Microsoft Windows facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Windows |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
Windows 11, the latest release of Windows
|
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
| Source model |
|
| Initial release | November 20, 1985 |
| Latest release | 23H2 (10.0.22631.3737) (June 11, 2024 ) [±] |
| Latest preview |
24H2 (10.0.26100.712) (May 22, 2024 )
23H2 (10.0.22635.3720) (June 7, 2024 )
24H2 (10.0.26120.770) (June 7, 2024 )
|
| Repository |
|
| Marketing target | Personal computing |
| Available in | 110 languages |
| Update method |
|
| Package manager | Windows Installer (.msi, .msp), App Installer (.msix,. msixbundle), Microsoft Store (.appx, .appxbundle), Windows Package Manager |
| Supported platforms | IA-32, x86-64, ARM, ARM64 Previously: 16-bit x86, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC, Itanium |
| Kernel type |
|
| Default user interface |
Windows shell |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
Windows is a group of computer programs made by Microsoft. These programs are operating systems, which means they control how your computer works. Windows uses a graphical user interface, so you interact with it using pictures, icons, and buttons, not just text.
The name "Windows" comes from the way programs appear on your screen. They show up in separate boxes, like little "windows." The first version, Windows 1.0, came out on November 20, 1985. It was an add-on for an older system called MS-DOS.
Over the years, Windows became very popular. It is the most used desktop operating system in the world. As of March 2023, about 70% of desktop computers use Windows. However, if you include phones and tablets, Android is more widely used.
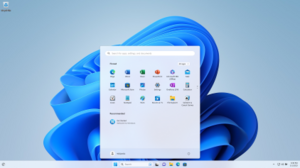
The newest version for home computers and tablets is Windows 11. For businesses, there's Windows 11 Enterprise. For powerful server computers, the latest is Windows Server 2025. As of July 2025, Windows 11 is the most common version of Windows installed on desktops, with 52.0% of the market.
Contents
Different Types of Windows
Windows is split into different groups, or "families," for various uses. The main family today is called Windows NT. This family started with Windows NT 3.1 in 1993. It was made for powerful servers and business computers. Now, it includes several types of Windows that share the same core system.
- Windows (for home and work computers): This is the Windows you probably know best. It's for personal computers and tablets. The latest version is Windows 11. Its main rivals are macOS from Apple and Linux.
- Windows Server: This version is made for server computers. Servers are powerful computers that manage networks and store data for many users. The newest version is Windows Server 2025. Linux is its main competitor.
- Windows PE: This is a small, lightweight version of Windows. It's used for special tasks like installing Windows on many computers at once, fixing problems, or recovering data.
- Windows IoT: (IoT stands for "Internet of Things"). This version is for small, specialized computers found in devices like smart home gadgets or industrial machines. The latest is Windows 11 IoT Enterprise. Linux also competes in this area.
Some older Windows families are no longer being developed:
- Windows 9x: This family was for home users. It included Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows Me. Windows Me was not very popular and was known for having many problems. These versions used MS-DOS as their base.
- Windows Mobile: This was an operating system for older mobile phones and PDAs.
- Windows Phone: This was made for smartphones. It was later replaced by Windows 10 Mobile, which is also no longer used.
- Windows Embedded Compact: Also known as Windows CE, this was for small devices with limited power and memory, like GPS systems.
How Windows Started
The idea for Windows began in 1981 at Microsoft. They were working on something called "Interface Manager." The name "Windows" was chosen because the system used graphical boxes, or "windows," to show programs.
Early Versions (1985-1988)
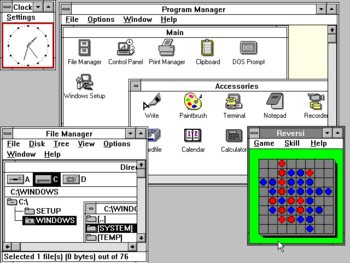
Windows 1.0 was released in November 1985. It wasn't a full operating system on its own. Instead, it added a graphical look to MS-DOS. It had basic tools like a calculator, calendar, and a simple drawing program. You couldn't overlap windows; they were all "tiled" next to each other.
