Amelia Island facts for kids

Marshes surrounding Amelia Island
|
|
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | North Atlantic |
| Coordinates | 30°36′56″N 81°27′14″W / 30.61556°N 81.45389°W |
| Length | 21 km (13 mi) |
| Width | 6.5 km (4.04 mi) |
| Administration | |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone | |
| • Summer (DST) | |
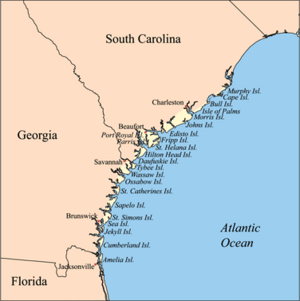
Amelia Island is a beautiful island off the coast of Florida. It's part of the Sea Islands chain, which stretches from South Carolina all the way to Florida. Amelia Island is the southernmost of these islands and the northernmost barrier island on Florida's Atlantic coast.
Located in Nassau County, Florida, the island is about 21 kilometers (13 miles) long. At its widest point, it's about 6.5 kilometers (4 miles) across. You'll find several communities on the island, including Fernandina Beach, Amelia City, and American Beach.
Contents
Exploring Amelia Island's Geography
Amelia Island is a great place for outdoor activities. The Amelia Island Trail is a popular path for walking and biking. It's actually part of the East Coast Greenway, a huge trail system. This system is 3,000 miles long and connects Maine to Florida!
What About the Airport?
The Fernandina Beach Municipal Airport (KFHB) is located right on Amelia Island. It's a general aviation airport, meaning it's mostly for private planes. Sometimes, the U.S. Navy, U.S. Coast Guard, and Florida Air National Guard also use it.
Amelia Island's Rich History
Amelia Island has a fascinating past! It was named after Princess Amelia of Great Britain, who was the daughter of King George II of Great Britain. What makes its history so unique is that eight different flags have flown over the island. These flags represent the many times the island changed hands between different countries and groups. The flags include French, Spanish, British, Floridian/Patriot, Green Cross, Mexican, Confederate, and United States.
Early People and European Arrivals
Around 1000 AD, Timucua people, who were Native Americans, settled on the island. They called it Napoyca. They lived there peacefully until the early 1700s.
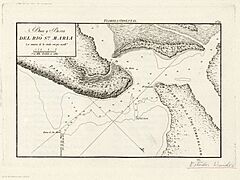
In 1562, a French explorer named Jean Ribault was the first European to visit Napoyca. He named it Île de Mai, which means "Island of May." A few years later, in 1565, Spanish forces arrived. They were led by Pedro Menendez de Aviles. The Spanish drove the French out of northeastern Florida. They attacked the French fort on the St. Johns River, which the French called Rivière de Mai.
Spanish Control and Missions
In 1573, Spanish Franciscan missionaries built a mission on the island. They named it Santa María de Sena. They also renamed the island Isla de Santa María. In the early 1600s, the Spanish moved the Mocama people, another Native American group, to this mission.
Later, in 1680, British attacks on nearby St. Catherines Island in Georgia caused the Christian Guale Indians to move to the Spanish missions on Isla de Santa María. However, in 1702, the Spanish left these missions. This happened after South Carolina's governor, James Moore Sr., led an invasion of Florida with British colonists and their Native American allies.
James Oglethorpe, who founded the colony of Georgia, later renamed the island "Amelia Island." He did this to honor Princess Amelia of Great Britain. Even though it was still Spanish territory, Oglethorpe tried to get the island for Britain. He even built a fort there. But King Philip V of Spain disagreed, and the island remained Spanish.
British Rule Begins
Oglethorpe pulled his troops out in 1742. For a while, the area was a neutral zone between the English and Spanish colonies. This changed after the Treaty of Paris (1763). This treaty ended the Seven Years' War, which Britain won. Spain traded Florida to Great Britain to get Havana, Cuba back. This treaty meant all Spanish land grants in Florida were no longer valid. The Proclamation of 1763 also set the St. Marys River as the border for East Florida.
During the early British period, the island was called Egmont Isle. This was after Lord Egmont, who owned a huge plantation there. His plantation covered almost the entire island! He started developing the island in 1770. He used the forced labor of enslaved African Americans to grow valuable indigo crops. However, American troops from Georgia destroyed the plantation in 1776.
Spanish Rule Returns Again
During the American Revolutionary War, many British loyalists fled to Amelia Island. They built new homes there and called their town Hillsborough. In 1783, the Second Treaty of Paris ended the Revolutionary War. Florida was given back to Spain. Most British people had to leave or promise loyalty to Spain.
After the British left, only Mary Mattair, her children, and an enslaved worker remained on the island. The Spanish allowed her to stay. She was given 150 acres of land where the historic Old Town Fernandina is today.
In 1795, American rebels attacked the Spanish fort on Amelia Island. The Spanish military, led by Colonel Charles Howard, fought back. The rebels were forced to flee back to Georgia.
