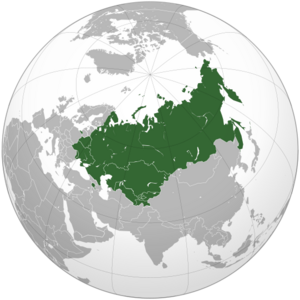
Commonwealth of Independent States facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Commonwealth of
Independent States (in other regional languages)
Armenian: Համագործակցություն Անկախ պետությունների
Hamagortsakts’ut’yun Ankakh petut’yunner Azerbaijani: Müstəqil Dövlətlər Birliyi (MDB) Belarusian: Садружнасць Незалежных Дзяржаў (СНД) Sadružnasć Niezaliežnych Dziaržaŭ Kazakh: Тәуелсіз Мемлекеттер Достастығы (ТМД) Täuelsız Memleketter Dostastyğy Kyrgyz: Көз карандысыз Мамлекеттер Шериктештиги (КМШ) Köz karandısız Mamleketter Şerikteştigi Romanian: Comunitatea Statelor Independente (CSI) Russian: Содружество Независимых Государств (СНГ) Sodruzhestvo Nezavisimykh Gosudarstv Tajik: Иттиходи Давлатҳои Мустақил Ittixodi Davlathoi Mustaqil (ИДМ) Uzbek: Мустақил Давлатлар Ҳамдўстлиги (МДХ) Mustaqil Davlatlar Hamdoʻstligi |
|
|---|---|
Member states
Associate state |
|
| Administrative seats | |
| Largest city | Moscow |
| Working language | Russian |
| Type | Intergovernmental |
| Membership |
9 member states
1 associate state
|
| Leaders | |
|
• General Secretary
|
Sergey Lebedev |
| Legislature | Interparliamentary Assembly |
| Establishment | |
|
• Belavezha Accords
|
8 December 1991 |
|
• Alma-Ata Protocol
|
21 December 1991 |
|
• Charter adopted
|
22 January 1993 |
|
• Free Trade Area
|
20 September 2012 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
20,368,759 km2 (7,864,422 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• 2025 estimate
|
(including Crimea) |
|
• Density
|
12.09/km2 (31.3/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$9.40 trillion |
|
• Per capita
|
$37,340 (approx.) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$2.81 trillion |
|
• Per capita
|
$11,417 (approx.) |
| HDI (2017) | 0.740 high |
| Currency | No common currencya
Member states
Armenian dram (֏)
Azerbaijani manat (₼) Belarusian ruble (Rbl) Kazakhstani tenge (₸) Kyrgyzstani som (с) Moldovan leu (L) Russian ruble (₽) Tajikistani somoni (SM) Uzbekistani soum (soʻm) Associate state
|
| Time zone | UTC+2 to +12 |
| Driving side | right |
| Internet TLD | .ru, .by, .am, .kz, .kg, .az, .md, .tj, .uz |
|
a Soviet ruble (руб) used from 1991 to 1994
|
|
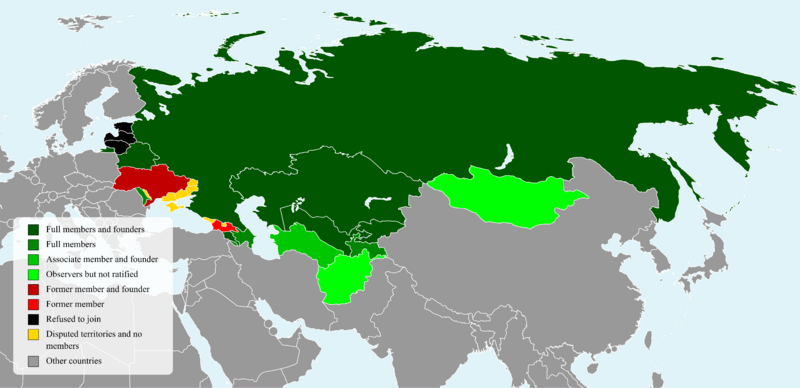
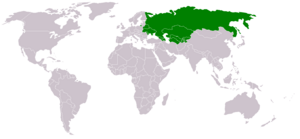
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a group of countries in Eurasia. It was formed in 1991 after the Soviet Union broke apart. The CIS helps these countries work together on things like their economies, politics, and security. It covers a huge area of over 20 million square kilometers.
