Qinling facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Qinling |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||||||||
| Highest point | |||||||||
| Peak | Mount Taibai | ||||||||
| Elevation | 3,767 m (12,359 ft) | ||||||||
| Naming | |||||||||
| Language of name | |||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 秦嶺 | ||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 秦岭 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Qin Peak(s) | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Former name is Southern Mountains | |||||||||
| Chinese | 南山 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Geography | |||||||||
| Country | |||||||||
| State/Province | Southern Shaanxi Province | ||||||||
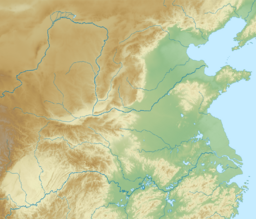
The Qinling Mountains (also called the Qin Mountains) are a big mountain range in southern Shaanxi Province, China. They used to be known as the Nanshan, which means "Southern Mountains".
These mountains act like a natural wall, separating the Yangtze River and Yellow River systems. This makes them a clear border between North and South China. They are also home to many different plants and animals, some of which you can't find anywhere else!
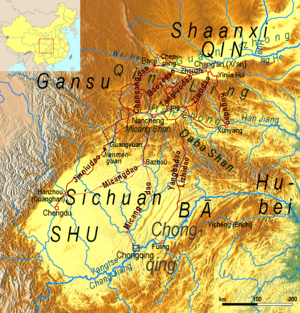
To the north of the Qinling Mountains is the busy Wei River valley. This area was an important center for ancient Chinese civilization. To the south, you'll find the Han River valley. To the west, the mountains connect to the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. East of the Qinling are the smaller Funiu and Dabie Mountains, which rise from the flat coastal plain.
The northern side of the Qinling Mountains can get very hot. Because of the mountains, the land to the north has a dry climate. This means it doesn't have rich, fertile soil and can't support a lot of wildlife. The mountains also helped protect against attacks from people living in the north. Only four main passes cross through these mountains. In the late 1990s, a railway tunnel and a special spiral track were built. This made it much easier to travel across the mountain range.
The tallest mountain in the Qinling range is Mount Taibai. It stands at 3,767 meters (12,359 ft) high. Mount Taibai is about 100 kilometers (62 mi) west of Xi'an, an ancient capital city of China. Three other important peaks in the range are Mount Hua (2,155 meters or 7,070 feet), Mount Li (1,302 meters or 4,272 feet), and Mount Maiji (1,742 meters or 5,715 feet).
Environment and Wildlife
The Qinling Mountains are covered by a type of forest where trees lose their leaves in autumn. This is called a deciduous forest.
The Qinling Mountains act as a natural dividing line for water. To the north, water flows into the Yellow River basin. This area used to have forests with trees that lost their leaves. To the south, water flows into the Yangtze River basin. This area has milder winters and more rain. It used to have forests with evergreen trees that kept their leaves all year. Because of this, the Qinling Mountains are often seen as the line that separates northern and southern China.
Plants and Trees
The forests at lower parts of the mountains have many temperate deciduous trees. These include different kinds of oaks, elm trees, walnut trees, maple trees, and ash trees. Some evergreen trees also grow here, like broadleaf chinquapins and certain types of pines.
Higher up in the mountains, you'll find conifers like Pinus armandii. These are mixed with broadleaf trees such as birch and hornbeam. Even higher, from 2,600 to 3,000 meters (8,500 to 9,800 ft) elevation, these forests change into subalpine forests. Here, you'll see fir trees, Cunninghamia, and more birch trees. Rhododendron plants are very common in the areas under these trees.
The Qinling region is home to many rare plants. About 3,000 different plant species have been found here so far. Some of the native plants and trees include the Ginkgo tree, which is thought to be one of the oldest tree species in the world. Other native trees include the Huashan or Armand pine and the Chinese fir. In the 18th century, a lot of timber was harvested from the Qinling Mountains.
Animals of the Qinling Mountains
The Qinling Mountains are famous for being home to the Qinling panda. This is a special type of giant panda. These pandas are protected in areas like the Changqing and Foping nature reserves. It's estimated that between 250 and 280 giant pandas live here. This is about one-fifth of all the wild giant pandas in the world!
Many other animals also live in the Qinling Mountains.
- Birds include the crested ibis, Temminck's tragopan, golden eagle, blackthroat, and golden pheasant.
- Mammals include the golden takin, golden snub-nosed monkey, yellow-throated marten, Asiatic golden cat, Asiatic black bear, clouded leopard, and leopard.
The Chinese giant salamander is also found here. It's the largest amphibian in the world, growing up to 1.8 meters (5 ft 11 in) long! Sadly, it is critically endangered. People collect it for food and for use in traditional Chinese medicine. To help protect these amazing creatures, there are programs to teach people about managing wild populations in a sustainable way. Also, special breeding programs have been set up to help increase their numbers.
See also
 In Spanish: Cordillera Qin para niños
In Spanish: Cordillera Qin para niños
- Gallery road
- Huaqing Pool
- Qinling Orogenic Belt
- Qinling panda
 | Percy Lavon Julian |
 | Katherine Johnson |
 | George Washington Carver |
 | Annie Easley |