Battle of Belgium facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Battle of Belgium |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Western Front of World War II | |||||||||
 German soldiers pictured with a Vickers Utility Tractor (VUT) of the Belgian Army, and a pile of Belgian rifles and helmets the day after the Belgian surrender, 29 May 1940 |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| 144 divisions 13,974 guns 3,384 tanks 2,249 aircraft |
141 Divisions 7,378 guns 2,445 tanks 5,446 aircraft (4,020 operational) |
||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
| 222,443+ casualties (200,000 captured) ~900 aircraft |
Unknown (see German casualties) but at least 43 paratroopers were killed and a further 100 wounded. | ||||||||
The Battle of Belgium was a major part of the Battle of France during World War II. It was a quick attack by Germany that lasted 18 days in May 1940. The battle ended when the Belgian Army surrendered. This led to Germany taking control of Belgium.
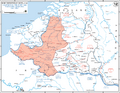
The Allied armies, including France and the United Kingdom, tried to stop the German advance in Belgium. They thought this was Germany's main attack. However, after the Allies sent their best troops into Belgium, the Germans surprised them. They quickly moved towards the English Channel, trapping the Allied armies. The Belgian Army surrendered on May 28, 1940.
This battle was important for several reasons:
- It included the first major tank battle of World War II.
- It was the biggest tank battle in history up to that time.
- It featured the Battle of Fort Eben-Emael, which was the first time paratroopers were used in a strategic airborne attack.
Germany occupied Belgium until late 1944 or early 1945. Belgium was then freed by the Western Allies.
Contents
What was the Battle of Belgium?
The Battle of Belgium was a fast and strong attack by Germany. It happened in May 1940. This battle was part of the larger German invasion of France and the Low Countries. Germany wanted to defeat the Allied forces quickly.
Why did Germany invade Belgium?
Germany's plan was to trick the Allies. They wanted the Allies to send their best armies into Belgium. While the Allies were busy there, Germany planned to launch another attack. This second attack would go through the Ardennes forest. This area was thought to be too difficult for tanks.
The German plan: "Sickle Cut"
The German plan was called Manstein Plan or "Sickle Cut." It aimed to cut off the Allied armies. The main German forces would push through Belgium. Meanwhile, a secret, powerful tank force would go through the Ardennes. This force would then turn north. It would trap the Allied armies in Belgium.
How did the battle begin?
The battle started on May 10, 1940. German forces crossed into Belgium. They also attacked the Netherlands and Luxembourg. The Allies quickly moved their troops into Belgium to meet the attack. This was exactly what Germany wanted them to do.
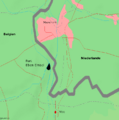
The Battle of Fort Eben-Emael
One of the first attacks was on Fort Eben-Emael. This was a very strong Belgian fort. It protected important bridges. German paratroopers landed on the fort using gliders. They used new explosives to destroy its defenses. The fort fell quickly. This allowed German troops to cross the bridges easily. This was a big shock to the Allies.
The First Tank Battle
The first major tank battle of the war happened in Belgium. It was called the Battle of Hannut. French and German tanks fought fiercely. The French tanks were often better armored. However, the Germans had better tactics. They used their tanks together with air support. This battle showed how important tanks would be in modern warfare.
What happened next?
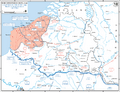
The Allies moved their best armies into Belgium. They thought they were stopping the main German attack. But the German forces that went through the Ardennes moved very fast. They reached the English Channel in just five days. This trapped the Allied armies in Belgium.
The Allied armies are trapped
The German advance cut off the Allied forces. They were pushed back towards the sea. The situation became very serious for the Belgian, British, and French armies. They were surrounded.
The Belgian surrender
The Belgian Army fought bravely. But they were running out of supplies. They were also cut off from the other Allied forces. On May 28, 1940, King Leopold III decided to surrender the Belgian Army. He did this to save his people and his soldiers. This decision was very controversial. Many Allied leaders disagreed with it.
After the surrender
After the surrender, Belgium was occupied by Germany. The Belgian government went into exile. They continued to fight from outside Belgium. Many Belgian soldiers who escaped joined the Free Belgian Forces. They fought alongside the Allies for the rest of the war.
Why was this battle important?
The Battle of Belgium was a quick and decisive German victory. It showed the power of Germany's new "Blitzkrieg" (lightning war) tactics. These tactics used fast-moving tanks and air support. The battle also led to the Dunkirk evacuation. Many Allied soldiers were saved there. However, it meant that France was now largely open to German attack.
Images for kids
-
A pacifist rally in Heysel, near Brussels, in 1936
-
King Leopold III, Belgian head of state, an advocate of the policy of neutrality
-
Leopold III, Belgium's monarch from 1934, reviewing Belgian troops in early 1940
-
German soldiers are welcomed into Eupen-Malmedy, a German border region annexed by Belgium in the Treaty of Versailles (1919)
-
British troops cross the Franco-Belgian border at Herseaux on 10 May
-
General Erich Hoepner commanded XVI Army Corps at the Battle of Hannut and the Gembloux gap offensive
-
Destroyed French tanks in Beaumont on 16 May
-
A destroyed French heavy Char B1 in Beaumont
See also
 In Spanish: Batalla de Bélgica para niños
In Spanish: Batalla de Bélgica para niños