Treaty of Bucharest (1812) facts for kids
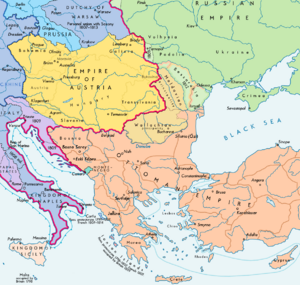
The Treaty of Bucharest was an important agreement signed between the Ottoman Empire and the Russian Empire. It was signed on May 28, 1812, in a place called Manuc's Inn in Bucharest. This treaty officially ended the Russo-Turkish War that had lasted from 1806 to 1812.
The Ottoman Empire had not done well in this war. Both empires wanted to end the fighting because a much bigger conflict was about to start: Napoleon's France was preparing to invade Russia. The Ottomans wanted to avoid being caught in that war. Russia also wanted peace so they could focus all their efforts on fighting France. The treaty helped the Ottomans avoid a much worse situation, even though they lost a small amount of land. This agreement then became the foundation for how Russia and the Ottoman Empire would deal with each other in the future.
Contents
Why the War Started
The Russo-Turkish War of 1806
This war began in 1806 between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire. It happened at the same time as the Napoleonic Wars were taking place across Europe.
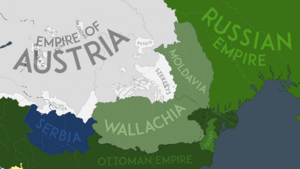
The French Empire encouraged the Ottoman ruler, Sultan Selim III, to remove some local leaders in Wallachia and Moldavia. These leaders were friendly with Russia, and Wallachia and Moldavia were states that were controlled by the Ottomans. At the same time, France also moved its armies into the Balkan Peninsula. This made Russia worried. To protect their borders from a possible French attack, Russia sent many soldiers into Moldavia and Wallachia. Because of this, the Sultan declared war on Russia.
Early Battles
At first, a large Ottoman army tried to attack Bucharest in Wallachia, which the Russians had taken over. But this attack failed. In Armenia, a few thousand Russian soldiers defeated about 20,000 Turkish troops. Russia also won a major naval battle, beating the Ottoman fleet. These early victories led to Sultan Selim III being removed from power. The Russians then completely destroyed the Ottoman fleet to control the seas.
In 1811, a top Ottoman commander named Ahmed Pasha gathered 60,000 Turkish soldiers in Bulgaria, which was controlled by the Ottomans. After a few months, they attacked the Russians. The Russians held them off long enough to retreat across the Danube River. The Turkish army chased them but were led into a trap and surrounded. Soon after these battles, Russia decided it was time to make peace.
How the Treaty Was Agreed Upon
The talks to make peace started in Bucharest on January 11, 1812. Important officials from both sides met to discuss the terms.
At first, Russia did not want to change its demands. They wanted to gain more land in the Balkans and Caucasus regions than the Ottomans wanted to give. Russia also wanted to control many Turkish ports and forts along the Black Sea and the Danube River.
This is when a British official named Stratford Canning came to Constantinople to help. Canning advised Russia to ask for less land in Europe and Asia. He warned that if the Ottomans were pushed too hard, they might become allies with France. However, France was actually trying to stop the peace agreement from happening.
In early May, Russia changed some of its demands, following Canning's advice. This helped the talks move forward. Finally, both sides signed the treaty in Manuc’s Inn, Bucharest, on May 28, 1812. The agreement was officially approved on July 5, 1812.
What the Treaty Said
Under the terms of the treaty:
- The Budjak area and the eastern part of the Principality of Moldavia were given to Russia. This land was between the Prut and Dniester Rivers and was known as Bessarabia. It was about 45,630 square kilometers (17,620 square miles). Moldavia had been a state controlled by the Ottoman Empire.
- Russia also gained the right to trade on the Danube River.
In the Transcaucasia region (near the Caucasus mountains):
- The Ottomans gave up their claims to most of western Georgia. They accepted that Russia had taken over the Kingdom of Imereti in 1810.
- In return, the Ottomans kept control of Akhalkalaki, Poti, and Anapa. Russian and Georgian troops had captured these places during the war.
Also, a ceasefire was agreed upon with the Serbian rebels. Serbia was given more freedom to govern itself.
The Treaty of Bucharest was signed by the Russian commander Mikhail Kutuzov. It was approved by Alexander I of Russia just 13 days before Napoleon's invasion of Russia began.
What Happened Later
On April 17, 2011, a group called Action 2012 was formed. This group supports the idea of Moldova and Romania becoming one country. The group was named "Action 2012" because the year 2012 marked 200 years since the Treaty of Bucharest was signed.
See also
- Bessarabian question
Sources
- Ismail, F. "The making of the treaty of Bucharest, 1811–1812," Middle Eastern Studies (1979) 15#2 pp 163–192 online.