Amalgam facts for kids
An amalgam is a special kind of alloy (a mix of metals) where one of the metals is always mercury. Amalgams can be liquid, a soft paste, or a solid. It all depends on how much mercury is mixed in.
Most metals can form amalgams with mercury. But there are a few exceptions, like iron, platinum, tungsten, and tantalum. Amalgams of silver and mercury are very important in dentistry (for tooth fillings). Also, gold-mercury amalgam is used to help get gold out of ore (rock containing metal).
What are some important amalgams?
Zinc amalgam
Zinc amalgam is used in chemistry to help make other chemicals. It can also be used to reduce (change) certain substances. Long ago, a small amount of mercury was added to the zinc plates in dry batteries. This helped the batteries last longer when stored.
Potassium amalgam
When alkali metals like potassium mix with mercury, they create heat. They can form specific chemical compounds, like KHg. These amalgams react very easily with air and water. Because of this, they must be handled carefully in a dry, special environment.
Sodium amalgam
Sodium amalgam is made as a side product in a process called the chloralkali process. It's a useful chemical that helps to change other substances in chemistry. When sodium amalgam mixes with water, it breaks down into sodium hydroxide (a strong chemical), hydrogen gas, and mercury. The mercury can then be used again in the chloralkali process.
Aluminium amalgam
You can make aluminium amalgam by grinding aluminium metal with mercury. Or, you can let aluminium react with a solution containing mercury. This amalgam is used in chemistry to help change certain compounds. The aluminium provides the electrons, and the mercury helps move them.
Making and using aluminium amalgam involves mercury. This means special safety steps are needed because mercury can be harmful. There are also other, more environmentally friendly ways to do similar chemical reactions. For example, an alloy of aluminium and gallium can be used. This mix makes the aluminium more reactive by stopping it from forming a protective oxide layer.
Tin amalgam
In the mid-1800s, tin amalgam was used to make the shiny, reflective coating on mirrors.
Other interesting amalgams
Many other amalgams exist, mostly for scientific research.
- Ammonium amalgam is a soft, grey, spongy material. It was discovered in 1808 by scientists Humphry Davy and Jöns Jakob Berzelius.
- Thallium amalgam has a very low freezing point, even lower than pure mercury. Because of this, it has been used in thermometers for very cold temperatures.
- Gold amalgam forms easily when finely ground gold touches clean mercury.
- Lead can also form an amalgam when its filings are mixed with mercury. This is even found naturally as a mineral called leadamalgam.
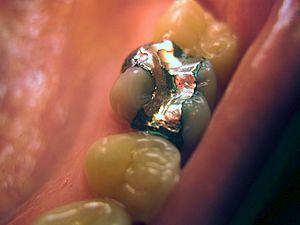
Dental amalgam
For many years, dentists have used amalgams for tooth fillings. These amalgams are usually a mix of mercury with metals like silver, copper, indium, tin, and zinc. Amalgam is a good material for fillings for several reasons. It's not expensive, and it's easy for dentists to use. It stays soft for a short time, so it can fill any space in a tooth. Then, it quickly becomes a hard filling.
Amalgam fillings often last a long time. However, newer materials like composite resins are also improving and lasting longer now. Amalgam is often compared to resin-based composites because they are used for similar things. Also, their properties and costs are quite similar.
In July 2018, the European Union (EU) made a rule. It said that amalgam should not be used for dental treatment in children under 15 years old. It also should not be used for pregnant or breastfeeding women.
How amalgams are used in mining
Mercury has been used in gold and silver mining for a long time. This is because mercury easily mixes with these valuable metals. In placer mining, where tiny bits of gold are washed from sand or gravel, mercury was often used. It helped separate the gold from other heavy minerals.
After most of the metal was taken from the ore, mercury was poured down a long copper trough. This created a thin layer of mercury on the trough. Then, the leftover ore was washed over this trough. Any gold in the ore would mix with the mercury. This gold-mercury mix (amalgam) was then scraped off. It was heated to make the mercury evaporate, leaving behind mostly pure gold.
The use of mercury for silver ores started in Mexico in 1557. Other methods for processing silver ores with mercury were also developed later.
Gold amalgam
Gold extraction (mining)
Gold amalgam was very helpful for getting tiny pieces of gold (called "flour gold") out of ore. These tiny pieces were too small to be collected by other methods. A lot of mercury was used in placer mining in the 1800s. In this method, gold-containing gravel was washed through long channels with ridges (riffle boxes). Mercury was added at the start of the channel. The gold would mix with the mercury, forming a heavy, dull gray solid. (The use of mercury in California's 19th-century placer mining is now banned. It caused a lot of pollution in rivers that still affects the environment today.)
Gold extraction (ore processing)
When stamp mills were used to crush gold-bearing ore into fine powder, mercury was also part of the process. The crushed ore was washed over copper plates coated with mercury. The tiny gold particles would stick to the mercury. Periodically, the plates were scraped clean, and more mercury was added. This collected amalgam was then processed further.
Gold extraction (retorting)
The gold amalgam collected from mining or ore processing was then heated in a special container called a distillation retort. This process recovered the mercury so it could be used again. It left behind the gold. However, this heating released mercury vapors into the air. This could harm people's health and cause long-term pollution.
Today, in developed countries, other methods are used to get gold and silver from ore. The dangers of mercury waste played a big role in stopping the use of mercury amalgams. However, mercury amalgamation is still sometimes used by small-scale gold miners, often illegally, especially in developing countries.
Amalgam probe
Mercury salts are much more toxic than mercury metal or amalgams because they can dissolve in water. You can detect these salts in water using a special probe. This probe uses the fact that mercury ions easily form an amalgam with copper. If you put a solution that might contain mercury salts onto a piece of copper foil, any mercury ions present will leave silvery spots of amalgam. Silver ions also leave similar spots, but they wash away easily. This helps tell the difference between silver and mercury.
See Also