English alphabet facts for kids
Quick facts for kids English alphabet |
|
|---|---|
An English-language pangram written with the FF Dax Regular typeface
|
|
| Type | Alphabet |
| Spoken languages | English |
| Time period | c. 16th century – present |
| Parent systems |
(Proto-writing)
|
| Child systems | |
| Unicode range | U+0000–U+007E Basic Latin |
| ISO 15924 | Latn |
| Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols in Unicode. | |
The English language we use today is written with an alphabet that has 26 letters. Each letter has a capital (uppercase) and a small (lowercase) form. The word alphabet comes from the first two letters of the Greek alphabet: alpha and beta.
English started being written down using the Latin alphabet around the 600s. Over many centuries, some letters were added, and others stopped being used. By the 1500s, the 26 letters we know today were mostly set.
Here are the 26 letters of the English alphabet:
Out of these 26 letters, five are usually vowels (A, E, I, O, U). Nineteen are consonants. The letters Y and W can sometimes act as vowels and sometimes as consonants.
English writing also uses many digraphs. These are two letters that make one sound, like ch, ea, oo, sh, and th. Unlike many other European languages, English usually doesn't use special marks (like accents) on its native words.
Contents
How We Name the Letters
We often use the names of letters in everyday words. Think of "tee-shirt" (T-shirt) or "deejay" (DJ). The names of letters like en and em are also used in printing.
The names of the letters mostly come from their Latin (and even older Etruscan) names. Over time, these names changed as the English language developed. For example, the letter C used to sound like 'k' in Latin, but its name changed to sound like 's' in English.
Some letters, like pee and bee, or em and en, can sound very similar. This can make them hard to tell apart, especially when talking on the phone or over a radio. To avoid confusion, people use spelling alphabets. For example, pilots use the ICAO spelling alphabet where each letter has a unique word, like "Alpha" for A and "Bravo" for B.
The Ampersand (&)
The symbol &, called the ampersand, has sometimes been seen as part of the English alphabet. In the past, it was even taught as the 27th letter to children. The & symbol is actually a combination of the letters E and t, which spells the Latin word et, meaning "and". In English, it simply means "and".
Old Letters We Don't Use Anymore
In Old English and Middle English (languages spoken long ago), there were letters that came from runes or were changed from Latin letters. These letters are not used in English today.
Here are some examples of old English letters:
- Æ æ (called Ash): Used for a vowel sound like the 'a' in "cat". Now we use "ae" or "e".
- Ð ð (called Eth): Used for the 'th' sound in words like "this" or "thin". Now we use "th".
- Þ þ (called Thorn): Also used for the 'th' sound. Now we use "th".
- Œ œ (called Ethel): Used for a vowel sound that disappeared early on. Now we use "oe" or "e".
- Ƿ ƿ (called Wynn): Used for the 'w' sound. The letter 'w' didn't exist back then! Now we use "w".
- Ȝ ȝ (called Yogh): Used for sounds like 'y' or 'ch' (as in Scottish "loch"). Now we use "y", "j", "gh", or "ch".
- ſ (called long s): This was just an older way to write the lowercase 's'. It looked a bit like an 'f'. It was used until the early 1800s. Now we just use 's'.
Special Marks (Diacritics)
Diacritic marks are small symbols added to letters, like the accent on é in "café". In English, you mostly see these marks in words borrowed from other languages, like naïve (from French) or façade (also from French).
When words become common in English, these marks often disappear. For example, we used to write hôtel but now it's just "hotel". However, if removing the mark would make the word confusing with another English word, it might stay. For instance, résumé keeps its accent to avoid confusion with "resume" (meaning to start again).
Sometimes, especially in older books or poetry, you might see diacritics in native English words. For example, cursèd (with two syllables) might be written to show it's different from cursed (one syllable). Also, a mark called a diaeresis can be used to show that two vowels next to each other are pronounced separately, like in coöperation. This is rare today.
