Languages of Africa facts for kids
The languages of Africa are super interesting! Africa has over 3,000 different languages. Some of these are native languages, meaning they started right there in Africa. Others are colonial languages, brought by people from Europe who settled there long ago. Africa has more languages than any other continent. About 30% of all the world's languages are spoken in Africa!
Sadly, some African languages have disappeared over time. This can happen because of wars or when groups of people disappear. Sometimes, people just stop speaking a language, and it dies out.
How African Languages Are Grouped
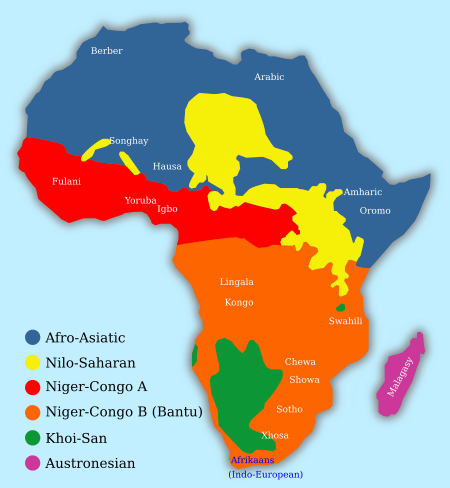
There are more than 3,000 languages spoken in Africa. People who study languages, called linguists, group these languages into major families. However, not all linguists agree on the best way to group them.
Most linguists today group African languages into four main families. These are:
- Afroasiatic languages: Spoken by about 350 million people. You can find these languages in the Middle East, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the Sahel region.
- Niger-Congo languages: This might be the largest language family in the world! Its languages are spoken across sub-Saharan Africa.
- Nilo-Saharan languages: About 50 million people speak these languages. They are found in the upper parts of the Chari River and Nile River areas.
- Khoisan languages: Spoken by about 120,000 people. This family includes all the "click" languages, which use unique clicking sounds!
This way of grouping languages comes from a linguist named Joseph Greenberg. He wrote a famous book called The Languages of Africa in 1963.
Historically, African languages were often grouped into six families. Today, some linguists are not sure if all these older groupings are correct. The six traditional families are:
- Afroasiatic languages: Found from North Africa to the Horn of Africa and Southwest Asia.
- Niger-Congo languages: Spoken in West, Central, and Southeast Africa.
- Nilo-Saharan languages: Spoken in countries like Sudan and Chad.
- Khoe languages: Spoken in the desert areas of Namibia and Botswana.
- Austronesian languages: Spoken in Madagascar.
- Indo-European languages: Spoken in Southern Africa.
Some other linguists think that the Nilo-Saharan languages and the Niger-Congo languages might actually be part of the same bigger family. If they are right, then African languages would only have three main families: Niger-Congo languages, Afroasiatic languages, and Khoisan languages.
No matter how the major language families are organized, there are also many smaller language groups. Some languages are called language isolates, meaning they don't seem to be related to any other known language. There are also some very obscure (rare or uncommon) languages that haven't been classified yet. Africa also has many different sign languages, and most of these are language isolates too.
See also
 In Spanish: Lenguas de África para niños
In Spanish: Lenguas de África para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |

