Seward Peninsula facts for kids
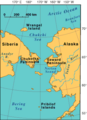
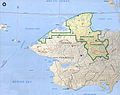
The Seward Peninsula is a large piece of land that sticks out from the western coast of Alaska. It reaches about 320 kilometers (200 miles) into the Bering Sea. This area is just below the Arctic Circle, a very cold part of the world. The peninsula is about 330 kilometers (205 miles) long and 145 to 225 kilometers (90 to 140 miles) wide.
It's interesting to know that the town of Seward, Alaska is not actually on the Seward Peninsula! That town is much further south on a different piece of land called the Kenai Peninsula.
Long, long ago, the Seward Peninsula was part of something called the Bering land bridge. This was a strip of land that connected Alaska with Siberia (in Russia) millions of years ago during the Pleistocene Ice Age. People, animals, and plants used this land bridge to cross into North America. Archaeologists have found proof that the Inupiat Eskimos have lived here for thousands of years.
Contents
Who Lives on the Seward Peninsula?
Not many people live on the Seward Peninsula today. There are no roads that connect it to other parts of Alaska. The biggest town is Nome, which has about 3,000 people. The next largest town, Shishmaref, has fewer than 600 people. Most other towns have only a few hundred residents. Some old mining towns are now completely empty, becoming ghost towns.
Land and Nature of the Seward Peninsula
The Seward Peninsula has some unique natural features. For example, the Devil Mountain Lakes are here. These lakes are special because they are maars, which means they were formed by volcanoes. The Devil Mountain Lakes are the biggest lakes of this type in the entire world!
There are four mountain ranges on the peninsula. The largest ones are the Kigluaik (also called Sawtooth) Mountains. The highest point on the peninsula is Mount Osborn, which is 1,437 meters (4,714 feet) tall. Other mountain ranges include the Bendeleben Mountains, Darby Mountains, and York Mountains. You can also find a large lava flow called The Lost Jim Lava Flow and several hot springs across the peninsula.
Rivers and Their Importance
The Seward Peninsula has many rivers. These rivers are very important to the people who live there. One reason is that people can catch fish in them for food. Another reason is that people use boats to travel on the rivers because there are no roads. This helps them get to other towns or to places where they can hunt animals. Finding food is very important because there aren't many stores, and it costs a lot to bring food in by airplane or boat. In the winter, these rivers freeze over.
Plants and Westernmost Point
The most common type of tree on the peninsula is the Black spruce, which is a kind of pine tree.
The Cape Prince of Wales is also on the peninsula. This cape is the westernmost point of mainland North America. It is only 84 kilometers (52 miles) away from Russia!
The peninsula was named after William H. Seward. He was the United States Secretary of State who arranged for the United States to buy Alaska from Russia in 1867.
Images for kids
-
Map of Beringia showing the Seward Peninsula.
See also
 In Spanish: Península de Seward para niños
In Spanish: Península de Seward para niños