Tokaido Shinkansen facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tokaido Shinkansen |
|
|---|---|
 |
|

A JR Central N700S Series train running Tokaido Shinkansen, September 2021
|
|
| Overview | |
| Native name | 東海道新幹線 |
| Status | Operational |
| Owner | |
| Locale | Tokyo, Kanagawa, Shizuoka, Aichi, Gifu, Shiga, Kyoto, and Osaka Prefectures |
| Termini | Tokyo Shin-Ōsaka |
| Stations | 17 |
| Color on map | Blue (#1153af) |
| Service | |
| Type | High-speed rail (Shinkansen) |
| System | Shinkansen |
| Services |
|
| Operator(s) | JR Central |
| Depot(s) | Tokyo, Mishima, Nagoya, Osaka |
| Rolling stock | N700A series N700S series |
| History | |
| Opened | October 1, 1964 |
| Technical | |
| Line length | 515.4 km (320.3 mi) |
| Number of tracks | Double-track |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge |
| Electrification | 25 kV 60 Hz AC (overhead catenary) |
| Operating speed | 285 km/h (177 mph) |
| Signalling | Cab signalling |
| Train protection system | ATC-NS |
| Maximum incline | 2.0% |
The Tokaido Shinkansen (東海道新幹線, Tōkaidō Shinkansen) is a famous Japanese high-speed rail line. It is part of the larger Shinkansen network, which means "new trunk line". This line connects two major cities: Tokyo and Shin-Ōsaka.
It first opened in 1964. This makes it Japan's very first high-speed rail line. It was also the first high-speed rail line in the entire world! Today, it is one of the busiest train lines anywhere. Since 1987, the Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central) has operated it.
There are three main types of trains on this line:
- Nozomi: This is the fastest train, making the fewest stops.
- Hikari: This train is semi-fast, stopping at more stations than the Nozomi.
- Kodama: This is the slowest train, stopping at every station.
Many Nozomi and Hikari trains continue their journey. They go onto the Sanyo Shinkansen line, reaching as far as Fukuoka's Hakata Station.
In 2000, this line was recognized as a special landmark. It was named a "Historic Mechanical Engineering Landmark" and an "IEEE Milestone". This shows how important its design and technology are.
Contents
How the Tokaido Shinkansen Started
The idea for a super-fast train between Tokyo and Shimonoseki began in the late 1930s. People called it a dangan ressha, which means "bullet train". This project was meant to be the first part of a large rail network in East Asia. However, World War II stopped these plans. But three tunnels were dug, and they were later used for the Shinkansen route.
By 1955, the regular Tokaido Line between Tokyo and Osaka was very crowded. Even after making it electric, it was still the busiest line in Japan. It had twice as many passengers as it could handle. In 1957, people discussed how to make the trip between Tokyo and Osaka in just three hours.
Japanese National Railways (JNR) decided to build a new, faster line. This new line would run next to the old one. Shinji Sogō, the president of JNR, worked hard to get politicians to support the project. He knew it would be very expensive. This was because it used new technology and needed many tunnels and bridges.
Building the Line
The Japanese government approved the plan in December 1958. They agreed to pay ¥194.8 billion for the project. The total cost was ¥300 billion over five years. Construction started on April 20, 1959.
In 1960, Sogō and chief engineer Hideo Shima went to the United States. They wanted to borrow money from the World Bank. They asked for US$200 million but only got $80 million. This was enough for about 15% of the project. This loan could not be used for "experimental technology."
The project cost more than expected. Because of this, both Sogō and Shima had to resign. The line was planned to open just before the 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo. This event brought a lot of international attention to Japan. At first, the line was called the New Tokaido Line in English. It was named after the old Tokaido road, which has been used for hundreds of years.
First Services and Speed Increases
When the line first opened, there were two types of trains. The faster Hikari (also called the Super Express) took four hours from Tokyo to Shin-Osaka. The slower Kodama (or limited express) made more stops and took five hours.