Punctuation Marks within Words
The Apostrophe (ʼ)
The apostrophe (ʼ) is a punctuation mark, but it's very important for spelling many English words. It has two main jobs:
- Showing possession: It shows that something belongs to someone or something. For example, "the dogs bone" means the bone belongs to the dog. For plural words ending in 's', we just add the apostrophe after the 's', like "the students desks".
- Making contractions: It shows when letters are missing in a shortened word. For example, "its" is short for "it is" or "it has". "Shed" is short for "she would" or "she had". The apostrophe helps us tell the difference between words like "its" (meaning belonging to it) and "it's" (meaning it is).
How Often Letters Are Used
The letter used most often in English is E. The letter used least often is Z. The exact frequency of letters can change depending on the type of text you are looking at.
Sounds of Letters (Phonology)
The letters A, E, I, O, and U are called vowel letters because they usually make vowel sounds. However, sometimes I and U can make consonant sounds, like in "onion" or "quail". The letter Y can be a consonant (like in "young") or a vowel (like in "myth").
The other letters are called consonant letters because they usually make consonant sounds.
The History of Our Alphabet
Old English Alphabet
The English language was first written using an alphabet called the Anglo-Saxon futhorc runes, starting around the 400s. These runes came to England with the Anglo-Saxon settlers. We don't have many examples of Old English written this way.
Around the 600s, Christian missionaries brought the Latin script to England. This new alphabet slowly replaced the runes, though both were used for a while. The Old English alphabet started to use parts of the Roman alphabet. However, some letters from the runes, like thorn (Þ þ) and wynn (Ƿ ƿ), were kept. The letter eth (Ð ð) was created by changing the letter 'd'. Later, yogh (Ȝ ȝ) was added.
Other special letters were also used, like ash (Æ æ) and ethel (Œ œ), which were combinations of other letters. The letter double-u (W w) was also used, which was a combination of two 'u's or 'v's.
In 1011, a monk named Byrhtferth wrote down the order of the Old English alphabet. He listed the 24 Latin letters, then the ampersand (&), and then 5 more English letters:
Modern English Alphabet
In the English we speak today, many of those old letters like thorn (þ), eth (ð), wynn (ƿ), yogh (ȝ), ash (æ), and ethel (œ) are no longer used. Thorn and eth were both replaced by the letters th. You might still see y used instead of th in old-fashioned signs like "Ye Olde Booke Shoppe". Wynn was replaced by uu, which became our modern w. Yogh was replaced by gh.
The letters u and j became separate letters from v and i in the 1500s. The w also became its own letter. Today, the English alphabet has these 26 letters:
Modern English also uses many digraphs (two letters that make one sound), but they are not considered separate letters of the alphabet:
- ch (as in "chair")
- ck (as in "duck")
- gh (as in "ghost" or "laugh")
- ng (as in "sing")
- ph (as in "phone")
- sh (as in "ship")
- th (as in "this" or "thin")
- wh (as in "what")
Ligatures in Modern Use
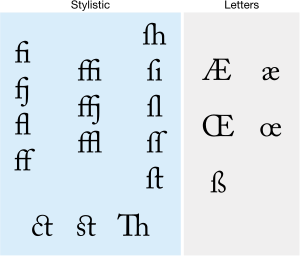
Ligatures are when two or more letters are joined together into a single symbol. In modern English, ligatures like æ and œ are rarely used. They used to be common in words from Greek or Latin, like encyclopædia. Now, these are usually written as "ae" or "oe" (or just "e" in American English, like "encyclopedia").
Some fonts (typefaces) you see on computers or in books have ligatures for common letter pairs like fi or fl. These are not separate letters, but just a way to make the text look better and easier to read.
Ideas for Changing the English Alphabet
People have sometimes suggested adding new letters to the English alphabet or even creating entirely new writing systems. For example, some have suggested adding a letter called eng (Ŋ ŋ) to represent the "ng" sound in words like "sing" with just one letter. Other ideas include completely new alphabets like the Deseret alphabet or the Shavian alphabet.
See Also
- Alphabet song
- NATO phonetic alphabet
- English orthography
- English-language spelling reform
- American manual alphabet
- English Braille