The CIS was created by Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine on December 8, 1991. They signed an agreement saying the Soviet Union no longer existed. Later that month, eight more countries joined. These were Armenia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Georgia joined in 1993 but left in 2008 after a conflict with Russia. Ukraine stopped taking part in 2014 and formally ended its involvement in 2018. Moldova has also been reducing its participation since 2022.
Many CIS countries are part of a Free Trade Area. This means they can trade with each other more easily. Some other groups also grew out of the CIS. These include the Collective Security Treaty Organization (a military alliance) and the Eurasian Economic Union (an economic group).
Contents
- How the CIS Was Formed and Works
- Who Belongs to the CIS?
- How the CIS Works: Politics and Cooperation
- Economy and Trade in the CIS
- Social Development in CIS Countries
- Other Activities of the CIS
- Population of CIS Countries
- Life Expectancy in CIS Countries
- Images for kids
- Related Organizations
- See also
How the CIS Was Formed and Works
The Beginning of the CIS
The idea for the CIS came from the history of the Russian Empire and later the Soviet Union. These were large areas where many different countries were once united. In 1991, the Soviet Union was facing big problems. Its president, Mikhail Gorbachev, tried to keep the union together. But an attempted coup in Moscow failed. This made many republics declare their independence.
Creating the CIS
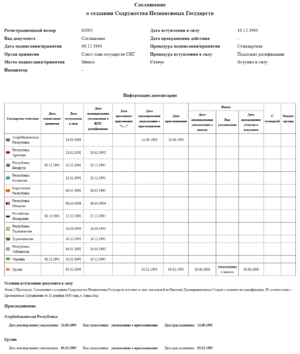
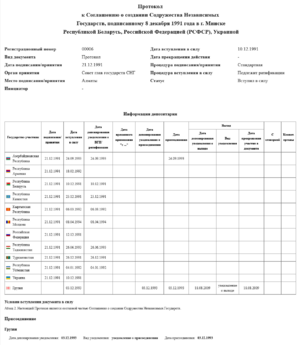
After the failed coup, Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine met in December 1991. They signed the "Agreement Establishing the Commonwealth of Independent States." This agreement is known as the Belovezh Accords. They announced that the Soviet Union had ended. They also said the new CIS would be open to other former Soviet republics.
Soon after, on December 21, 1991, leaders from eight more republics joined. This was done by signing the Alma-Ata Protocol. This brought the total number of participating countries to eleven. The Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania) did not join. The Soviet Union officially dissolved on December 26, 1991.
The CIS Charter
On January 22, 1993, the CIS countries signed the Charter. This document set up the rules and different parts of the CIS. It explained how the organization would work. It also said that only countries that signed the Charter would be full members.
Ukraine and Turkmenistan did not sign the Charter. However, they still took part in many CIS activities. Turkmenistan later became an associate member in 2005. Georgia left the CIS completely in 2009. Ukraine stopped participating in 2018.
General Secretary of the CIS
The General Secretary helps coordinate the work of the CIS. Here are the people who have held this important role:
| Name | Term |
|---|---|
| May 14, 1993 – April 29, 1998 | |
| April 29, 1998 – March 4, 1999 | |
| March 4, 1999 – April 2, 1999 | |
| April 2, 1999 – July 14, 2004 | |
| July 14, 2004 – October 5, 2007 | |
| October 5, 2007 – present |
Interparliamentary Assembly
The Interparliamentary Assembly was created in 1992. It is like a meeting place for the parliaments of CIS countries. They discuss common issues and create "model laws." These model laws can then be used by each country to help make their own laws similar. This helps the countries work together better. The Assembly also sends observers to watch national elections.