A test run happened on August 25, 1964. It was a Hikari service and was very successful. It was even shown on TV! On October 1, 1964, the line officially opened. The first train, Hikari 1, traveled from Tokyo to Shin-Osaka. Its top speed was 210 km/h (130 mph). By November 1965, the travel times were even faster. The Hikari took 3 hours, and the Kodama took 4 hours.
The 1970s were tough for JNR. Money from the Tokaido Shinkansen helped other train lines that were losing money. This meant the Shinkansen didn't get many upgrades for about 15 years. However, the loan from the World Bank was paid back in 1981.
In 1988, after JNR became a private company, JR Central started improving the line. They wanted to make trains go faster. This led to the new 300 Series trains. The Nozomi service started on March 14, 1992. It traveled the route in two and a half hours, reaching a top speed of 270 km/h (168 mph).
New platforms opened at Shinagawa Station in October 2003. This also brought a big change to the train schedule. More Nozomi trains ran each day than Hikari trains. From March 2008, all trains stopped at both Shinagawa and Shin-Yokohama.
The next speed increase happened on March 14, 2015. Trains now go up to 285 km/h (177 mph). This was possible thanks to better braking technology. At first, only one train per hour ran at this new speed. By March 2020, older trains were replaced with the N700 series. This allowed for more services to use the higher speed. An automated system is planned for the line by 2028. Tests for this system started in 2021.
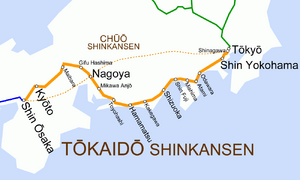
Stations and Train Services
Here is a guide to the symbols used in the station table:
| ● | All trains stop |
|---|---|
| ▲ | Some trains stop |
| | | All trains pass |
Here are the stations on the Tokaido Shinkansen line and what services stop at them:
| Station | Distance (km) | Service | Transfers | Location | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | Japanese | Nozomi | Hikari | Kodama | ||||
| Tokyo | 東京 | 0.0 | ● | ● | ● |
|
Chiyoda | Tokyo |
| Shinagawa | 品川 | 6.8 | ● | ● | ● | Minato | ||
| Shin-Yokohama | 新横浜 | 25.5 | ● | ● | ● | Kōhoku-ku, Yokohama | Kanagawa Prefecture | |
| Odawara | 小田原 | 76.7 | | | ▲ | ● | Odawara | ||
| Atami | 熱海 | 95.4 | | | ▲ | ● |
|
Atami | Shizuoka Prefecture |
| Mishima | 三島 | 111.3 | | | ▲ | ● | Mishima | ||
| Shin-Fuji | 新富士 | 135.0 | | | | | ● | Fuji | ||
| Shizuoka | 静岡 | 167.4 | | | ▲ | ● | Aoi-ku, Shizuoka | ||
| Kakegawa | 掛川 | 211.3 | | | | | ● | Kakegawa | ||
| Hamamatsu | 浜松 | 238.9 | | | ▲ | ● | Naka-ku, Hamamatsu | ||
| Toyohashi | 豊橋 | 274.2 | | | ▲ | ● | Toyohashi | Aichi Prefecture | |
| Mikawa-Anjō | 三河安城 | 312.8 | | | | | ● | Anjō | ||
| Nagoya | 名古屋 | 342.0 | ● | ● | ● | Nakamura-ku, Nagoya | ||
| Gifu-Hashima | 岐阜羽島 | 367.1 | | | ▲ | ● | TH Meitetsu Hashima Line (Shin-Hashima Station,TH09) | Hashima | Gifu Prefecture |
| Maibara | 米原 | 408.2 | | | ▲ | ● | Maibara | Shiga Prefecture | |
| Kyōto | 京都 | 476.3 | ● | ● | ● | Shimogyo-ku, Kyoto | Kyoto Prefecture | |
| Shin-Ōsaka | 新大阪 | 515.4 | ● | ● | ● | Yodogawa-ku, Osaka | Osaka Prefecture | |
| ↓ Through services towards Hakata via the |
||||||||
Types of Trains (Rolling Stock)
The Tokaido Shinkansen uses very modern trains.