Windows 2.0 came out in December 1987. It was more popular and allowed windows to overlap, which was a big improvement. This change even led to a lawsuit from Apple, who thought Microsoft copied their ideas, but Microsoft won.
Windows 2.1 was released in two versions: Windows/286 and Windows/386. These versions used different ways to manage computer memory, making them work better on different types of processors.
Even these early versions of Windows did more than just add a graphical look. They had their own ways of running programs and managing devices like printers and mice. They also allowed users to run several programs at the same time.
Windows 3.x (1990-1994)
Windows 3.0, released in 1990, was a huge success. It improved how Windows used memory and allowed programs to run more smoothly. It also had a better-looking user interface. Microsoft sold 2 million copies in just six months!
Windows 3.1 came out in 1992 with a refreshed look. A special version, Windows for Workgroups, added features for computers to connect and share files easily.

Windows 9x (1995-2000)
The next big release for home users was Windows 95, on August 24, 1995. It was still based on MS-DOS but brought many new features. It could run newer, more powerful programs and made it easier to connect new hardware (called "plug and play"). Windows 95 also introduced the Start menu, taskbar, and Windows Explorer, which are still part of Windows today. It was a massive success.
Windows 98 followed on June 25, 1998. It added support for USB devices, hibernation, and using multiple monitors. An updated version, Windows 98 Second Edition, came out in 1999.
On September 14, 2000, Microsoft released Windows Me (Millennium Edition). This was the last Windows version based on DOS. It had some new features for multimedia and system recovery, but many people found it slow and unstable. PC World magazine even called it one of the worst tech products ever.
Windows NT Family (1993-Present)
The Windows NT family was designed to be more powerful and secure than the DOS-based Windows versions.
Early NT Versions (1993-2000)
Work on Windows NT began in 1988. It was meant to be a very secure system that could handle many users and different types of computer processors. The first release, Windows NT 3.1, came out in July 1993.
Later versions like Windows NT 3.5, Windows NT 3.51, and Windows NT 4.0 improved performance and added features. Windows NT 4.0 even brought the new look of Windows 95 to the NT series. On February 17, 2000, Microsoft released Windows 2000, which was a big step forward for business computers.
Windows XP (2001)

Windows XP was a major release on October 25, 2001. It combined the home-user focus of Windows 9x with the powerful NT architecture. Windows XP had a fresh new look, improved multimedia features, and better networking. It also included a "compatibility mode" to help older programs run.
Windows XP came in "Home" and "Professional" editions. There were also special versions like "Media Center" for home theater PCs and "Tablet PC" for tablets. Windows XP was very popular and supported for a long time, with extended support ending in April 2014.
Windows Vista (2007)
After a long development, Windows Vista was released to the public on January 30, 2007. It had many new features, including a redesigned look and a strong focus on security. However, it also received some criticism for being slow and having strict user account controls.
Windows 7 (2009)
Windows 7 was released on October 22, 2009. Unlike Vista, it was designed to be a smaller, more focused update. It aimed to be more compatible with existing programs and hardware. Windows 7 added multi-touch support, an improved taskbar, and a new home networking system called HomeGroup.
Windows 8 and 8.1 (2012-2013)
Windows 8 came out on October 26, 2012. It brought big changes, especially for touch-based devices like tablets. It introduced the Start screen with large, colorful "tiles" that showed live information. It also had a new type of app designed for touchscreens.
An update, Windows 8.1, was released on October 17, 2013. It added new tile sizes and better integration with OneDrive (Microsoft's cloud storage). Some users criticized Windows 8 for removing the traditional Start menu.
Windows 10 (2015)
Windows 10 was announced on September 30, 2014, and released on July 29, 2015. It brought back the familiar Start menu and allowed Windows Store apps to run in windows on the desktop. Windows 10 was offered as a free upgrade for many users of Windows 7 and 8.1.
Microsoft announced that support for the last version of Windows 10 will end on October 14, 2025.
