Bay of Gibraltar facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Bay of Gibraltar |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Coordinates | 36°7′51.91″N 5°23′45.63″W / 36.1310861°N 5.3960083°W |
| River sources | Río de San Roque, Guadarranque, Río de Palmones, Río de la Miel |
| Ocean/sea sources | Strait of Gibraltar, Alboran Sea, Mediterranean Sea, Atlantic Ocean |
| Max. length | 10 km (6.2 mi) |
| Max. width | 8 km (5.0 mi) |
| Surface area | 75 km2 (29 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 400 m (1,300 ft) |
| Settlements | Gibraltar, Algeciras |
The Bay of Gibraltar (also called Gibraltar Bay) is a large bay at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula. It is about 10 km (6.2 mi) long and 8 km (5.0 mi) wide. The bay covers an area of around 75 km2 (29 sq mi). In its deepest part, it reaches a depth of up to 400 m (1,300 ft).
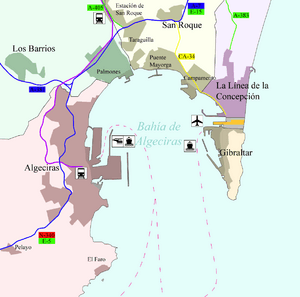
The bay opens south into the Strait of Gibraltar and the Mediterranean Sea. Its shoreline is home to many towns and cities. From west to east, you'll find the Spanish towns of Algeciras, Los Barrios, San Roque, and La Línea de la Concepción. The British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar is also on the bay's eastern side. Most of the shoreline is Spanish, but part of the eastern bay belongs to Gibraltar.
The bay's entrances are marked by lighthouses. On the east, there's the Europa Point Lighthouse in Gibraltar. On the west, near Algeciras, is the Punta Carnero lighthouse.
Contents
A Look Back in Time: The Bay's History
People have lived around the Bay of Gibraltar for thousands of years. The bay itself has been a busy place for ships for at least 3,000 years. Ancient people like the Phoenicians and Romans used this area. The Romans even built a town called Portus Alba, which is where modern Algeciras is today.
Later, groups like the Moors and the Spanish also built settlements along the shore. One important place was the strong port at Gibraltar. This port became part of England in 1704.
The bay's location is very important because it's at the entrance to the Mediterranean Sea. This has made it a much-desired area over the centuries. Several big sea battles have happened here. These include the Battle of Gibraltar (1607) and the Battle of Algeciras bay (1801). During the Second World War, Italy tried to sink British ships in Gibraltar's harbor using special underwater devices.
Disagreements Over the Bay
There has been a long-standing disagreement between Spain and Gibraltar about who controls the waters in the Bay of Gibraltar. Spain believes it controls most of the bay's waters. It says that when Gibraltar was given to Great Britain in 1713, only the city and its port were included, not the surrounding waters.
However, the UK says it has control over the waters around Gibraltar, usually up to 3 nmi (5.6 km; 3.5 mi) from its coast. This means the UK sees a boundary in the middle of the bay. Both sides have signed the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. This agreement helps define how countries claim territorial waters.
These different views have sometimes caused problems, especially when Spanish fishermen operate in waters that Gibraltar considers its own. After a Spanish fishing boat was stopped in 1998, the issues became less frequent. An incident in 2007 involving a sunken treasure was settled in court, with Spain winning ownership of the treasure.
Nature and Wildlife: The Bay's Ecology
The Bay of Gibraltar is a special place for marine life. It's a breeding area for several types of dolphins, such as common dolphins, striped dolphins, and bottlenose dolphins. Large whales also visit the bay as they migrate. Many tourists enjoy taking boat trips from Algeciras or Gibraltar to watch these amazing creatures.
Another popular activity for visitors is scuba diving. The bay is full of interesting things to explore underwater. Divers can find old shipwrecks and historical items. There are even crashed Avro Shackleton aircraft and Sherman tanks from the Second World War. You can also find ancient anchors from Phoenician and Roman ships.
To help protect and increase the variety of marine life, an artificial reef was built in the bay. It is located near the end of the runway.
Industry and Shipping Around the Bay

The Spanish side of the bay is a busy industrial area. There are large petrochemical factories near San Roque. These include the CEPSA oil refinery and the Acerinox stainless steel factory. Both Algeciras and Gibraltar have active ports.
Many large and medium-sized ships use the bay's waters. These include oil tankers and freighters (cargo ships). A lot of "bunkering" also happens here. This is the process of fueling ships.
CEPSA Refinery
The CEPSA Gibraltar-San Roque Refinery is a very large industrial site in Spain. It covers 1.5 million square meters and employs 1,000 people. This refinery produces a lot of fuel and other chemicals.
In the past, there have been concerns about pollution from the refinery, such as sulfur releases. These incidents have caused public protests. Because of this, an independent check was ordered to investigate the problems. Local groups continue to work closely to monitor the refinery's activities and ensure safety.
Fueling Ships (Bunkering)
The fuel tanks on ships are called "bunkers," and the process of filling them with fuel is called bunkering.
Because of its location on a major shipping route, Gibraltar is one of the biggest bunkering ports in the Mediterranean Sea. Nearby Algeciras in Spain is also very important for bunkering. The ports in the Strait of Gibraltar area (Algeciras, Ceuta, and Gibraltar) form the second-largest bunkering market in Europe.
Bunkering is now the main activity at the Port of Gibraltar. In 2007, over 5,600 ships that visited Gibraltar were supplied with fuel. The local CEPSA refinery produces much of the fuel used for bunkering in the bay. It delivers this fuel to both Algeciras and Gibraltar using special barges.
Environmental Concerns: Pollution in the Bay
Due to the many industries and heavy shipping, air and water pollution are serious issues in the Bay of Gibraltar. Environmental groups are worried about the risk of oil spills and other types of pollution. This is especially concerning because the bay is so important for wildlife.
In 1998, an accident at the Acerinox plant in Los Barrios released a radioactive cloud. This radiation was detected far away in several European countries.
Because so many ships pass through the Strait, there is always a risk of accidents. In recent years, there have been some ship sinkings, groundings, and collisions in the bay. These incidents have led to oil spills from ships like the New Flame and Fedra.
A report by Greenpeace on pollution in Spain has highlighted the Bay of Gibraltar. It states that the bay suffers from "chronic pollution" from hydrocarbons. This pollution comes not only from accidents but also from regular activities like cleaning ship tanks.
Environmental groups from both Spain and Gibraltar have called for action to protect the bay. They want measures put in place to reduce pollution. Despite these challenges, a 2015 report by the Gibraltar government stated that the water quality in Gibraltar Coastal Waters was "good" for both ecological and chemical health.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bahía de Algeciras para niños
In Spanish: Bahía de Algeciras para niños