Local government in Wales facts for kids
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. To help manage things locally, Wales is divided into 22 main areas. These are called principal areas. Since April 1, 1996, these areas have their own elected councils. These councils are in charge of important services for people living there. This includes things like schools, social work, protecting the environment, and maintaining most roads.
Some of these principal areas are called counties, others are county boroughs, and some are cities or city and county. Even though they have different names, many people, including the BBC, often just call all 22 of them "counties."
The King or Queen of Britain also appoints a special person called a Lord Lieutenant for each of the eight preserved counties of Wales. These preserved counties are groups of principal areas used for special events and ceremonies.
Also, some services like the police, emergency services, and the National Health Service are organized by grouping several principal areas together. For example, the Dyfed-Powys Police force covers the areas of Powys, Pembrokeshire, Ceredigion, and Carmarthenshire.
Contents
Cities in Wales
Wales has six cities in total. Three of these cities are also principal areas: Cardiff, Swansea, and Newport. The other three cities are smaller communities: Bangor, St David's, and St Asaph. A place gets city status through a special official document called a letters patent.
Here are the cities and when they became cities:
- Bangor – The exact date is not known, but it's very old.
- Cardiff – 1905
- Swansea – 1969
- St David's and the Cathedral Close – 1994
- Newport – 2002
- St Asaph – 2012
St Asaph was historically called a city because it had a bishop's seat. However, this status wasn't officially recognized for many years. When St David's got its city status back in 1994, St Asaph tried too. But they were told there was no old document proving their city status. After trying again in 2000 and 2002, St Asaph finally became a city in 2012. This happened as part of the Queen's Diamond Jubilee celebrations. It was chosen because of its rich history, cultural importance, and its role as a center for technology and business.
Principal Areas of Wales
There are 22 main areas in Wales that manage local government. They were created on April 1, 1996, by a law called the Local Government (Wales) Act 1994.
Eleven of these areas are called counties. This includes the Cities and Counties of Cardiff and Swansea. The other eleven are called county boroughs. In 2002, Newport became a city, so its county borough is now called the "City of Newport."
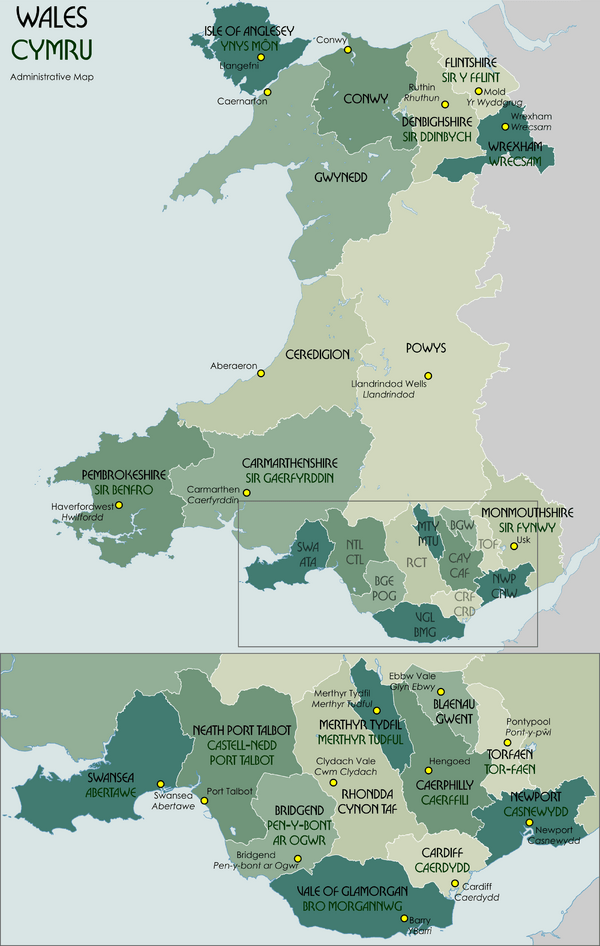 |
|
| Areas are Counties, unless marked * (for Cities) or † (for County Boroughs). Welsh-language forms are given in parentheses, where they differ from the English. | |
Changes to Names
Some of the principal areas have different names now than when they were first created. These changes happened on April 2, 1996:
- Conwy used to be called Aberconwy and Colwyn.
- Isle of Anglesey was simply Anglesey.
- Gwynedd was Caernarfonshire and Merionethshire.
