Safari (web browser) facts for kids
 |
|
|
|
| Developer(s) | Apple Inc. |
|---|---|
| Initial release | January 7, 2003 |
| Stable release(s) | |
| Preview release(s) [±] | |
| Non | |
| Written in | C++, C, assembly language, Objective-C, JavaScript |
| Operating system | macOS iOS iPadOS Windows (2007–2012) visionOS |
| Included with | macOS iOS iPadOS visionOS |
| Type | Web browser |
| License | Freeware (pre-installed on Apple devices); some components (e.g. rendering engine) GNU LGPL |
Safari is a web browser made by Apple. It comes built into many of Apple's devices. These include computers running macOS, iPhones with iOS, iPads with iPadOS, and the Apple Vision Pro with visionOS. Safari uses Apple's special browser engine called WebKit. This engine helps Safari show websites correctly.
Safari first appeared in January 2003 for Mac computers. It quickly became the main web browser for Macs. Since 2007, it has also been on every iPhone. Safari was known for being very fast on Macs. Apple also made a version for Microsoft Windows computers between 2007 and 2012. However, they stopped making it because not many people used it. Over the years, Safari has added many cool features. These include a reader mode, extensions, and tools for developers. Newer versions also added "Intelligent Tracking Prevention" to help protect your privacy online.
Contents
- Exploring Safari's Journey
- How Safari Started
- Safari 1: The Beginning
- Safari 2: Faster and Better
- Safari 3: Going Mobile and Windows
- Safari 4: New Look and Features
- Safari 5: Reader Mode and Extensions
- Safari 6: Mac Only
- Safari 7 & 8: Performance and Privacy Boosts
- Safari 9 & 10: New Look and HTML5 Focus
- Safari 11 & 12: Smart Tracking Prevention
- Safari 13 & 14: Security and Translation
- Safari 15 & 16: Redesigned and Shared Tabs
- Safari 17: Profiles and Privacy
- Safari 18: Highlights and Unified Menu
- Safari 26: Future Design
- Key Features of Safari
- How Safari Works
- Safari on Other Devices
- Safari's Popularity
- See also
Exploring Safari's Journey
How Safari Started
Before Safari, other web browsers were popular on Mac computers. Netscape Navigator was very common. Then, Microsoft released Internet Explorer for Mac. Apple even made a deal to make Internet Explorer the main browser on Macs for a while.
But Apple wanted to create its own browser. On January 7, 2003, Steve Jobs, the head of Apple, showed off Safari. He said it was a "turbo browser" for Mac computers. Apple designed Safari to be super fast. Jobs even showed how it was faster than other browsers at the time. Apple also wanted to make a browser that could do new and exciting things.
Safari 1: The Beginning
Safari 1.0 was released on June 23, 2003. It was based on WebKit, Apple's own version of a browser engine. This engine helps Safari display web pages. At first, you had to download Safari separately for Mac OS X. But with Mac OS X Panther, Safari became the main browser that came with the computer.
Safari 2: Faster and Better
In April 2005, Safari 2.0 was released. Apple said it was 1.8 times faster than the previous version. This version also became the main browser for Mac OS X 10.4. A big step for Safari was when it became the first browser to pass the Acid2 test. This test checks how well a browser shows web pages correctly.
Safari 3: Going Mobile and Windows
On January 9, 2007, Apple announced Safari 3. This version was made for the very first iPhone. It could show full websites, just like on a computer. Apple also released Safari 3 for Windows XP and Windows Vista. They claimed it was the fastest browser on Windows. Safari 3 also added features to protect users from fake websites (phishing).
Safari 4: New Look and Features
Safari 4 came out on June 8, 2009. It was the first version to fully pass the Acid3 test, showing it could display web pages very accurately. It also supported HTML5, which is a key part of how modern websites are built. Safari 4 made JavaScript run much faster, which helps websites load quickly. It also had a cool "Top Sites" feature that showed your most visited websites as thumbnails.
Safari 5: Reader Mode and Extensions
Safari 5 was released on June 7, 2010. A popular new feature was "Reader" mode. This mode removes ads and other distractions from web pages, making them easier to read. Safari 5 also introduced "Extensions," which are small programs that add new features to your browser. This version was the last one available for Windows computers.
Safari 6: Mac Only
Safari 6.0 was released on July 25, 2012, along with OS X Mountain Lion. From this version on, Safari was only available for Mac computers. It was no longer offered for Windows. Safari 6 added "iCloud Tabs," which lets you see open tabs from your other Apple devices. It also had new privacy features, like asking websites not to track you.
Safari 7 & 8: Performance and Privacy Boosts
Safari 7, released in October 2013, brought many improvements to how fast JavaScript runs. Safari 8, released in 2014, added stronger privacy tools and better integration with iCloud. It also became even faster and more efficient.
Safari 9 & 10: New Look and HTML5 Focus
Safari 9, released in 2015, added features like muting audio on web pages. Safari 10, released in September 2016, redesigned the Bookmark and History views. It also focused on using HTML5 versions of websites instead of older plug-ins.
Safari 11 & 12: Smart Tracking Prevention
Safari 11, released in September 2017, introduced "Intelligent Tracking Prevention." This smart feature uses artificial intelligence to limit how advertisers can track you across different websites. Safari 12, released in September 2018, improved this tracking prevention even further. It also added icons in tabs and automatic strong passwords.
Safari 13 & 14: Security and Translation
Safari 13, released in September 2019, added important security features. These included support for Apple Pay on the web and using security keys for logging in. Safari 14, released in September 2020, brought new privacy features like a "Privacy Report." This report shows you which trackers Safari has blocked on web pages. It also added a built-in translation service for web pages.
