Tenpeak Mountain facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tenpeak Mountain |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 8,200 ft (2,500 m) |
| Prominence | 400 ft (120 m) |
| Isolation | 2.12 mi (3.41 km) |
| Parent peak | Luahna Peak |
| Geography | |
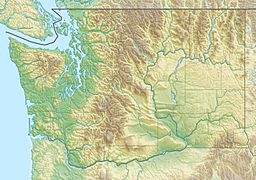
| Location | Glacier Peak Wilderness Washington, U.S. |
| Parent range | North Cascades Cascade Range |
| Topo map | USGS Glacier Peak East |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Cretaceous |
| Type of rock | granitic |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | 1940 |
| Easiest route | class 4 scrambling |
Tenpeak Mountain is a tall mountain in the Glacier Peak Wilderness area of the North Cascades in Washington state. It stands about 8,200 feet (2,500 meters) high and is made of a type of rock called granite.
This mountain sits right on the top of the Cascade Range. It is on the border between Snohomish County and Chelan County. It also divides two large forests: the Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest and the Wenatchee National Forest.
Tenpeak Mountain's closest taller neighbor is Luahna Peak, which is about 2.5 miles (4 km) away. The northern side of Tenpeak Mountain rises very steeply. It goes up 4,200 feet (1,280 meters) from the Suiattle Valley in just about 1.5 miles (2.4 km).
Small, unnamed glaciers hang in the bowl-shaped areas around the top of the mountain. The end of the Honeycomb Glacier is also found below the mountain's western side. Water from the mountain and melting glaciers flows south into the White River or north into the Suiattle River.
The climbing club called The Mountaineers suggested the name "Tenpeak." The U.S. Board on Geographic Names officially adopted it in 1918. The first people to climb to the top were Lloyd Anderson and Tom Campbell on September 21, 1940.
How Tenpeak Mountain Was Formed
The North Cascades mountains have very rugged shapes. You can see sharp peaks, long ridges, and deep valleys carved by glaciers. These amazing shapes were created by geological events that happened millions of years ago. These events also caused big changes in height across the Cascade Range, leading to different climates.
The Cascade Mountains started forming millions of years ago, during the late Eocene Epoch. At that time, the North American Plate was slowly moving over the Pacific Plate. This movement caused many volcanoes to erupt. Also, small pieces of the Earth's crust, called terranes, came together to form the North Cascades about 50 million years ago.
During the Pleistocene period, which began over two million years ago, large sheets of ice called glaciers moved across the land. They carved and shaped the mountains again and again. Glaciers were biggest about 18,000 years ago. Most valleys were free of ice by 12,000 years ago. The land rising up and cracks in the Earth's crust, along with the glaciers, created the tall peaks and deep valleys we see today.
Volcanic activity in this area began about 90 million years ago. A lot of volcanic eruptions started about 35 million years ago. Glacier Peak, a large volcano, began forming in the middle of the Pleistocene period. It is only about 4.4 miles (7.1 km) northwest of Tenpeak Mountain. Because Glacier Peak is so close, you can find volcanic ash all over the area.
Weather Around Tenpeak Mountain
Tenpeak Mountain is in a marine west coast climate zone. This means it gets a lot of moisture from the ocean. Most weather systems start over the Pacific Ocean. They then travel northeast towards the Cascade Mountains.
When these weather systems reach the North Cascades, the tall peaks force the air to rise. As the air goes up, it cools and drops its moisture. This process is called Orographic lift. Because of this, the western side of the North Cascades gets a lot of rain or snow. This is especially true during the winter months.
In winter, the weather is usually cloudy. But in summer, high-pressure systems over the Pacific Ocean become stronger. This often leads to clear skies with little or no clouds. Because of the ocean's influence, the snow tends to be wet and heavy. This can create a high risk of avalanches.
Images for kids
 | Chris Smalls |
 | Fred Hampton |
 | Ralph Abernathy |