Recent Changes in the CIS
Between 2003 and 2005, some CIS countries had changes in their governments. Georgia left the CIS in 2009 after a war with Russia. In 2009, several CIS countries also joined the Eastern Partnership. This is a project started by the European Union to build closer ties.
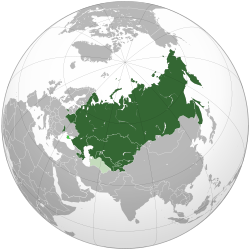
Who Belongs to the CIS?
There are nine full member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States. A country becomes a member by ratifying the CIS Charter. Countries that signed the first agreement are called "Founding states."
Member States
| Country | Signed Agreement | Charter Ratified | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21 December 1991 | 16 March 1994 | Founding state. | |
| 21 December 1991 | 14 December 1993 | ||
| 8 December 1991 | 18 January 1994 | Founding state. | |
| 21 December 1991 | 20 April 1994 | Founding state. | |
| 21 December 1991 | 12 April 1994 | Founding state. | |
| 21 December 1991 | 27 June 1994 | Moldova has been reducing its participation since November 2022. It plans to leave most agreements by the end of 2024. | |
| 8 December 1991 | 20 July 1993 | Founding state. | |
| 21 December 1991 | 14 August 1993 | ||
| 21 December 1991 | 9 February 1994 | Founding state. |
Moldova's Participation
Moldova has been thinking about leaving the CIS for a while. In 2022, Moldova's Foreign Minister said they would suspend their participation in CIS meetings. By May 2023, Moldova started withdrawing from many treaties it had signed with the CIS. This is because Moldova wants to join the European Union. By the end of 2023, Moldova announced it plans to fully withdraw from the CIS by the end of 2024. However, it will keep some agreements related to economy, social protection, and healthcare.
Associate Member
A country can also be an associate member if the main leaders of the CIS agree.
| Country | Signed Agreement | Charter Ratified | Associate from | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 December 1991 | Not ratified | August 2005 | Founding state. Turkmenistan has never been a full member. It became an associate member to match its neutral status. |
Founding State (Not a Full Member)
Ukraine was one of the first countries to sign the agreement creating the CIS. However, Ukraine never officially ratified the CIS Charter. This means it was a "Founding state" but never a full "member."
| Country | Signed Agreement | Charter Ratified | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 December 1991 | Not ratified | Founding state. Ukraine largely stopped participating in 2014. It formally ended its participation in CIS bodies in May 2018. Ukraine has been withdrawing from various CIS treaties since then. |
Ukraine participated in the CIS for many years. But after conflicts with Russia starting in 2014, Ukraine began to distance itself. In April 2018, Ukraine's President said the country would formally leave the CIS. By May 2018, Ukraine officially ended its participation in CIS bodies. Ukraine has continued to withdraw from many CIS agreements.
Former Member States
| Country | Signed Agreement | Charter Ratified | Withdrawn | Effective | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 December 1993 | 19 April 1994 | 18 August 2008 | 18 August 2009 | Georgia left the CIS after a conflict with Russia in 2008. |
How the CIS Works: Politics and Cooperation

Human Rights Efforts
One of the CIS's goals is to discuss social and economic development. This includes promoting human rights. In 1995, the CIS adopted a Convention on Human Rights. It also created a Human Rights Commission. However, many experts say that human rights in some CIS countries, especially in Central Asia, still face big challenges.
Military Cooperation
The CIS has a Council of Ministers of Defense. This group helps coordinate military cooperation among countries that want to participate. In 1992, six CIS countries signed the Collective Security Treaty. This treaty created a military alliance. In 2002, this alliance became the Collective Security Treaty Organisation (CSTO). The CSTO aims to help resolve conflicts between its members. However, some conflicts, like those involving Russia and Ukraine, have shown that the CSTO has not always been effective in this role.
Economy and Trade in the CIS
Corruption and too much bureaucracy can be problems for trade in CIS countries. Some leaders have suggested using digital tools to modernize their economies.
