Mexico.
- Hohokam – located in southern Arizona.
- Mogollon – found in southeastern Arizona, southern New Mexico, and northern Mexico.
- Patayan – located in western Arizona, California, and Baja California.
Important Pueblo I Sites
| Arizona | Colorado | New Mexico | Utah |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cohonina Glen Canyon Navajo Pueblos Petrified Forest |
Canyons of the Ancients Chimney Rock Durango Rock Shelters Hovenweep La Plata River valley Mesa Verde Ute Mountain |
Canyon de Chelly | Glen Canyon Hovenweep |
Images for kids
-
A pit-house ventilator at Mesa Verde National Park.
-
A pit-house at Mesa Verde National Park.
-
An example of an early kiva at Mesa Verde National Park.
See also
 In Spanish: Periodo Pueblo I para niños
In Spanish: Periodo Pueblo I para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |