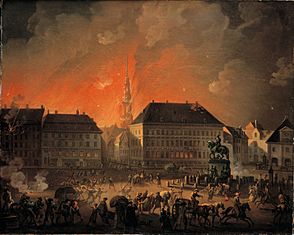Battle of Copenhagen (1807) facts for kids
The Second Battle of Copenhagen (also called the Bombardment of Copenhagen) happened from August 16 to September 7, 1807. It was a big attack by the British navy on Copenhagen, the capital of Denmark–Norway. The main goal was to take or destroy the Danish-Norwegian fleet during the Napoleonic Wars. This event caused the Anglo-Russian War to start, which ended in 1812. Many countries criticized Britain for attacking Denmark, which was a neutral country at the time.
Britain's attack was a response to Napoleon's plan called the Continental System. This system aimed to stop trade with Britain. Even though Denmark was neutral, France was pressuring it to join Napoleon and use its navy against Britain. In September 1807, the British Royal Navy bombed Copenhagen. They took the Danish fleet, which helped Britain control the sea routes in the North Sea and Baltic Sea for its trading ships. After the attack, Denmark did join Napoleon's side, but without its fleet, it couldn't do much to help.
The attack was so impactful that it led to a new term, "to Copenhagenize", meaning to force a country to do something by military action.
Quick facts for kids Battle of Copenhagen 1807 |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Gunboat War and the Napoleonic Wars | |||||||
 A painting of the British bombardment by Christoffer Wilhelm Eckersberg |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 25,000 | 10,000 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 42 killed 145 wounded 24 missing |
3,000 Entire fleet surrendered |
||||||
| 195 civilians killed and 768 wounded | |||||||
Contents
Why the Battle Happened
Even after losing many ships in the first Battle of Copenhagen in 1801, Denmark-Norway still had a strong navy. It also controlled important areas like Jutland, Norway, and Iceland. Most of the Danish Army, led by the Crown Prince, was busy defending the southern border from a possible French attack.
Britain was worried that Napoleon might force Denmark to close the Baltic Sea to British ships. This could happen if French troops marched into Zealand, the island where Copenhagen is located. The British believed that access to the Baltic Sea was very important for trade. It was also a key source of materials needed to build and repair warships.
Britain also wanted to help its allies, Sweden and Russia, against France. After Prussia was defeated in December 1806, Denmark's independence seemed to be in danger from France. Britain's foreign minister, George Canning, tried to get Denmark to secretly ally with Britain and Sweden, but it didn't work.
In July 1807, Britain received secret information that Napoleon planned to use the Danish navy against them. Some reports even suggested that Denmark had secretly agreed to this. The British government decided they had to act quickly. On July 18, the British Admiralty ordered over 50 ships to sail under Admiral James Gambier. General Lord Cathcart was also ordered to bring his troops to the area.
Britain gathered a large force of 25,000 soldiers. They offered Denmark an alliance and protection, promising to return the Danish fleet after the war. However, Denmark refused to give up its neutrality. On August 15, the British demanded that Denmark hand over its fleet. Denmark responded with a declaration of war.
As the first step, a group of British ships blocked the island of Zealand. This stopped the Danish army in Holstein from crossing over to help defend Copenhagen. The city was left to defend itself with about 10,000 soldiers against the 25,000 British troops.
Before the main attack, on August 15, a British ship called HMS Comus captured the Danish frigate Friderichsværn off Marstrand. This happened even though war had not been officially declared yet.
The Bombardment of Copenhagen
The British troops were led by General Lord Cathcart. They had many different units, including cavalry, artillery, and infantry divisions. The Danish forces inside Copenhagen had about 5,000 regular soldiers and a similar number of local militias. Most of the people living in Copenhagen were moved out before the city was completely surrounded.
On August 29, a British force led by General Sir Arthur Wellesley (who later became the Duke of Wellington) quickly defeated Danish troops near Køge. These Danish troops had been sent to try and help the city.
Since the Danes refused British demands, the Royal Navy fleet, led by Admiral Gambier, started bombing Copenhagen. The bombardment lasted from September 2 to September 5. Besides the Danish soldiers, about 195 civilians were killed and 768 were injured.
The British used 300 Congreve rockets during the attack, which caused many fires. Because most civilians had left, there weren't enough people to put out the fires, and over a thousand buildings were burned.
On September 5, the Danes asked for peace. The surrender agreement was signed on September 7. Denmark agreed to give up its navy and all its naval supplies. In return, the British promised to leave Copenhagen within six weeks.
The Danish commander, Ernst Peymann, had been ordered by the Crown Prince to burn the Danish fleet so the British couldn't get it. However, he failed to do this. On September 7, Peymann surrendered the fleet, which included 18 large ships of the line, 11 frigates, and many smaller ships and gunboats. The British also destroyed or broke up several ships that were still being built.
After being captured, one Danish ship, Neptunos, ran aground and was burned. A storm in the Kattegat also caused the British to destroy or abandon 23 of the captured gunboats. The British added 15 of the captured ships of the line to their own navy, but only four of them were used in active service later on.
The British fleet left Copenhagen for the United Kingdom on October 21. However, the Gunboat War between Britain and Denmark continued until 1814, when the Treaty of Kiel was signed.
