Six-Day War facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Six-Day War |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Arab–Israeli conflict | |||||||||
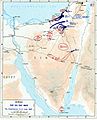
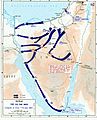
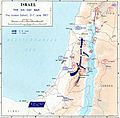
 Map of the military movements and territorial changes during the Six-Day War. The territory of Israel before the war is colored royal blue on this map, while the territories captured by Israel during the war are depicted in light blue. |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
Minor involvement: |
|||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
|
50,000 troops 100,000 deployed |
Egypt: 240,000 240,000 deployed |
||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
776–983 killed 400 tanks destroyed 46 aircraft destroyed |
Egypt: 10,000–15,000 killed or missing Hundreds of tanks destroyed 452+ aircraft destroyed |
||||||||
| 20 Israeli civilians killed 34 US Navy, Marine, and NSA personnel killed 17 Soviet Marines killed (allegedly) |
|||||||||
The Six-Day War was a short but important war that happened from June 5 to June 10, 1967. It was fought between Israel and a group of Arab countries: Egypt, Jordan, and Syria. Other countries also played smaller roles. This war is a key part of the larger Arab–Israeli conflict.
Contents
Why the War Started
The war began because of growing tensions in the Middle East. Egypt, led by President Gamal Abdel Nasser, took actions that Israel saw as a direct threat.
Rising Tensions
- Egypt blocked the Straits of Tiran, which is a very important waterway for Israel's ships. This was like closing a main road for a country.
- Egypt also sent many of its soldiers and military equipment into the Sinai Peninsula, which is right next to Israel.
- Egypt asked the United Nations (UN) peacekeeping forces to leave the area, which they did.
- Syria supported groups like the Fedayeen, who sometimes crossed into Israel.
These actions made Israel believe that Egypt and its allies were planning an attack. At the same time, Arab leaders openly talked about wanting to destroy Israel. Israel then moved its own troops to its borders with Syria, Egypt, and Jordan to prepare for any attack.
How the War Unfolded
The war lasted only six days, which is how it got its name. It started with a surprise attack by Israel.
The Surprise Air Attack
On June 5, 1967, Israel launched a surprise air attack against Egypt. This was a "preemptive strike," meaning they attacked first to prevent an expected attack on themselves.
- Israel targeted Egyptian airfields while most of Egypt's planes were still on the ground.
- In just a few hours, nearly all of Egypt's air force was destroyed. This was a huge blow to Egypt.
- Israel had about 300 attack planes, while Egypt had around 960. But Israel's pilots and ground crews were very well-trained. They could refuel and rearm their planes much faster than the Arab air forces. This allowed Israel to send many waves of attacks.
Ground Battles and Victories
After crippling Egypt's air force, Israel attacked on the ground.
- Even though Syria and Jordan then attacked Israel, Israel managed to defeat them both.
- The Israeli army had about 264,000 soldiers, including reserves. Egypt had around 100,000 soldiers in the Sinai, and with Syria, Jordan, and Iraq, the Arab forces had over 500,000 troops in total.
After the War
The Six-Day War had a big impact on the Middle East.
New Territories
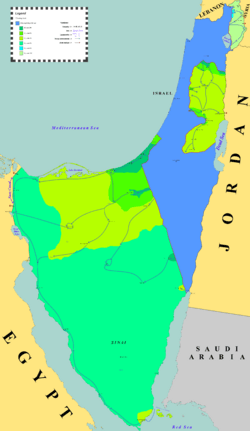
Israel gained control of several important areas:
- The Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula from Egypt.
- The West Bank (including East Jerusalem) from Jordan.
- The Golan Heights from Syria.
These lands were very important for Israel's safety and also had historical meaning.
Lasting Impact
- The war led to the 1973 Yom Kippur War, where Egypt tried to take back the Sinai.
- Eventually, Israel returned the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt as part of a peace treaty.
- However, Israel kept the lands it gained from Jordan and Syria.
- The United Nations asked Israel to go back to the borders it had before 1967 and to help create an Arab-Palestinian state.
- Talks and occasional fighting continued for many years after the war.
Military Forces and Equipment
Both sides had large armies and different types of weapons.
Armies and Soldiers
- Israel had about 264,000 soldiers, including many who were called up from reserve duty. About 40,000 of these troops were actively fighting.
- Egypt had around 100,000 soldiers in the Sinai region alone. Many of these soldiers had experience from other conflicts.
- Combined, Egypt, Syria, Jordan, and Iraq had a much larger number of soldiers, totaling over 500,000.
Weapons Used
- Most Arab countries, except Jordan, used weapons from the Soviet Union.
- Jordan's army used American weapons, and its air force had British planes.
- Egypt had the largest and most modern air force among the Arab nations. It had about 420 combat aircraft, including advanced MiG-21 jets.
- Israel mainly used French-built aircraft for its air force.
Images for kids
-
On 22 May 1967, President Nasser addressed his pilots at Bir Gifgafa Airfield in Sinai: "The Jews are threatening war—we say to them ahlan wa-sahlan (welcome)!"
-
Dassault Mirage at the Israeli Air Force Museum. Operation Focus was mainly conducted using French built aircraft.
-
Major General Ariel Sharon during the Battle of Abu-Ageila
-
David Rubinger's photograph of IDF paratroopers at Jerusalem's Western Wall shortly after its capture. The soldiers in the foreground are (from left) Zion Karasenti, Yitzhak Yifat, and Haim Oshri.
-
From left, General Uzi Narkiss, Defense Minister Moshe Dayan, and Chief of Staff Lt. General Yitzhak Rabin in the Old City of Jerusalem after its fall to Israeli forces
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra de los Seis Días para niños
In Spanish: Guerra de los Seis Días para niños