Trade Agreements
The CIS countries have worked to create free trade areas. This means they try to remove taxes and other barriers on goods traded between them.
Early Free Trade Agreements
In 1994, 12 CIS countries signed an agreement to create a Free Trade Area. This agreement helped set up many bilateral (two-country) trade deals. In 1999, a new agreement was signed to make trade multilateral, meaning it applied to many countries at once. This helped remove more trade barriers.
The 2011 Free Trade Area Treaty
In 2011, a new and more detailed free trade agreement was signed by eight CIS prime ministers. These countries were Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, and Ukraine. Uzbekistan later joined in 2013. This agreement removes many import and export taxes. Azerbaijan is the only full CIS member not part of this free trade area.
Free Trade in Services Agreement (2023)
In June 2023, seven CIS countries signed an agreement for free trade in services. This means it will be easier for businesses to offer services and invest in each other's countries. The countries are Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
Social Development in CIS Countries
Studies show that many people in CIS countries face social challenges. For example, the number of people who feel poor is often higher than official poverty rates. Unemployment benefits also vary greatly between countries. In some places, very few unemployed people receive benefits.
Average monthly salaries in 2015 were quite low in many CIS countries. For example, in Tajikistan, it was $142, and in Ukraine, it was $193. In Russia and Kazakhstan, it was around $560-$565. A large part of these salaries is often spent on food.
Other Activities of the CIS
Election Monitoring
The CIS has an Election Monitoring Organisation. It was formed in 2002 to observe elections in CIS member countries. However, this group has sometimes approved elections that other international observers criticized. For example, in 2004, the CIS questioned the Ukrainian presidential election, while other groups found no major problems. In 2005, the CIS praised elections in Uzbekistan and Tajikistan that other observers said did not meet international standards.
Russian Language Status
Russia has asked that the Russian language be made an official language in all CIS countries. Currently, Russian is an official language in Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. It is also used officially in some regions of Moldova.
Sports Events
When the Soviet Union broke up in 1991, its sports teams were still set to compete in 1992 events. A joint "Unified Team" from the CIS countries competed in the 1992 Winter Olympics and 1992 Summer Olympics. A CIS football team also played in the UEFA Euro 1992.
Since then, the CIS has hosted its own sports events. In 2017, a festival of national sports and games was held in Ulyanovsk, Russia. The first official CIS Games took place in Kazan in 2021. The second games were held in Belarus in 2023.
Cultural Events
The CIS also helps promote cultural ties between former Soviet republics. In 2006, they created a foundation to support education, science, and culture. This foundation has helped organize many cultural events. One example is the 'CIS Capital of Culture' program. In 2017, Goris, Armenia, was the CIS Cultural Capital. In 2022, it was Karakol, Kyrgyzstan.
Population of CIS Countries
The total population of all CIS member states is about 246.2 million people as of 2024.
|
Largest cities or towns in Commonwealth of Independent States
Russia , Uzbekistan , Azerbaijan , Kazakhstan , Belarus , Tajikistan , Kyrgyzstan |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Pop. | |
| 1 | Moscow | 13,149,803 |
| 2 | Saint Petersburg | 5,597,763 |
| 3 | Tashkent | 3,075,232 |
| 4 | Baku | 2,300,500 |
| 5 | Almaty | 2,275,541 |
| 6 | Minsk | 1,992,862 |
| 7 | Novosibirsk | 1,633,851 |
| 8 | Dushanbe | 1,564,700 |
| 9 | Yekaterinburg | 1,536,183 |
| 10 | Astana | 1,502,102 |
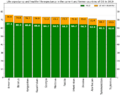
Life Expectancy in CIS Countries
Here is the average life expectancy at birth in CIS countries in 2021, according to the World Bank Group:
| Countries | 2021 | Historical data | COVID-19 impact | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Male | Female | Sex gap | 2000 | 2000 →2014 |
2014 | 2014 →2019 |
2019 | 2019 →2020 |
2020 | 2020 →2021 |
2021 | 2019 →2021 |
2014 →2021 |
|
| Belarus | 72.37 | 67.30 | 77.70 | 10.40 | 68.91 | 4.06 | 72.97 | 1.26 | 74.23 | −1.77 | 72.46 | −0.09 | 72.37 | −1.86 | −0.60 |
| Armenia | 72.04 | 66.55 | 77.35 | 10.80 | 70.62 | 3.43 | 74.06 | 1.38 | 75.44 | −3.27 | 72.17 | −0.13 | 72.04 | −3.40 | −2.02 |
| Kyrgyzstan | 71.90 | 67.90 | 76.10 | 8.20 | 68.56 | 1.84 | 70.40 | 1.20 | 71.60 | 0.20 | 71.80 | 0.10 | 71.90 | 0.30 | 1.50 |
| Tajikistan | 71.59 | 69.57 | 73.73 | 4.17 | 63.26 | 5.81 | 69.07 | 1.80 | 70.87 | −2.87 | 67.99 | 3.60 | 71.59 | 0.73 | 2.52 |
| Uzbekistan | 70.86 | 68.33 | 73.39 | 5.06 | 65.72 | 4.51 | 70.23 | 1.11 | 71.34 | −1.01 | 70.33 | 0.53 | 70.86 | −0.48 | 0.63 |
| Kazakhstan | 70.23 | 66.33 | 74.03 | 7.70 | 65.45 | 5.99 | 71.44 | 1.74 | 73.18 | −1.81 | 71.37 | −1.14 | 70.23 | −2.95 | −1.21 |
| Azerbaijan | 69.37 | 65.65 | 73.29 | 7.64 | 64.89 | 6.22 | 71.12 | 1.99 | 73.10 | −6.23 | 66.87 | 2.50 | 69.37 | −3.74 | −1.75 |
| Russia | 69.36 | 64.21 | 74.77 | 10.56 | 65.48 | 5.26 | 70.74 | 2.34 | 73.08 | −1.75 | 71.34 | −1.98 | 69.36 | −3.72 | −1.38 |
| Turkmenistan | 69.26 | 65.86 | 72.66 | 6.80 | 65.03 | 3.59 | 68.61 | 0.39 | 69.00 | −0.31 | 68.69 | 0.58 | 69.26 | 0.26 | 0.65 |
| Moldova | 68.85 | 64.44 | 73.55 | 9.10 | 66.42 | 2.61 | 69.03 | 1.90 | 70.94 | −0.77 | 70.17 | −1.32 | 68.85 | −2.09 | −0.19 |
Images for kids
-
Life expectancy and healthy life expectancy in countries of CIS in 2019
Related Organizations
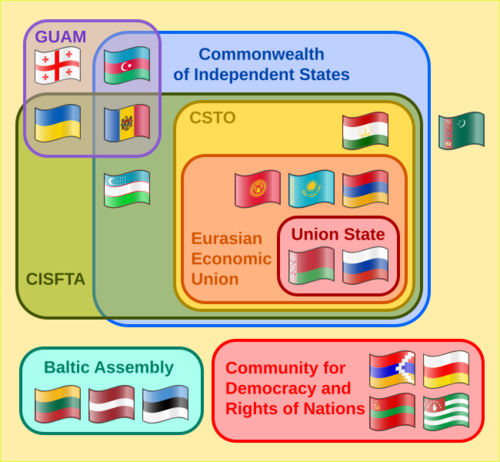
- Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) - A military alliance.
- Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) - An economic union.
- Union State - A closer union between Russia and Belarus.
- GUAM Organization for Democracy and Economic Development - A group of Georgia, Ukraine, Azerbaijan, and Moldova.
See also
 In Spanish: Comunidad de Estados Independientes para niños
In Spanish: Comunidad de Estados Independientes para niños
 | May Edward Chinn |
 | Rebecca Cole |
 | Alexa Canady |
 | Dorothy Lavinia Brown |