Cathedral Cliff facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Cathedral Cliff |
|
|---|---|

Southeast aspect
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 5,810 ft (1,770 m) |
| Prominence | 360 ft (110 m) |
| Isolation | 1.16 mi (1.87 km) |
| Parent peak | Table Mesa ( 5,850 ft) |
| Geography | |
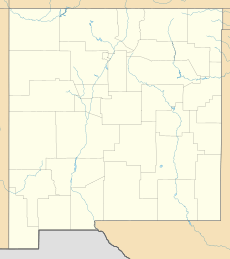
| Location | San Juan County, New Mexico, US |
| Parent range | Chuska Mountains Colorado Plateau |
| Topo map | USGS Table Mesa |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Oligocene |
| Mountain type | Volcanic plug |
| Type of rock | Volcanic breccia |
Cathedral Cliff is an amazing natural landmark in northwest New Mexico, USA. This tall rock formation stands about 5,810 feet (1,771 meters) high! It's located on land belonging to the Navajo Nation, a Native American tribe. You can easily spot it from U.S. Route 491, a main road in the area. It's about 13 miles south of the town of Shiprock, New Mexico.
Cathedral Cliff is actually what's left of an ancient volcano. It's called a volcanic plug because it's the hardened magma that once filled the vent of a volcano. It rises about 400 feet (122 meters) above the flat desert ground, making it a very noticeable sight. It's part of a group of old volcanoes in the Four Corners area. This area is where New Mexico, Arizona, Utah, and Colorado meet. Cathedral Cliff is in the Navajo Volcanic Field. This field has many interesting rocks that formed about 30 million years ago. Its closest taller neighbor is Table Mesa, about a mile away.
Contents
How Cathedral Cliff Was Formed
Cathedral Cliff is what remains of a special type of volcano. This volcano is called a maar-diatreme volcano. It formed when hot, melted rock, called magma, rose up from deep inside the Earth. This magma then hit groundwater, which is water stored underground.
Explosive Eruptions
When the hot magma met the water, it caused huge, explosive eruptions! These explosions created a deep, tube-like channel in the ground. This channel is known as a diatreme or volcanic pipe. They also made a wide, shallow crater on the surface, called a maar.
What We See Today
Over millions of years, wind and water have worn away the softer rocks around the volcano. This process is called erosion. Erosion has removed about 1,640 to 3,280 feet (500 to 1,000 meters) of the rock layers that used to cover the diatreme. This means we can now see the deeper parts of the volcanic pipe. Geologists, who are scientists who study rocks, have learned a lot from studying Cathedral Cliff. They can see how these unique volcanoes work.
Inside the Volcanic Pipe
The pipe we see today is a mix of different rocks. It has layers of pyroclastic rock, which are pieces of rock and ash thrown out by the volcano. These layers were deposited higher up. Later, they sank deeper into the pipe. Some of these rocks were even broken apart by powerful blasts of gas and debris during the eruption.
Weather and Water Around the Cliff
Cathedral Cliff is in a semi-arid climate zone. This means it has cold winters and hot summers. It doesn't get a lot of rain.
Water Flow
When it does rain, the water runs off the cliff. This water flows into a place called Dead Mans Wash. Dead Mans Wash is a stream that eventually leads to the San Juan River. The San Juan River is a big river that flows through the area.
See also
 | Madam C. J. Walker |
 | Janet Emerson Bashen |
 | Annie Turnbo Malone |
 | Maggie L. Walker |