Well facts for kids
A well is a hole dug into the Earth to reach water. People also dig wells to find crude oil or natural gas. Many cities that are not near fresh water lakes or rivers get their water from wells.
Wells have been made in different ways throughout history. Some are dug by hand, especially in rural areas. These are simple and use mostly people power. They can be lined with brick or stone. A newer way uses strong concrete rings that are lowered into the hole. Deeper wells are made using machines that drill into the ground with a special bit. Drilled wells usually have a pipe made of steel or plastic inside them. They can reach water much deeper than hand-dug wells.
Contents
History of Wells
The very first wells were found in the Eastern Mediterranean area during the Neolithic period (New Stone Age). The oldest well we know for sure is from Cyprus, around 8400 BC. It was a round shaft dug through limestone to reach water about 8 meters (26 feet) deep. Another well from the same place was 13 meters (43 feet) deep.
Wells lined with wood have been found from the early Neolithic period in places like the Czech Republic, Germany, and Austria, dating back to around 5200-5300 BC.
Ancient Chinese people also dug deep wells to get drinking water. A Chinese book called The Book of Changes, written a long time ago (around 1000 BC), talks about how to take care of wells. A well found at the Hemedu site is thought to be from the Neolithic era. It was lined with four rows of logs. Many other old wells, some made of tile, were found near Beijing and are believed to be from around 600 BC. They were used for drinking and watering crops.

In Egypt, people used tools like shadoofs and sakias to lift water. A sakia is much better, as it can bring water up from 10 meters (33 feet) deep, while a shadoof can only go about 3 meters (10 feet). The sakia is like the Egyptian version of a noria (a water wheel).
Wells for other uses came much later. The first known salt well was dug in China about 2,250 years ago. This was the first time people used well technology to get salt, starting China's salt drilling industry. The earliest known oil wells were also drilled in China in 347 CE. These wells were up to 240 meters (787 feet) deep and were drilled using bits attached to bamboo poles. The oil was used to boil brine (salty water) to make salt. By the 10th century, long bamboo pipes connected oil wells to salt springs.
Types of Wells
Dug Wells

For many centuries, all wells were dug by hand. They are still a very important way to get drinking water in some rural areas today.
Hand-dug wells are wide enough for one or more people to dig down to the water table (where the ground is full of water). The sides of the hole are supported to stop them from collapsing. They can be lined with stone or brick. Building a wall around the top of the well helps keep it clean and stops people from falling in.
A more modern way to make hand-dug wells uses strong concrete rings. These rings are lowered into the hole as people dig underneath them. This protects the workers from the sides of the well collapsing.
Hand-dug wells are cheap and simple to build. They use mostly manual labor to get water in developing countries. They can be dug as deep as 60 meters (200 feet). They are also cheap to use and maintain because water can be pulled out by hand, without a pump. If the water level drops, these wells can be made deeper.
However, hand-dug wells have some problems. It can be hard to dig them in areas with hard rock. They also take a long time to dig and line. Because they get water from shallow sources, the amount of water can change, and they can easily get dirty from surface water, like sewage. Digging them can also be dangerous because the well walls might collapse, objects might fall, or people might not get enough fresh air.
The Woodingdean Water Well in England, dug between 1858 and 1862, is the deepest hand-dug well at 392 meters (1,285 feet). The Big Well in Greensburg, Kansas, is known as the world's largest hand-dug well. It is 33 meters (109 feet) deep and 10 meters (32 feet) wide.
Driven Wells
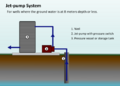
Driven wells are simple to make in soft ground. They use a special pipe with a sharp, hard point and a screen at the end. This point is hammered into the ground, with more pipe sections added as it goes deeper. When water is found, the well is cleaned, and a pump is put in.
Drilled Wells
Drilled wells are made using different types of drilling machines. These machines use rotating parts to cut into the ground.
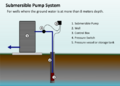
Drilled wells can get water from much deeper places than dug wells, sometimes hundreds of meters down. They are used all over the world, especially in rural areas. Most drilling machines are mounted on large trucks. Water wells are usually 3 to 18 meters (10 to 60 feet) deep, but some can go deeper than 900 meters (3,000 feet).

Rotary drilling machines use long sections of steel pipe that are screwed together, with a drill bit at the bottom. Air or water is pumped down to remove the drilled bits of rock and cool the drill. Another type, called mud rotary, uses a special mud that helps keep the sides of the hole from collapsing. Wells drilled into solid rock usually don't have a pipe inside until after the drilling is finished.
The oldest type of drilling machine is the cable tool, which is still used today. It works by lifting and dropping a bit into the hole, twisting it a little with each drop. This breaks up the rock. Unlike rotary drilling, cable tool drilling needs to stop often so the drilled material can be removed from the hole. Cable tool rigs are much slower than modern rotary rigs.
Drilled wells usually have a factory-made pipe inside, often made of steel or plastic/PVC. These pipes are joined together and lowered into the well. They are usually 6 meters (20 feet) or more long and 10 to 30 centimeters (4 to 12 inches) wide.
To stop pollution from the surface, a "surface seal" is often used. A larger hole is drilled first, then a smaller hole for the well. The space between the large hole and the well pipe is filled with clay or concrete. This creates a seal that stops dirt and pollution from getting into the water. Wells are also usually covered with a cap that lets air in but keeps out insects, small animals, and people.
At the bottom of wells, there is often a screen or a filter to let water flow in while keeping unwanted materials out. In soft ground like sand or gravel, a screen lets water through. In rock wells, a PVC pipe with slots is used to stop rocks from getting into the pump. Some wells use a "filter pack" where a special material is placed around the screen to filter the water before it enters the well.
Similar Water Structures
- Types of old wells:
* Brick-lined well * Castle well, used in castles * Cistern, an ancient Greek water storage tank * Stepwell, ancient wells in India with steps leading down to the water
- Modern ways to build wells:
* Baptist well drilling, a simple technique * Rodriguez well, used to get drinking water in very cold places * Spring supply, water piped from a natural spring
- Uses of wells:
* Holy well, wells considered sacred in different religions * Abraham's well, a sacred well in Israel * Ghat, sacred steps leading to water in Hinduism and Buddhism
* For drainage and watering crops: * Drainage by wells * Shadoof, a tool used to lift water for irrigation
* For washing: * Lavoir, a public place for washing clothes
Images for kids
-
A dug well in a village in Faryab Province, Afghanistan.
-
Water use, from a 14th-century book called Tacuinum Sanitatis.
See also
 In Spanish: Pozo para niños
In Spanish: Pozo para niños