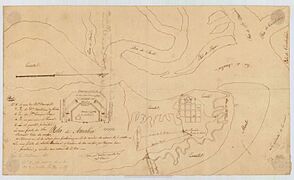
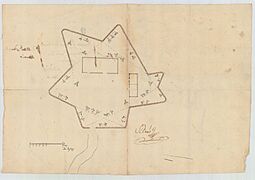
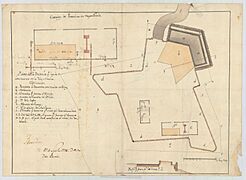
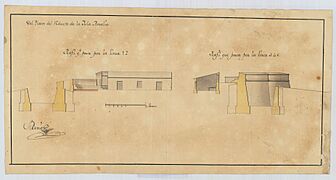
During these years, a Spanish engineer named Pedro Díaz Berrio drew plans for several forts on the island. These plans show how important the island was for defense.
In 1811, the town of Fernandina was planned. It was named after King Ferdinand VII of Spain.
The "Patriot War" and U.S. Involvement
On March 16, 1812, a group of Americans called the "Patriots of Amelia Island" invaded and took over Amelia Island. This was led by General George Mathews. President James Madison of the United States quietly approved this action.
American gunboats lined up in the harbor. General Mathews demanded that the Spanish commander, Don Justo Lopez, surrender. Lopez gave up the fort and town. The Patriots raised their own flag. The next day, U.S. troops arrived, and the Patriots handed the town over to General Mathews. He officially took possession for the United States.
This was part of a plan by General Mathews and President Madison to take over East Florida. However, the U.S. Congress worried about starting a war with Spain while fighting the War of 1812 with Great Britain. So, the U.S. troops left Amelia Island in May 1813. Spain quickly regained control. In 1816, the Spanish finished building the new Fort San Carlos to protect Fernandina.
The Green Cross Flag and New Republics
Even after Spain regained control, there were more attempts to take the island. In 1817, a Scottish soldier named Gregor MacGregor led an attack on Fort San Carlos. He took the fort and raised his own flag, the "Green Cross of Florida." He declared the "Republic of the Floridas." But he soon left due to lack of money and support.
Later, a French privateer (a legal pirate) named Louis-Michel Aury took control of Amelia Island. He claimed it for the revolutionary Republic of Mexico, which was fighting for independence from Spain. Aury even created a "Supreme Council of the Floridas" and invited all of Florida to join him. For a few months, the flag of the revolutionary Republic of Mexico flew over Amelia Island.
U.S. Takes Control Permanently
The United States had plans to annex Florida. On December 23, 1817, a U.S. naval force captured Amelia Island. Aury surrendered the island to U.S. forces. President James Monroe said the U.S. would hold it "in trust for Spain." This event is known as the Amelia Island Affair.
Even though Spain was upset, they eventually gave Florida to the United States. The Adams-Onis Treaty officially transferred East Florida to the U.S. on February 22, 1821. After this, the U.S. Army didn't use Fort San Carlos much, and it was soon abandoned. The island then became home to plantations worked by enslaved Black people.
Amelia Island During the Civil War
Before the American Civil War, Confederate supporters took control of Fort Clinch on January 8, 1861. This was just two days before Florida officially left the United States. The fort was still being built at the time.
Union forces took back control of the island on March 3, 1862. They had 28 gunboats. Many enslaved people came to the Union lines on the island to gain their freedom. By 1863, there were 1200 freed people and their children living on the island.
People from the North helped the freed people on Amelia Island. Chloe Merrick from Syracuse, New York, came to the island. She taught the freed people and started a school and orphanage in 1863. She continued to support education and welfare in Florida even after marrying Governor Harrison Reed in 1869.
Fun Events on Amelia Island
Amelia Island is a lively place with many exciting events!
- The annual Isle of Eight Flags Shrimp Festival attracts over 150,000 visitors every May.
- You can also enjoy the Amelia Island Jazz Festival, the Amelia Island Chamber Music Festival, and the Amelia Island Film Festival.
- Car lovers enjoy the Amelia Island Concours d'Elegance, a charity event featuring classic cars.
- There's also the Amelia Island Blues Festival.
Amelia Island has also been a filming location! The 2002 movie Sunshine State and The New Adventures of Pippi Longstocking (1988) were filmed here.
The island used to host a Women's Tennis Association tournament for 28 years (1980-2008). Since 2009, it has hosted the annual Pétanque America Open, a game similar to boules.
Golfing on Amelia Island
If you love golf, Amelia Island has five great courses:
- Oak Marsh Course
- Long Point Course (The Amelia Island Club)
- Golf Club of Amelia Island
- Amelia River Golf Club
- Fernandina Beach Golf Club
See also
 In Spanish: Isla de Amelia para niños
In Spanish: Isla de Amelia para niños