- Ceredigion was Cardiganshire.
- Neath Port Talbot was Neath and Port Talbot.
Preserved Counties of Wales
Wales is also divided into 8 "preserved counties." These are used for special ceremonial duties, like when the King or Queen's representative visits. These preserved counties are based on older county divisions that existed between 1974 and 1996.
Historic Counties of Wales
Wales has even older divisions called historic counties. These have been used for different purposes for hundreds of years. The very first ones appeared around 1138.
By 1066, all of England was divided into counties, but Wales didn't have any until the 13th century. The first two Welsh counties, Cardiganshire and Carmarthenshire, were set up in the 1240s. Later, in 1284, the area of Gwynedd was divided into three counties: Anglesey, Caernarvonshire, and Merionethshire. This was an arrangement made by the English during the time of Prince Llywelyn II. Before the end of that century, Flintshire also became a county. This meant nearly half of Wales was under English rule.
The creation of counties was finished in 1536 with the Act of Union. This act created Pembrokeshire, Montgomeryshire, Denbighshire, Radnorshire, Glamorganshire, Brecknockshire, and Monmouthshire. These 13 counties were the main administrative divisions of Wales from 1889 until 1974.
Local Communities
At the smallest level of local government in Wales are the communities. Each principal area is divided into these communities. Many communities have elected community councils. These councils do things like provide local facilities and speak for their community to the larger local government bodies. Community councils are similar to parish councils in England. A community council can even call itself a "town council" if it wants to. The councils for the cities of Bangor, St Asaph, and St David's and the Cathedral Close are called "city councils." If a community is too small for a council, it might have a community meeting instead. This is a way for people to make decisions directly.
Proposed Changes to Local Government
For a while, there have been discussions about changing how local government is organized in Wales.
Williams Commission Report
In April 2013, a big review was started to look at how local government in Wales worked. A group called the Commission on Public Service Governance and Delivery was set up, led by Sir Paul Williams. The First Minister, Carwyn Jones, said that public money was getting tighter, and there was a need to find ways to keep services going and improve them.
The Commission released its report on January 20, 2014. It suggested that the number of councils should be reduced from 22 to 10, 11, or 12. This would happen by merging existing councils. The report believed that the money saved from these mergers would cover the costs of merging within about two years.
First Minister Carwyn Jones said that change was "inevitable and essential" to make public services more efficient and effective. Other politicians also shared their thoughts, agreeing that improvements were needed for the people of Wales.
Draft Local Government Bill
Following the Williams Commission's ideas, the Welsh Government published a draft law in November 2015. This draft law suggested two ways to reduce the number of local authorities: one with eight authorities and one with nine. The only difference between the two plans was how North Wales would be divided. The law didn't give names to the new authorities, just listed them as combinations of the current principal areas. The area of Powys was not affected by either proposal. These changes were planned to happen by April 2020.
Eight Local Authorities Model
| Proposed local authority | Proposed area |
|---|---|
| County 1 | Anglesey, Gwynedd, Conwy |
| County 2 | Denbighshire, Flintshire, Wrexham |
| County 3 | Ceredigion, Pembrokeshire, Carmarthenshire |
| County 4 | Swansea, Neath Port Talbot |
| County 5 | Bridgend, Rhondda Cynon Taff, Merthyr Tydfil |
| County 6 | Cardiff, Vale of Glamorgan |
| County 7 | Monmouthshire, Blaenau Gwent, Caerphilly, Torfaen and Newport |
| Powys | Powys |
Nine Local Authorities Model
| Proposed local authority | Proposed area |
|---|---|
| County 1 | Anglesey, Gwynedd |
| County 2 | Conwy, Denbighshire |
| County 3 | Flintshire, Wrexham |
| County 4 | Ceredigion, Pembrokeshire, Carmarthenshire |
| County 5 | Swansea, Neath Port Talbot |
| County 6 | Bridgend, Rhondda Cynon Taff, Merthyr Tydfil |
| County 7 | Cardiff, Vale of Glamorgan |
| County 8 | Monmouthshire, Blaenau Gwent, Caerphilly, Torfaen and Newport |
| Powys | Powys |
Changes in 2016
After the assembly elections in 2016, First Minister Carwyn Jones said that the plans for local government reform would be re-evaluated. A new agreement on how to change local government in Wales would be sought.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Organización territorial de Gales para niños
In Spanish: Organización territorial de Gales para niños