Safari 15, released in September 2021, had a big redesign of its look. It also introduced "Tab Groups," which let you organize your open tabs. These tab groups can sync across all your Apple devices. Safari 16, released in September 2022, added shared tab groups. This means you can share a group of tabs with friends or family.
Safari 17: Profiles and Privacy
Safari 17 was released in September 2023. A cool new feature is "Profiles." This lets you separate your browsing for different uses, like one for school and one for personal use. Each profile has its own favorites, history, and extensions. Safari 17 also added more privacy features, like locked private browsing and removing tracking parts from web links.
Safari 18: Highlights and Unified Menu
Safari 18 was released in September 2024. It brought another redesign, especially to the start page and reader mode. A new feature called "Highlights" uses artificial intelligence to find and show you important information on a page. It also has a new menu that looks the same across all Apple devices.
Safari 26: Future Design
Safari 26 is planned for release in fall 2025. It will have a new design style called "Liquid Glass." This version will also use the year number instead of a regular version number, just like Apple's operating systems.
Key Features of Safari
Safari has many features designed to make your web browsing experience better and safer.
Private Browsing
Safari has a "Private Browsing" mode. When you use this, the browser does not save your history, cookies, or other information about the websites you visit. This helps keep your online activity more private.
Intelligent Tracking Prevention
This feature helps protect your privacy by limiting how advertisers can track you online. It uses smart technology to identify and block trackers. This means fewer companies can follow your browsing habits across different websites.
Extensions and Add-ons
Safari allows you to add "extensions." These are small programs that can add new tools or change how websites look. For example, some extensions can block ads or help you save articles to read later.
iCloud Syncing
Safari can sync your bookmarks, browsing history, reading list, and open tabs across all your Apple devices. If you open a tab on your iPhone, you can easily see it and open it on your Mac or iPad thanks to iCloud.
Tab Groups
With "Tab Groups," you can organize your open tabs into different collections. For example, you could have a "School" tab group and a "Hobbies" tab group. These groups also sync across your devices. You can even share tab groups with others.
Handoff
The "Handoff" feature lets you start something on one Apple device and continue it on another. For example, if you are reading an article in Safari on your iPhone, you can easily pick up exactly where you left off on your Mac.
Sidebar for Easy Access
The Safari sidebar helps you quickly get to your bookmarks, reading list, and open tabs. In newer versions, you can even see your tabs arranged vertically in the sidebar, which can be helpful if you have many tabs open.
Visual Look Up
This feature lets you learn more about things in images. If you see a landmark or a plant in a picture, you can select it to get more information. You can also easily lift the main subject out of an image and paste it into other apps.
Live Text
"Live Text" lets you interact with text that appears in images or paused videos. You can copy, translate, or look up words directly from a picture, without leaving Safari.
Built-in Translation
Safari can instantly translate entire web pages into different languages. It can even translate text found within images or paused videos.
Quick Note
The "Quick Note" feature lets you quickly write down ideas or thoughts while you are browsing. These notes are saved directly into your Notes app.
Passkeys for Secure Login
Safari now supports "Passkeys." These are a new way to log into websites without needing a password. They are very secure and help protect you from online scams. Passkeys sync safely across your devices.
Highlights
"Highlights" is a smart feature that uses machine learning. It automatically finds and shows you important information on a web page, like summaries or related links. This helps you discover more content easily.
Link Tracking Protection
Safari helps protect your privacy by removing special tracking codes from web links when you share them. This stops other websites from following your online movements. This feature is on by default in apps like Messages and Mail, and in Private Browsing mode.
How Safari Works
Safari is built using Apple's WebKit engine. WebKit is made of two main parts: WebCore and JavaScriptCore. WebCore helps display web pages, and JavaScriptCore helps run the code that makes websites interactive. These parts are open-source, meaning their code can be seen and used by others.
Newer versions of Safari use something called WebKit2. This means that the part of Safari that shows web content runs separately from the main application. If a website crashes, it's less likely to crash the entire browser.
Safari on Other Devices
iPhones and iPads
Safari was first released for the original iPhone in 2007. People really liked it because it was much better than other mobile browsers at the time. Safari is also available on iPadOS devices. On iPads, Safari often shows websites as if you were on a desktop computer. It also has features like a download manager and support for extensions.
Apple Vision Pro
A special version of Safari was released for the Apple Vision Pro headset in 2024. This version lets you move browser windows around in a virtual space. Many people found this feature very impressive.
Windows Computers
Apple released Safari for Windows XP and Windows Vista in 2007. They wanted more people to use Safari. However, Apple stopped making Safari for Windows after version 5.1.7 in 2012 because not enough people used it.
Safari's Popularity
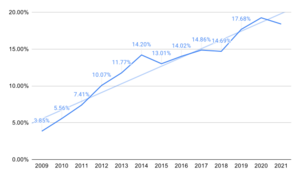
Safari has grown in popularity over the years. In 2009, it had a small share of the web browser market. But by 2015, Safari became the second most-used web browser worldwide, right after Google Chrome. It has generally stayed in second place for many years. In May 2022, Safari briefly dropped to third place for desktop browsers, but it quickly moved back to second place a year later.
| Desktop/laptop browser statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google Chrome | 69.68% | |||
| Microsoft Edge | 11.80% | |||
| Safari | 6.51% | |||
| Mozilla Firefox | 5.32% | |||
| Opera | 2.20% | |||
| Other | 4.48% | |||
| Desktop web browser market share according to StatCounter for July 2025. | ||||
See also
 In Spanish: Safari (navegador) para niños
In Spanish: Safari (navegador) para niños
- List of web browsers
- History of web browsers