Windows 11 (2021)
Windows 11 was announced on June 24, 2021, and released on October 5, 2021. It was designed to be more user-friendly and easier to understand. Windows 11 is a free upgrade for Windows 10 users whose computers meet the system requirements.
Windows 365 (2021)
In July 2021, Microsoft launched Windows 365. This service lets people use a virtual Windows computer over the internet. It's like having Windows running in the "cloud." You can access it from any device with a web browser, even Apple or Android devices. This service is helpful for businesses that have employees working from home or in different locations.
Multilingual Support
Windows has supported many languages since Windows 3.0. You can change the language for your keyboard and the entire Windows interface. Microsoft offers "Language Interface Packs" (LIPs) that translate most of Windows, and "Full Language Packs" that translate everything.
Windows 8 and later versions made it easier to change languages and download language packs from one central place.
Platform Support
Windows NT was originally designed to work on different types of computer processors, not just the common x86 ones. Over time, it focused more on x86 processors.
In 2005, Microsoft released 64-bit versions of Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to support the newer x64 architecture. Today, x64 is the main architecture for Windows.
Windows also has versions for ARM processors, which are often found in mobile devices. Windows RT was an early ARM version for tablets, and newer Windows 10 and 11 versions also support ARM-based PCs.
How Windows is Developed
For a long time, Microsoft used its own system called Source Depot to manage the Windows code. But as Windows grew, this system became too big to handle.
In 2017, Microsoft started using Git, an open-source system created by Linus Torvalds. Git helps large teams work on code together more efficiently. Because the Windows code is so huge, Microsoft developed special tools like VFSForGit (now called Scalar) to make Git work well with it.
Windows Usage Around the World
Windows is the most used operating system for desktop and laptop computers. In August 2021, it had about 76% to 91% of the market share for these devices.
However, if you include all types of personal computers, like phones and game consoles, Windows has a smaller share. In August 2021, Android was the most used, followed by iOS/iPadOS, and then Windows. These numbers usually come from tracking which operating systems are used to browse the internet.
Keeping Windows Safe
Older versions of Windows were not designed with strong security in mind. They didn't have features to stop different users from accessing each other's files or to protect important system memory. This made them more vulnerable to malware like viruses.
The Windows 9x versions, while allowing different user profiles, didn't truly protect files from other users. Also, a faulty program could crash the entire system.
Windows NT and its later versions were much more secure. They added features like access privileges and full memory protection. However, before Windows Vista, the main user account was often an "administrator" account. This meant that the user, and any program they ran, had full control over the computer. This made it easier for viruses to cause damage.
In 2002, Bill Gates, the founder of Microsoft, made security a top priority.
Windows Vista introduced User Account Control (UAC). This system asks for your permission before a program can make big changes to your computer. Even if you're an administrator, programs usually run with limited permissions until you approve them. This helps protect your computer from harmful software.
Microsoft regularly releases security updates for Windows, usually once a month. These updates fix problems and help keep your computer safe. Windows also includes built-in security tools like Windows Defender antivirus, a firewall, and features to protect against ransomware.
In July 2024, Microsoft announced plans to make Windows even more secure by limiting how much access programs have to the core system. They are also rewriting parts of Windows using a safer programming language called Rust.
File Permissions
All Windows NT versions use a system called AGDLP to manage file permissions. This system helps control who can access and change files and folders on a computer, especially in a network with many users. It makes it easier to manage permissions for groups of users without having to change each file individually.
Other Ways to Run Windows Programs
Because Windows is so popular, other software has been created to help run Windows programs on different operating systems.
- Wine: This is a free program that lets you run many Windows applications on Linux and macOS. It works by acting like Windows, so programs think they are running on a Windows computer.
- CrossOver: This is a commercial version of Wine that includes licensed fonts and extra support.
- Proton: This is a version of Wine made by Valve (a game company) specifically for running Windows games on Linux.
- ReactOS: This is an open-source operating system that aims to work just like Windows. It has been in development since 1996.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Microsoft Windows para niños
In Spanish: Microsoft Windows para niños