Sippar facts for kids
|
Sippar
|
|
| [[File::None at this time|frameless]] | |
| Lua error in Module:Location_map at line 420: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). | |
| Location | Baghdad Governorate, Iraq |
|---|---|
| Region | Mesopotamia |
| Type | settlement |
| History | |
| Periods | Early Dynastic, Old Babylonian, Kassite, Neo-Assyrian, Neo-Babylonian |
| Site notes | |
| Excavation dates | 1880-1881, 1894, 1972-1973, 1977-present |
| Archaeologists | Hormuzd Rassam, Jean-Vincent Scheil, H. Gasche, Walid al-Jadir |
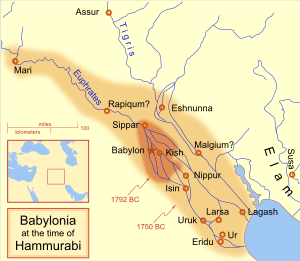
Sippar was an ancient city in Mesopotamia, a region in the ancient Near East. It was located on the east bank of the Euphrates river. Today, its ruins are found at a place called Tell Abu Habbah in Iraq. This is about 69 kilometers (43 miles) north of Babylon and 30 kilometers (19 miles) southwest of Baghdad.
Sippar was often linked with another city, Sippar-Amnanum, which was on the other side of the Euphrates river. Sometimes, Sippar was called Sippar-Yaḫrurum to tell it apart from its sister city. This name came from the Yaḫrurum tribe who lived there.
Contents
Sippar's Ancient History
Even though thousands of cuneiform clay tablets have been found at Sippar, we still don't know everything about its long history. Like many cities in Mesopotamia, Sippar was part of a pair, with its sister city, Sippar-Amnanum, on the opposite side of the river.
Ancient lists of kings, like the Sumerian king list, mention a ruler named En-men-dur-ana from Sippar. He is listed as one of the very early kings before the main dynasties began.
Important Time Periods
Archaeologists have found pottery that shows people lived at Sippar as early as the Uruk period. However, the city really grew and became important during these times:
- The Early Dynastic Period (around 3000-2350 BC)
- The Old Babylonian and Kassite periods (around 2000-1155 BC)
- The Neo-Babylonian period (around 626-539 BC)
People continued to use the site, but less intensely, during the later Persian, Greek, and Parthian empires.
Gods and Temples
Sippar was a very important religious center for the sun god. In Sumerian, he was called Utu, and in Akkadian, he was called Shamash. His wife, Aya, was also worshipped there.
The main temple in Sippar was called E-babbara, which means "white house." This is where a special stone monument called the Cruciform Monument of Manishtushu was found. Other goddesses also had temples in Sippar, including Mamu (Shamash's daughter), Nin-Isina, Ninḫegal, Ninkarrak, and Tašmētum.
Sippar's Role in Ancient Times
During the early Babylonian dynasties, Sippar was known for making wool. It's also believed that the famous Code of Hammurabi stone pillar was set up in Sippar. Shamash, the sun god, was also the god of justice. On top of the Code of Hammurabi pillar, Shamash is shown giving power to the king. This idea was also seen on small stone cylinder seals made in Sippar. By the end of the 19th century BC, Sippar was creating some of the best Old Babylonian cylinder seals.
Kings like Sumu-la-El and Hammurabi of Babylon worked on building and repairing Sippar's city walls. These walls, usually made of mud bricks, needed a lot of care. Later kings, Nebuchadnezzar II and Nabonidos, also repaired the great Shamash temple, E-babbara.
Some people think Sippar might be the city of Sepharvaim mentioned in the Old Testament of the Bible. The name Sepharvaim sounds like it refers to two parts of a city, which fits Sippar and Sippar-Amnanum.
Digging Up the Past

The ruins of Sippar, known as Tell Abu Habba, cover more than one square kilometer. The first major excavations were done by Hormuzd Rassam between 1880 and 1881. He worked for the British Museum and found tens of thousands of clay tablets, including the famous Tablet of Shamash in the temple of Shamash. Most of these tablets were from the Neo-Babylonian period.
Many of the tablets found by Rassam are still being studied today at the British Museum. In the early days of archaeology, detailed records of where things were found were not always kept. This makes it hard to know if some tablets came from Sippar or its sister city, Sippar-Amnanum. Many other tablets from Sippar were also bought by museums around the world. Because the site is close to Baghdad, it was often targeted by people digging illegally.
In 1894, Jean-Vincent Scheil also worked at Sippar for a short time. The tablets he found, mostly from the Old Babylonian period, are now in the Istanbul Museum.
More recently, archaeologists from Belgium worked at Sippar in the 1970s. They found that Sippar was protected by a large wall, about 1200 meters (3,900 feet) long and 800 meters (2,600 feet) wide. This wall helped protect the city from floods. Iraqi archaeologists from the University of Baghdad have been digging at Tell Abu Habbah since 1977. They found a library with over 300 tablets! After 2000, the German Archaeological Institute joined the work.
The famous Babylonian Map of the World tablet was also found in Sippar.
Gallery
See also
- List of cities of the ancient Near East
- Cylinders of Nabonidus
- Nadītu in Sippar