Babylonian Gods facts for kids
Babylonian religion was greatly influenced by Sumerian religion. This meant that many Babylonian gods were actually old Sumerian gods, sometimes with the same names and sometimes with new ones.
The ancient land of Babylonia mainly focused on the god Marduk. He was the national god of the Babylonian empire. Marduk was one of the "new" Mesopotamian gods that the Sumerians didn't worship before. However, many other gods were also important and worshipped.
Major gods were often linked to specific planets or stars. In fact, the modern seven-day week comes from the ancient Babylonians! Each day was connected to one of their seven main planetary gods.
Contents
Important Babylonian Gods
Utu (Shamash)
Utu, later known as Shamash, was the ancient Mesopotamian god of the Sun. People also saw him as the god of truth, justice, and good behavior. It was believed that the Sun-god could see everything that happened during the day. He was also thought to help people who were in trouble. Utu and his sister, Inanna, made sure that divine justice was carried out. His special metal was Gold and his color was yellow.
Nanna-Suen (Sin)
Nanna, also called Enzu or Zuen in Sumerian, later became known as Suen and Sin in Akkadian. He was the ancient Mesopotamian god of the Moon. The Moon-god was very important among the main gods. He was seen as representing all the powers of the gods combined. The crescent moon, which was his symbol, was often placed at the top of Mesopotamian temples. His special metal was Silver and his color was green.
Nergal
Nergal was a god connected to the Underworld, which was the land of the dead. He was also linked to things like forest fires, fevers, diseases, and war. In old stories, he was known for causing destruction and chaos. His special metal was Iron and his color was red.
Nabu
Nabu was the Mesopotamian god of scribes, who were people who wrote things down. He was also the god of writing itself. His wife was the goddess Tashmetu. Nabu was linked to the planet Mercury. Over time, he also became known as a god of wisdom and farming. His special metal was Mercury and his color was orange.
Marduk
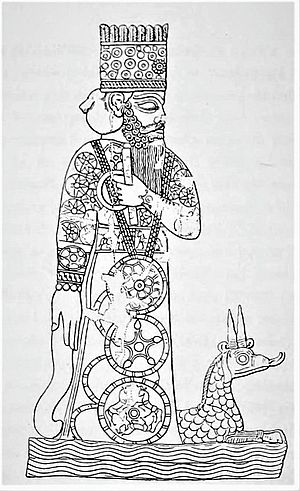
Marduk was the national god of the Babylonians. As the city of Babylon grew in power, so did the worship of Marduk. He eventually became the most important Babylonian god. His wife was the goddess Sarpānītu. His special metal was Tin and his color was white.
Inanna (Ishtar)
Inanna, later known as Ishtar, was the most important female god in ancient Mesopotamia. She was the goddess of love and war. She was also seen as the divine form of the planet Venus. The ancient Sumerians had more myths and stories about her than any other god. Along with her twin brother Utu, Inanna helped to carry out divine justice. Her special metal was Copper and her color was blue.
Ninurta
Ninurta, also known as Ningirsu, was a Mesopotamian warrior god. People in Sumer worshipped him from very early times. Ninurta was a god of war and hunting. He was also a god of farming and was seen as the protector of farmers. In an old story called Lugal-e, he defeats a demon named Asag. He then uses stones to build the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, making them useful for watering crops. His main symbols were a bird sitting on a perch and a plow. His special metal was Lead and his color was black.
Related pages
Images for kids