Spirula facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Spirula |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
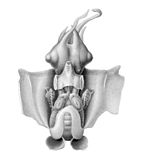
| Dorsal view of female | |
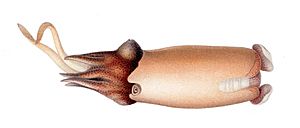 |
|
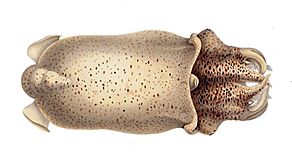
| Ventral view of female (chromatophores of mantle missing) |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Cephalopoda |
| Order: | Spirulida |
| Family: | Spirulidae Owen, 1836 |
| Genus: | Spirula Lamarck, 1799 |
| Species: |
S. spirula
|
| Binomial name | |
| Spirula spirula (Linnaeus, 1758)
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
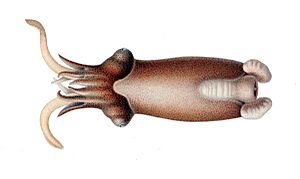
The Spirula spirula is a special type of deep-water creature. It's a cephalopod, which means it's related to squids and octopuses. This animal is the only living member of its group, the Spirula genus, the Spirulidae family, and the Spirulida order.
People often call it the ram's horn squid or the little post horn squid. This is because of the unique shape of its shell inside its body. It's also sometimes called the tail-light squid because it can make its own light.
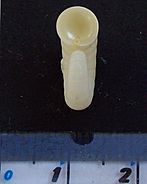
It's very rare to see a live Spirula spirula because they live deep in the ocean. However, their small, light shells are often found by beachcombers (people who walk along beaches looking for interesting things). These shells are super light and float easily. They are also very strong, so they often wash up on tropical beaches all over the world. Sometimes, they even reach colder beaches. Shell collectors know this seashell as the ram's horn shell or just Spirula.
Contents
What Does the Ram's Horn Squid Look Like?
The Spirula spirula has a body that looks a bit like a squid. It is usually between 35 and 45 millimeters long. That's about the size of a small paperclip!
Arms and Tentacles
Like other decapods, it has eight short arms and two longer tentacles. All of these have suckers, which help the squid grab things. The amazing thing is that it can pull all its arms and tentacles completely inside its mantle, which is its main body part.
The Special Shell
The most unique part of the Spirula spirula is its special shell. This shell is inside its body and helps it float. It's shaped like a flat spiral, almost like a ram's horn, and the coils don't touch each other. This shell helps the squid control how much it floats in the water. It's also made of minerals, which is something only seen in cuttlefish and nautiluses among living species.
How Does the Ram's Horn Squid Behave?
The Spirula spirula can make a green light! It has a special organ called a photophore at the very tip of its mantle, between its ear-shaped fins. This light helps it hide from predators. It points the light downwards while swimming upright, making it harder for creatures below to see its shadow against the dim light from the surface. This is called counter-illumination.
Where Does the Ram's Horn Squid Live?
During the day, Spirula lives in very deep parts of the ocean, sometimes as deep as 1,000 meters (about 3,300 feet). At night, it swims up closer to the surface, usually between 100 and 300 meters deep. It likes water that is around 10°C (50°F). It often lives near oceanic islands and close to the edge of continents.
Most people think this species lives in tropical areas. They are very common in the subtropical seas around the Canary Islands. Their shells are often found along the western coasts of South Africa. However, many shells from dead Spirula also wash up on beaches in colder places, like New Zealand. Because the shells float so well, ocean currents can carry them very far.
Scientists still don't know much about the life of the Spirula spirula. For example, they think the squid lays its eggs in winter in deep water, but no one has ever seen the baby squid directly. We know they must sometimes swim closer to the surface because they have been found in the stomachs of albatrosses, which are seabirds.
The first time a live Spirula was seen in its natural home was in 2020. A special underwater robot from the Schmidt Ocean Institute filmed it deep near the northern Great Barrier Reef.
Who Are the Ram's Horn Squid's Relatives?
The group Spirulida also includes two types of squid that are now extinct. These are the Groenlandibelina and Belopterina.
The Spirula is probably the closest living relative to the extinct belemnites and aulacocerids. These three groups are also closely related to cuttlefish and the true squids we know today.
Images for kids
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |