Danish Realm facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kingdom of Denmark
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: Forbundet, forpligtet - for kongeriget Danmark (United, committed - for the Kingdom of Denmark)
|
|
|
Anthems:
Der er et yndigt land ("There is a lovely country") Kong Christian stod ved højen mast ("King Christian stood by the lofty mast") |
|
 |
|
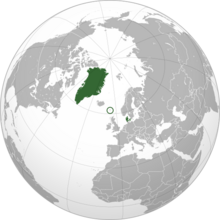
Clockwise from top left (sizes not to scale): maps of Greenland, the Faroe Islands, Denmark
|
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Copenhagen |
| Official languages | Danish |
| Recognised regional languages | Faroese Greenlandic German |
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Countries (non‑sovereign parts) | |
| Government | Devolved unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch
|
Frederik X |
| Mette Frederiksen | |
| Aksel V. Johannesen | |
| Legislature |
|
| History | |
|
• Unification
|
c. 965 |
|
• Faroese home rule
|
24 March 1948 |
|
• Greenlandic home rule
|
1 May 1979 |
|
• Faroese takeover act
|
29 July 2005 |
|
• Greenlandic self rule
|
21 June 2009 |
| Area | |
|
• Denmark
|
42,926 km2 (16,574 sq mi) (12th) |
|
• Faroe Islands
|
1,396 km2 (538.999 sq mi) |
|
• Greenland
|
2,166,086 km2 (836,330 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• Q2 2023 estimate
|
6,049,579 (112th) |
|
• Denmark
|
5,941,388 |
|
• Greenland and Faroe Islands
|
108,191 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total
|
€380 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
€62,814 |
| HDI (2021) | 0.948 very high |
| Currency | Danish krone (DKK) Faroese króna |
| Time zone | |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
|
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code |
3 codes
+45 (Denmark)
+298 (Faroe Islands) +299 (Greenland) |
| ISO 3166 code | DK |
| Internet TLD | |
The Danish Realm, also known as the Kingdom of Denmark, is a country made up of three main parts. It includes Denmark itself, which is in Europe. It also includes two special areas that govern themselves: the Faroe Islands in the North Atlantic Ocean and Greenland in North America. The King or Queen of Denmark is the head of state for all three parts.
Even though it has three parts, the Kingdom of Denmark is not like a team of separate countries. It's a single country with one ruler. However, the Faroe Islands and Greenland have a lot of freedom to make their own rules. This special connection between the three parts is sometimes called The unity of the Realm.
The Faroe Islands and Greenland have been connected to Denmark for a very long time, since 1397. Over time, they have gained more control over their own laws and daily life. This is because they have their own unique histories and cultures.
The main law for the whole Kingdom is the Constitution of the Realm of Denmark. This law says that the Danish Parliament (called the Folketing), the Danish Government, and the Danish Supreme Court are in charge of laws and decisions for the whole Kingdom.
The Faroe Islands started governing themselves more in 1948. Greenland got its own self-rule in 1979, and even more in 2009. This means the Danish government has less say in the daily matters of Greenland and the Faroe Islands.
The Kingdom of Denmark shares a land border with Germany. It also has a land border with Canada on Hans Island. A bridge and tunnel connect Denmark to Sweden across the Øresund Strait.
Contents
What is the Danish Realm Called?
The official name for the country's territory in the Danish Constitution is Danmarks Rige, which means "The Realm of Denmark".
The Danish phrase rigsfællesskabet is used to describe the special relationship between Denmark, the Faroe Islands, and Greenland. It means "The unity of the Realm" or "the Danish Commonwealth". This term became popular in the 1990s. It shows that while they are united, each part has its own unique identity.
How Big is the Danish Realm?

Denmark has the largest population of the three parts, with about 5.8 million people. The Faroe Islands have about 52,000 people, and Greenland has about 56,000. To compare, Denmark alone has ten cities with more than 50,000 people.
The people of Denmark are called Danes. The people of the Faroe Islands are called Faroese. The people of Greenland are called Greenlandic Inuit. About 7.6% of the people in the Faroe Islands and Greenland are Danes. Also, about 11,000 Faroese-born and 17,000 Greenlandic-born people live in Denmark.
When it comes to size, Greenland is by far the biggest part. It makes up 98% of the entire Realm. The whole Kingdom covers about 2.2 million square kilometers. This makes it the twelfth largest country in the world. Denmark alone is much smaller, about 43,000 square kilometers.
Denmark is in Northern Europe and has flat, farmable land. The Faroe Islands are in the Northern Atlantic and have rugged coasts with cliffs. Greenland is in the North Atlantic and Arctic regions. About 79% of Greenland is covered in ice. Greenland is the least crowded place in the world.
| Part | Area | Population (2023) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | % | Population | % | Density | |
| 42,926 | 1.94% | 5,964,059 | 98.17% | 135.65 per km2 | |
| 1,396 | 0.06% | 54,547 | 0.88% | 37.36 per km2 | |
| 2,166,086 | 98.00% | 56,643 | 0.95% | 0.03 per km2 | |
| Entire realm | 2,210,408 | 100.00% | 6,075,249 | 100.00% | 2.68 per km2 |
The Kingdom has made claims to the United Nations about its sea areas in the Arctic Ocean. These claims include areas near the North Pole. Some of these claims overlap with other countries' claims, which are settled through talks. For example, in 2019, Denmark, Iceland, and Norway agreed on their claims north of the Faroe Islands.
The Kingdom also had a friendly discussion with Canada about who owned Hans Island between 1978 and 2022. They decided to split the island in half, creating a land border between the two countries.
A Look at the Past
The Faroe Islands were settled by Vikings from Norway in the 800s. Norsemen also settled Iceland in the 800s. Iceland was a free state until it came under Norwegian rule in the 1200s. Greenland, where the Greenlandic Inuit already lived, was settled by Norwegians in the 900s. One famous settler was Erik the Red.
In 1814, Denmark gave Norway to Sweden, but it kept control of the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Iceland. Denmark sold its Danish West Indies to the United States in 1917. As part of that deal, the U.S. agreed that Denmark owned all of Greenland.
In Iceland, people wanted more independence in the 1800s. Iceland got its own constitution in 1874 and more self-rule in 1904. It became fully independent in 1918, but still had a special connection with Denmark. Denmark helped with Iceland's defense and foreign affairs. In 1944, during World War II, Iceland became a full republic. This happened while Denmark was occupied by Germany and Iceland by the United States.
The Faroe Islands became a Danish county in 1816. They got a say in the Danish Parliament in 1849. During World War II, the United Kingdom occupied the Faroe Islands, and they largely managed themselves. After the war, the Faroe Islands were given "home rule" in 1948. This meant they could make many of their own decisions.
Greenland was first managed as two separate colonies. In 1950, they were joined into one colony. In 1953, Greenland became a county of Denmark and got representatives in the Danish Parliament. When Denmark joined the European Communities (EC) in 1972, Greenland joined too, even though most Greenlanders voted against it. They wanted home rule so they could leave the EC, which they did in 1985. Greenland got home rule in 1979, and then "self rule" in 2009, giving them even more control.
How the Government Works
The Danish constitution applies to all parts of the Kingdom. This means that the Danish state holds the main power over the Faroe Islands and Greenland. The Kingdom of Denmark is a single state, and the Danish Parliament (the Folketing) makes laws for the whole country.
The Faroe Islands and Greenland each elect two members to the Danish Parliament. The other 175 members are elected in Denmark.
Home Rule and Self Rule
The Danish Parliament has given the Faroe Islands and Greenland a lot of power to govern themselves. The Faroe Islands got "home rule" in 1948, and Greenland got it in 1979. Greenland's home rule was later changed to "self rule" in 2009, giving it even more power.
There is some discussion about how strong these self-governing agreements are. Some people think the Danish Parliament can change these laws whenever it wants. Others believe that changes need to be agreed upon by the Faroese Parliament (the Løgting) or the Greenlandic Parliament (the Inatsisartut).
Greenland's Path to Independence

The Greenlandic self-rule law of 2009 allows Greenland to become fully independent. First, the people of Greenland must decide they want independence. Then, the Greenlandic government and the Danish government would talk about how to make it happen. Any agreement would need to be approved by the Greenlandic Parliament and by a vote in Greenland. It would also need approval from the Danish Parliament.
Denmark has recognized the Greenlandic Inuit as an Indigenous people. The 2009 self-rule law also says that the Greenlandic people have the right to decide their own future.
What Powers Do They Have?
The Kingdom of Denmark is one country, but its parts have equal standing. The Faroe Islands and Greenland have been given the power to make many of their own decisions. This is called Devolution.
The governments of the Faroe Islands and Greenland manage the tasks they have taken over from Denmark. They make laws in these areas and are responsible for the money needed to do these tasks. The Danish government gives money each year to help cover the costs of these areas.
The 1948 "Home Rule Act of the Faroe Islands" explains how the Faroe Islands govern themselves. It says the Faroe Islands are a "self-governing community within the State of Denmark." This act created the Faroese government (Landsstýrið) and its parliament, the Løgting. The act lists the powers given to the Faroese government. These include things like local government, taxes, police, housing, schools, farming, and fishing. In 2005, these powers were expanded, and the Faroese government was called an "equal partner" with the Danish government.
The 1978 "Greenland Home Rule Act" gives powers to Greenland in a similar way. It created a home rule government and a Greenlandic parliament. Specific areas of control include local government, fishing, farming, welfare, and protecting the environment.
On June 21, 2009, Greenland took over responsibility for its own courts, policing, natural resources, and immigration. Greenlanders were also recognized as a separate people under international law. Greenland now has "self rule," meaning its government has even more powers.
However, some things cannot be controlled by the Faroe Islands or Greenland. These include the main Constitution, foreign policy, defense, the Supreme Court, citizenship, and monetary policy (money matters). The parliaments of the Faroe Islands and Greenland are also under the Danish Parliament.
International Relations
Before, Denmark handled almost all international relations for the whole Realm. But now, the Faroe Islands and Greenland play a bigger role in foreign policy. Their representatives sometimes join Danish groups for international talks, especially about things like fishing rights.
The Kingdom of Denmark is a member of important international groups like the United Nations, NATO, and the World Trade Organization. The Faroe Islands and Greenland are also connected to the Nordic Council.
Even though the Kingdom of Denmark is part of the European Union, both the Faroe Islands and Greenland have special rules and are not part of the EU. Greenland joined the EU with Denmark in 1973 but chose to leave in 1985. The Faroe Islands have never been part of the EU, mainly because of disagreements about fishing rules.
The Danish government issues special passports for its citizens living in the Faroe Islands and Greenland. These passports allow them to choose a regular Danish passport too. Faroese passports also say Føroyingur (Faroese) and Føroyar (Faroe Islands) after the Danish words.
Images for kids
-
Tinganes, in the capital Tórshavn, is the location of the Faroese Home Government.
See also
 In Spanish: Reino de Dinamarca para niños
In Spanish: Reino de Dinamarca para niños
- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- Realm of New Zealand