-
An illustration by C.W. Eckersberg showing the Church of Our Lady being bombed.
-
British Tars Towing the Danish Fleet into Harbour by James Gillray.
What Happened After
The news of the British victory was celebrated in Britain. Many people, including politicians like George Canning, felt that taking the Danish fleet was necessary for Britain's safety. They argued that Denmark was too close to Britain and could easily be used by Napoleon.
However, some people disagreed strongly. They felt that attacking a neutral country was wrong and damaged Britain's reputation. One politician, Lord Erskine, even said that "if hell did not exist before, Providence would create it now to punish ministers for that damnable measure."
The attack also had an unexpected effect on history. It destroyed the 20-year work of a scholar named Grímur Jónsson Thorkelin, who was preparing to publish a modern version of the old English poem Beowulf. Luckily, two copies of the original writings were saved, and Thorkelin eventually published the poem in 1815.
A famous horse born in 1808, the year after the battle, was named "Copenhagen" in honor of the event. This horse later became the favorite mount of Arthur Wellesley and was ridden by him during the famous Battle of Waterloo.
Danish Privateers
Within a week of the British leaving Copenhagen, the Danish government declared war on Britain. They started allowing "privateers," which were private ships given permission to attack and capture enemy merchant ships. Denmark issued these special permits, called Kaperbreve (letters of marque), from 1807 to 1813. Danish shipping companies even gave ships to the state to be used as privateers.
Ships Involved
Many ships took part in the Battle of Copenhagen. The British fleet included 126 ships of different sizes, plus many merchant ships carrying troops and supplies.
Here are some of the main British ships that sailed with Admiral Gambier:
- Prince of Wales (98 guns) - Admiral Gambier's flagship
- Pompee (74 guns)
- Centaur (74 guns)
- Ganges (74 guns)
- Alfred (74 guns)
- Brunswick (74 guns)
- Captain (74 guns)
- Goliath (74 guns)
- Hercule (74 guns)
- Maida (74 guns)
- Orion (74 guns)
- Resolution (74 guns)
- Spencer (74 guns)
- Vanguard (74 guns)
- Dictator (64 guns)
- Nassau (64 guns)
- Ruby (64 guns)
- Surveillante (38 guns)
- Sibylle (38 guns)
- Franchise (36 guns)
- Nymphe (36 guns)
More British ships joined later, including:
- Superb (74 guns)
- Minotaur (74 guns)
- Valiant (74 guns)
- Inflexible (64 guns)
- Leyden (64 guns)
- Defence (74 guns)
- Mars (74 guns)
- Agamemnon (64 guns)
- Africaine (32 guns)
Ships Surrendered by Denmark
On September 7, Denmark surrendered the following warships to the British:
Ships of the line (large warships)
- Christian den Syvende (84 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Christian VII
- Neptunus (80 guns) - wrecked and burned on the way to Britain
- Valdemar (80 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Waldemar
- Danmark (76 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Danmark
- Norge (78 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Norge
- Fyen (70 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Fyen
- Kronprins Friderich (70 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Kron Princen
- Tre Kroner (74 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Tree Kronen
- Arveprins Friderich (70 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Heir Apparent Frederick
- Skjold (70 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Skiold
- Odin (74 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Odin
- Justitia (74 guns) - taken by Britain as Justitia
- Kronprinsesse Maria (70 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Kron Princessen
- Prindsesse Sophia Frederica (74 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Princess Sophia Frederica
- Prindsesse Caroline (66 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Princess Carolina
- Ditsmarsken (60 guns) - burned because it was useless
- Mars (64 guns) - burned because it was useless
- Sejeren (64 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Syeren
Frigates (medium-sized warships)
- Perlen (46 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Perlen
- Rota (40 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Rota
- Freja (40 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Freya
- Iris (40 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Iris
- Najaden (44 guns) - taken by Britain as Nyaden
- Havfruen (40 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Hasfruen
- Nymfen (36 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Nymphen
- Venus (36 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Venus
- Friderichsstein (26 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Frederickstein
- St Thomas (22 guns) - burned because it was useless
- Triton (24 guns) - burned because it was useless
- Lille Belt (20 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Little Belt
- Fylla (22 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Fylla
- Eyderen (18 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Eyderen
- Elven (18 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Elvin
- Glückstadt (12 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Gluckstadt
Brigs (smaller warships)
- Nidelven (18 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Nid Elven
- Sarpen (18 guns) - taken by Britain as Sarpen
- Glommen (18 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Glommen
- Mercurius (18 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Mercurius
- Delphinen (18 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Delphinen
- Allart (18 guns) - taken by Britain as Allart
- Brevdrageren (18 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Brev Drageren
- Flyvende Fiske (14 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Flying Fish
- Ørnen (10 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Ornen
Gunboats
- Stege (2 guns) - taken by Britain as HMS Warning
Twenty-five other gunboats were either lost in a storm or destroyed by the British. Six gunboats were later recovered by the Danes.
Gun Barges
Four large floating gun platforms were sunk by the British because they couldn't be moved easily. Only one of these, Hajen, was not raised and repaired by the Danes later.
See also
- List of ships captured in the 19th century
 | William M. Jackson |
 | Juan E. Gilbert |
 | Neil deGrasse Tyson |