Collective Security Treaty Organization facts for kids
|
Организация Договора о коллективной безопасности
|
|

Emblem
|
|

Flag
|
|
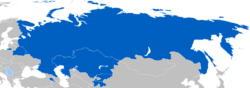
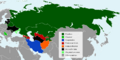
Member states Observer states
|
|
| Abbreviation | CSTO, ОДКБ (ODKB) |
|---|---|
| Formation |
|
| Type | Military alliance |
| Headquarters | Moscow, Russia |
| Location | |
|
Region served
|
Eastern Europe, Caucasus, Central Asia, Northern Asia |
|
Membership
|
|
|
Official language
|
Russian |
|
Secretary General
|
Imangali Tasmagambetov |
|
Chief of the Joint Staff
|
Andrey Serdyukov |
The Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) is a team of countries that have agreed to protect each other. It is a military alliance, which means the member countries use their armies to help one another. The CSTO is located in Eurasia, a large landmass that includes Europe and Asia.
The six member countries are Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan. These are all post-Soviet states, meaning they were once part of the Soviet Union. Some countries, like Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Uzbekistan, used to be members but have since left.
The main rule of the CSTO is in Article 4 of its treaty. It says that if an enemy attacks one member country, it is considered an attack on all of them. This is very similar to Article 5 of NATO, another famous military alliance. Members of the CSTO are not allowed to join other military alliances.
Contents
What Does the CSTO Do?
The CSTO does several things to keep its member countries safe and working together.
Military Training
Every year, the CSTO holds military exercises. These are like practice sessions for the armies of the member countries. They learn to work together and improve their skills. In 2011, one of the biggest exercises had over 10,000 soldiers and 70 airplanes.
Peacekeeping Force
The CSTO has a special peacekeeping force. These soldiers can be sent to areas where there is conflict to help bring peace and safety. For example, in January 2022, about 2,000 CSTO peacekeepers went to Kazakhstan to help calm down major protests.
Collective Rapid Reaction Force
In 2009, some members created the Collective Rapid Reaction Force (KSOR). This is a special group of soldiers ready to act quickly. Their job is to fight against military attacks, terrorism, and crime. They also help during natural disasters like earthquakes or floods.
History of the CSTO
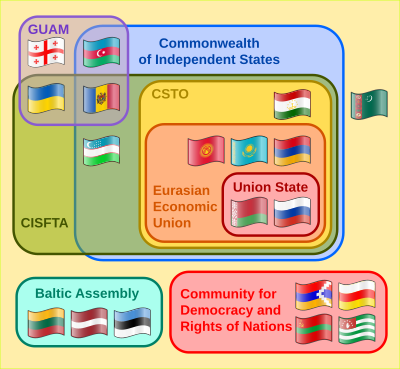
The CSTO has its roots in the old Soviet Armed Forces. After the Soviet Union broke apart in 1991, a new group of countries called the Commonwealth of Independent States was formed.
How It Started
On May 15, 1992, six countries signed the Collective Security Treaty. These countries were Russia, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Later, Azerbaijan, Belarus, and Georgia also joined. The treaty was meant to last for five years.
In 1999, six of the countries decided to renew the treaty. However, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Uzbekistan chose to leave. In 2002, the remaining members decided to create a stronger group, which they named the Collective Security Treaty Organization, or CSTO.
Key Events Over the Years
- 2006: Uzbekistan rejoined the CSTO after leaving another group.
- 2007: The CSTO agreed to create a peacekeeping force. They also agreed that members could buy Russian weapons at the same price as Russia.
- 2009: Belarus had a trade disagreement with Russia and boycotted a CSTO meeting.
- 2010: There was trouble in Kyrgyzstan, but the CSTO did not send troops to help. Some people felt the organization was not strong enough because it did not act.
- 2012: Uzbekistan left the CSTO again.
- 2022: CSTO peacekeepers were sent to Kazakhstan to help with unrest. This was the first time the force was used in a real situation.
Recent Challenges and Changes
In recent years, the CSTO has faced some difficult situations, especially involving its members.
Disagreements Over Conflicts
Since 2021, there have been border clashes between Armenia and Azerbaijan. Armenia, a CSTO member, asked the alliance for help. However, many in Armenia felt that the CSTO did not do enough to support them. This caused a lot of debate in Armenia about whether being in the CSTO was still a good idea.
The relationship between Russia and Kazakhstan also became tense after the Russian invasion of Ukraine began in 2022. Kazakhstan did not support Russia's actions in Ukraine.
Armenia Freezes Its Membership
Because Armenia felt a lack of support, its leaders began to distance the country from the CSTO. In 2022, Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan refused to sign a joint statement at a CSTO meeting.
In February 2024, Prime Minister Pashinyan announced that Armenia had "frozen" its participation in the CSTO. This means they stopped taking part in meetings and activities. He said the CSTO was a "threat to the national security of Armenia." Later that year, Armenia announced it would formally leave the alliance in the future.
Who Are the Members?
The CSTO is made up of member states, former members, and observers.
Current Member States
As of 2025, there are six full members of the CSTO.
 Armenia (participation frozen)
Armenia (participation frozen) Belarus
Belarus Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan Russia
Russia Tajikistan
Tajikistan
Former Member States
Three countries were once members but left the organization.
Observer States
Some countries are not full members but can attend meetings as observers. Serbia has observer status. The former government of Afghanistan also had this status until 2021.
Images for kids
See also
- Soviet Armed Forces
- Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS)
- Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU)
- Military alliance
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- Post-Soviet states
- Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)
- Warsaw Pact