- N700A series: These trains have 16 cars. They have been used since July 1, 2007. JR Central and JR West own them.
- N700A series: These are also 16-car sets. They started running on February 8, 2013. JR Central and JR West own these too.
- N700S series: These are the newest 16-car sets. They started running on July 1, 2020. JR Central owns them.
Since March 1, 2020, only N700A series or N700S series trains are used on the Tokaido Shinkansen.
Older Train Models
Over the years, many different types of trains have run on the Tokaido Shinkansen. Here are some of the older models:
- 0 series: These were the original Shinkansen trains. They ran from 1964 to 1999.
- 100 series: These trains ran from 1985 to 2003.
- 300 series: These were used from 1992 to 2012.
- 500 series: These trains ran from 1997 to 2010.
- 700 series: These were used from 1999 to March 2020.
Special Purpose Trains
- 923 (Set T4): This is a special train used to check the tracks and overhead lines. It's not for passengers.
-
JR Central's Class 923 "Doctor Yellow" set T4 on the Tokaido Shinkansen, September 2021
Train History Timeline
Train Classes and Services Onboard
All Tokaido Shinkansen trains have two main types of seating:
- Green Cars (First Class): These cars have very comfortable seats. There are two seats on each side of the aisle (2+2 layout). All seats in Green Cars must be reserved.
- Ordinary Cars: These cars have three seats on one side and two on the other (2+3 layout). You can find both reserved and unreserved seats here.
On all Shinkansen trains, you can buy snacks and drinks from vending machines in some cars. There is also a trolley service that comes through each car. It offers a wider selection of items. In Japan, it's common to buy food before you get on the train. Many stations sell Bento Boxes. These are complete meals packed in a box, perfect for eating on the train.
Since 2020, if you have large luggage, you need to reserve space for it on Tokaido Shinkansen trains.
Japan Rail Pass
The Japan Rail Pass is a special ticket for visitors from other countries. This pass can be used on Kodama and Hikari trains. Hikari trains are very similar to Nozomi trains in speed. The main difference is that Hikari trains make more stops.
How Many People Ride the Train?
The Tokaido Shinkansen is incredibly popular. From 1964 to 2012, about 5.3 billion passengers rode this line. That's a huge number!
In 1964, about 61,000 people rode the train each day. By 2012, this number grew to 391,000 people per day. In 2016, the line carried 452,000 passengers daily on 365 trains. This makes it one of the busiest high-speed railway lines in the world.
Here are some numbers showing how many people have ridden the Tokaido Line:
| Year | 1967 | 1976 | 2004 | Mar 2007 | Nov 2010 | 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ridership (Cumulative) | 100 | 1,000 | 4,160 | 4,500 | 4,900 | 5,300 |
Here are the yearly ridership numbers for the Tokaido Line:
| Year | 1967 | April 1987 | April 2007 | April 2008 | April 2009 | April 2010 | April 2011 | April 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ridership | 22 | 102 | 151 | 149 | 138 | 141 | 149 | 143 |
Future Plans for Stations
In June 2010, JR Central said they were thinking about a new Shinkansen station. It might be built in Samukawa, Kanagawa Prefecture. If it is built, it would open after the new maglev train service starts.
Shizuoka Prefecture has also asked JR Central for a station at Shizuoka Airport. The train line goes right under the airport. But the railway has said no so far. This is because there are already stations nearby, like Kakegawa and Shizuoka. If a station were built there, it would make travel from Tokyo to the airport faster. This could make it a third major airport for Tokyo. Since the station would be under an active airport, it would likely open after the new maglev line.
See also
 In Spanish: Tōkaidō Shinkansen para niños
In Spanish: Tōkaidō Shinkansen para niños
- Chuo Shinkansen, a new high-speed MagLev train line being built between Tokyo and Nagoya